Thermolysin (EC 3.4.24.27, Bacillus thermoproteolyticus neutral proteinase, thermoase, thermoase Y10, TLN) is a thermostable neutral metalloproteinase enzyme produced by the Gram-positive bacteria Bacillus thermoproteolyticus.[2] It requires one zinc ion for enzyme activity and four calcium ions for structural stability.[3] Thermolysin specifically catalyzes the hydrolysis of peptide bonds containing hydrophobic amino acids. However thermolysin is also widely used for peptide bond formation through the reverse reaction of hydrolysis.[4] Thermolysin is the most stable member of a family of metalloproteinases produced by various Bacillus species. These enzymes are also termed 'neutral' proteinases or thermolysin -like proteinases (TLPs).
| Thermolysin | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
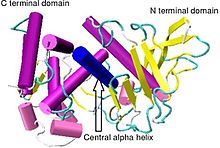 Crystallographic structure of Bacillus thermoproteolyticus thermolysin.[1] | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 3.4.24.27 | ||||||||
| CAS no. | 9073-78-3 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Synthesis
editLike all bacterial extracellular proteases thermolysin is first synthesised by the bacterium as a pre-proenzyme.[5] Thermolysin is synthesized as a pre-proenzyme consisting of a signal peptide 28 amino acids long, a pro-peptide 204 amino acids long and the mature enzyme itself 316 amino acids in length. The signal peptide acts as a signal for translocation of pre-prothermolysin to the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. In the periplasm pre-prothermolysin is then processed into prothermolysin by a signal peptidase. The prosequence then acts as a molecular chaperone and leads to autocleavage of the peptide bond linking pro and mature sequences. The mature protein is then secreted into the extracellular medium.[6]
Structure
editThermolysin has a molecular weight of 34,600 Da. Its overall structure consists of two roughly spherical domains with a deep cleft running across the middle of the molecule separating the two domains. The secondary structure of each domain is quite different, the N-terminal domain consists of mostly beta pleated sheet, while the C-terminal domain is mostly alpha helical in structure. These two domains are connected by a central alpha helix, spanning amino acids 137–151.[7]
In contrast to many proteins that undergo conformational changes upon heating and denaturation, thermolysin does not undergo any major conformational changes until at least 70 °C.[8] The thermal stability of members of the TLP family is measured in terms of a T50 temperature. At this temperature incubation for 30 minutes reduces the enzymes activity by half. Thermolysin has a T50 value of 86.9 °C, making it the most thermo stable member of the TLP family.[9] Studies on the contribution of calcium to thermolysin stability have shown that upon thermal inactivation a single calcium ion is released from the molecule.[10] Preventing this calcium from originally binding to the molecule by mutation of its binding site, reduced thermolysin stability by 7 °C. However, while calcium binding makes a significant contribution to stabilising thermolysin, more crucial to stability is a small cluster of N-terminal domain amino acids located at the proteins surface.[9] In particular a phenylalanine (F) at amino acid position 63 and a proline (P) at amino acid position 69 contribute significantly to thermolysin stability. Changing these amino acids to threonine (T) and alanine (A) respectively in a less stable thermolysin-like proteinase produced by Bacillus stearothermophillus (TLP-ste), results in individual reductions in stability of 7 °C (F63→T) and 6.3 °C (P69→A) and when combined a reduction in stability of 12.3 °C.[9]
Applications
edit- In the synthesis of aspartame, less bitter-tasting byproduct is produced when the reaction is catalyzed by thermolysin.[11]
- Determining protein stability in cell lysate using the fast parallel proteolysis (FASTpp) assay.[12]
References
edit- ^ PDB: 3TMN; Holden HM, Matthews BW (March 1988). "The binding of L-valyl-L-tryptophan to crystalline thermolysin illustrates the mode of interaction of a product of peptide hydrolysis". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (7): 3256–60. doi:10.2210/pdb3tmn/pdb. PMID 3343246.
- ^ Endo, S. (1962). "Studies on protease produced by thermophilic bacteria". J. Ferment. Technol. 40: 346–353.
- ^ Tajima M, Urabe I, et al. (1976). "Role of calcium ions in the thermostability of thermolysin and Bacillus subtilis var. amylosacchariticus neutral protease". Eur. J. Biochem. 64 (1): 243–247. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10293.x. PMID 819262.
- ^ Trusek-Holownia A. (2003). "Synthesis of ZAlaPheOMe, the precursor of bitter dipeptide in the two-phase ethyl acetate-water system catalysed by thermolysin". J. Biotechnol. 102 (2): 153–163. doi:10.1016/S0168-1656(03)00024-5. PMID 12697393.
- ^ Yasukawa K, Kusano M, Inouye K (2007). "A new method for the extracellular production of recombinant thermolysin by co-expressing the mature sequence and pro-sequence in Escherichia coli". Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 20 (8): 375–383. doi:10.1093/protein/gzm031. PMID 17616558.
- ^ Inouye K, Kusano M, et al. (2007). Engineering, expression, purification, and production of recombinant thermolysin. Biotechnology Annual Review. Vol. 13. pp. 43–64. doi:10.1016/S1387-2656(07)13003-9. ISBN 978-0-444-53032-5. PMID 17875473.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Holmes MA, Matthews BW (1982). "Structure of thermolysin refined at 1.6 A resolution". J. Mol. Biol. 160 (4): 623–639. doi:10.1016/0022-2836(82)90319-9. PMID 7175940.
- ^ Matthews BW, Weaver LH, Kester WR (1974). "The conformation of thermolysin". J. Biol. Chem. 249 (24): 8030–8044. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)42067-X. PMID 4214815.
- ^ a b c Eijsink VG, Veltman OR, et al. (1995). "Structural determinants of the stability of thermolysin-like proteinases". Nat. Struct. Biol. 2 (5): 374–379. doi:10.1038/nsb0595-374. PMID 7664094. S2CID 37785818.
- ^ Dahlquist FW, Long JW, Bigbee WL (1976). "Role of Calcium in the thermal stability of thermolysin". Biochemistry. 15 (5): 1103–1111. doi:10.1021/bi00650a024. PMID 814920.
- ^ Yagasaki, Makoto; Hashimoto, Shin-ichi (November 2008). "Synthesis and application of dipeptides; current status and perspectives". Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology. 81 (1): 13–22. doi:10.1007/s00253-008-1590-3. PMID 18795289. S2CID 10200090.
- ^ Minde, David P.; Maurice, Madelon M.; Rüdiger, Stefan G. D. (2012). "Determining Biophysical Protein Stability in Lysates by a Fast Proteolysis Assay, FASTpp". PLOS ONE. 7 (10): e46147. Bibcode:2012PLoSO...746147M. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046147. PMC 3463568. PMID 23056252.
External links
edit- The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: M04.001[permanent dead link]
- Thermolysin at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)