This article is missing information about all storms that formed after January. (May 2022) |
During 1991, tropical cyclones formed within seven different tropical cyclone basins, located within various parts of the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. During the year, a total of 100 systems formed with 75 of these developing further and were named by the responsible warning centre. The strongest tropical cyclone of the year was Typhoon Yuri, which was estimated to have a minimum barometric pressure of 895 hPa (26.43 inHg). The deadliest tropical cyclone was Cyclone BOB 01, which caused 138,866 fatalities in Bangladesh, Northeastern India, Myanmar, Yunnan, while the costliest was Typhoon Mireille, which caused an estimated $10 billion USD in damage after striking Japan. Four Category 5 tropical cyclones formed in 1991.
| Tropical cyclones in 1991 | |
|---|---|
| Year boundaries | |
| First system | Alison |
| Formed | January 8, 1991 |
| Last system | Bryna |
| Dissipated | January 10, 1992 |
| Strongest system | |
| Name | Yuri |
| Lowest pressure | 895 mbar (hPa); 26.43 inHg |
| Longest lasting system | |
| Name | Nat |
| Duration | 19 days |
| Year statistics | |
| Total systems | 100 |
| Named systems | 75 |
| Total fatalities | 144,609 total |
| Total damage | $13.71 billion (1991 USD) |
Tropical cyclone activity in each basin is under the authority of an RSMC. The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is responsible for tropical cyclones in the North Atlantic and East Pacific. The Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC) is responsible for tropical cyclones in the Central Pacific. Both the NHC and CPHC are subdivisions of the National Weather Service. Activity in the West Pacific is monitored by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA). Systems in the North Indian Ocean are monitored by the India Meteorological Department (IMD). The Météo-France located in Réunion (MFR) monitors tropical activity in the South-West Indian Ocean. The Australian region is monitored by five TCWCs that are under the coordination of the Australian Bureau of Meteorology (BOM). Similarly, the South Pacific is monitored by both the Fiji Meteorological Service (FMS) and the Meteorological Service of New Zealand Limited. Other, unofficial agencies that provide additional guidance in tropical cyclone monitoring include the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) and the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC).
Global conditions and hydrological summary
editThis section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (February 2022) |
Summary
edit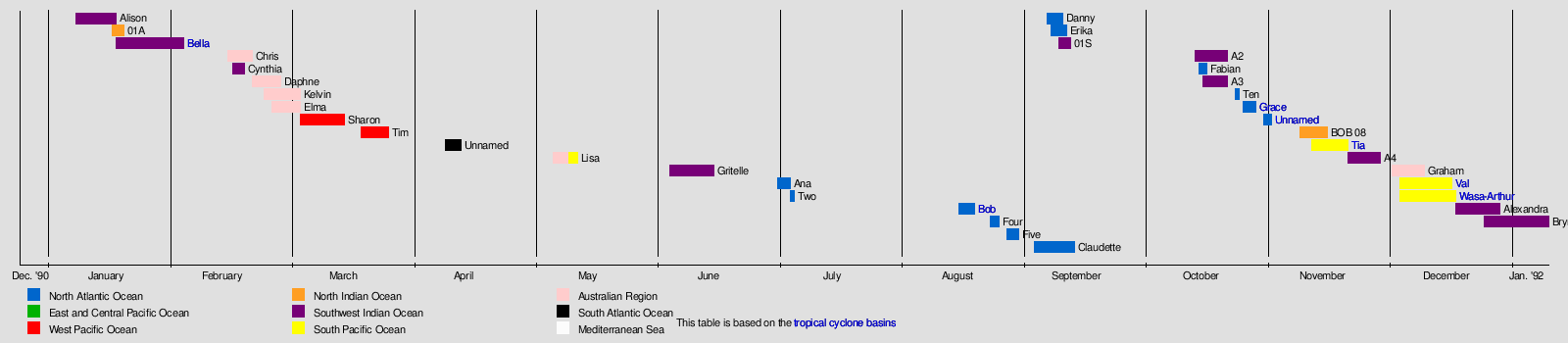
Systems
editJanuary
editJanuary was the least active in terms of tropical cyclogenesis and named storms, with only three cyclones forming, two being named. Tropical Cyclone Bella caused flooding in Rodrigues.
| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alison | January 8 – 18 | 110 (70) | 966 | None | None | None | |
| 01A | January 14 – 20 | 65 (40) | 997 | None | None | None | |
| Bella | January 18 – February 4 | 155 (100) | 936 | Rodrigues | None | None |
February
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|
March
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|
April
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|
May
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|
June
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|
July
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ana | 2–5 July | 85 (50) | 1000 | Florida, Bahamas, South Carolina | Minimal | None | |
| Two | 5–7 July | 55 (35) | 1007 | Mexico | Minimal | None |
August
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bob | August 16–20 | 185 (115) | 950 | North Carolina, Mid-Atlantic, New England, Atlantic Canada, Iberian Peninsula | $1.47 billion | 17 | |
| Four | August 24–26 | 55 (35) | 1007 | None | None | None | |
| Five | August 28–31 | 55 (35) | 1007 | None | None | None |
September
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|
October
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|
November
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|
December
edit| Storm name | Dates active | Max wind km/h (mph) |
Pressure (hPa) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs |
|---|
Global effects
edit- ^ The sum of the number of systems and fatalities in each basin will not equal the number shown as the total. This is because when systems move between basins, it creates a discrepancy in the actual number of systems and fatalities.
See also
editNotes
edit1 Only systems that formed either on or after January 1, 1991 are counted in the seasonal totals.
2 Only systems that formed either before or on December 31, 1991 are counted in the seasonal totals.
3 The wind speeds for this tropical cyclone/basin are based on the IMD Scale which uses 3-minute sustained winds.
4 The wind speeds for this tropical cyclone/basin are based on the Saffir Simpson Scale which uses 1-minute sustained winds.
5The wind speeds for this tropical cyclone are based on Météo-France which uses gust winds.
References
editExternal links
editRegional Specialized Meteorological Centers
- US National Hurricane Center – North Atlantic, Eastern Pacific
- Central Pacific Hurricane Center – Central Pacific
- Japan Meteorological Agency – NW Pacific
- India Meteorological Department – Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea
- Météo-France – La Reunion – South Indian Ocean from 30°E to 90°E
- Fiji Meteorological Service – South Pacific west of 160°E, north of 25° S
Tropical Cyclone Warning Centers
- Meteorology, Climatology, and Geophysical Agency of Indonesia – South Indian Ocean from 90°E to 141°E, generally north of 10°S
- Australian Bureau of Meteorology (TCWC's Perth, Darwin & Brisbane) – South Indian Ocean & South Pacific Ocean from 90°E to 160°E, generally south of 10°S
- Papua New Guinea National Weather Service – South Pacific Ocean from 141°E to 160°E, generally north of 10°S
- Meteorological Service of New Zealand Limited – South Pacific west of 160°E, south of 25°S
This article incorporates public domain material from websites or documents of the National Weather Service.