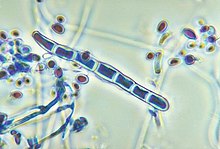
Trichophyton erinacei is a species in the fungal genus Trichophyton that is associated with hedgehogs. The fungi is normally isolated from the quills and underbelly of hedgehogs. Common symptoms of infection include crusting around the face and loss of spines.[1] Trichophyton erinacei is also known to affect humans through hedgehog contact that transmits the fungi. Infections can also occur with indirect contact.[2]
| Trichophyton erinacei | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order: | Onygenales |
| Family: | Arthrodermataceae |
| Genus: | Trichophyton |
| Species: | T. erinacei
|
| Binomial name | |
| Trichophyton erinacei (J.M.B. Smith & Marples) Quaife
| |
References
edit- ^ Abarca, M. L; Castellá, G; Martorell, J; Cabañes, F. J (2017). "Trichophyton erinacei in pet hedgehogs in Spain: Occurrence and revision of its taxonomic status". Medical Mycology. 55 (2): 164–172. doi:10.1093/mmy/myw057. PMID 27486214. Retrieved 8 May 2022.
- ^ Borges-Costa, João; da Luz Martins, Maria (2014). "Trichophyton erinacei skin infection after recreational exposure to an elephant in Southeast Asia". Pathogens and Global Health. 108 (1): 58–59. doi:10.1179/2047773213Y.0000000117. PMC 4083169. PMID 24548162.