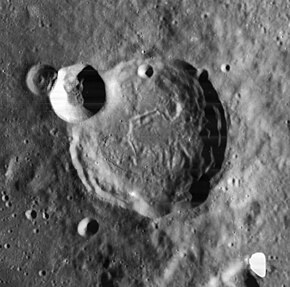
Thebit is a lunar impact crater located on the southeast shore of Mare Nubium. To the north-northwest is the crater Arzachel, and Purbach lies to the south-southwest. To the southwest is the flooded remnants of Thebit P, which is actually larger in diameter than Thebit itself.
 Lunar Orbiter 4 image | |
| Coordinates | 22°00′S 4°00′W / 22.0°S 4.0°W |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 57 km |
| Depth | 3.3 km |
| Colongitude | 5° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Thābit ibn Qurra |


The rim of Thebit is generally circular in outline, with a double-notch in the southwest wall. A prominent bowl-shaped crater, Thebit A, lies across the west-northwestern rim. The west-northwestern rim of this crater is overlain in turn by the even smaller Thebit L. Together this forms an elegant arrangement that makes Thebit relatively simple to identify. The floor of Thebit crater is rough and has no central peak. The rim displays a terrace, and has a hilly outer rampart.
Due west of Thebit is a 110-kilometer-long ridge named Rupes Recta, which rises to 240 meters. This linear feature runs north-northwest to south-southeast across the Mare Nubium.
Name
editThebit is a Latinization of the name of the 9th century Iraqi astronomer and mathematician Thābit ibn Qurra.[2]
Satellite craters
editBy convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Thebit.
| Thebit | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 21.5° S | 4.9° W | 20 km |
| B | 22.3° S | 6.2° W | 4 km |
| C | 21.2° S | 4.1° W | 6 km |
| D | 19.8° S | 8.3° W | 5 km |
| E | 23.1° S | 4.6° W | 7 km |
| F | 23.0° S | 5.3° W | 4 km |
| J | 22.5° S | 5.5° W | 10 km |
| K | 23.1° S | 3.7° W | 5 km |
| L | 21.5° S | 5.4° W | 12 km |
| P | 24.0° S | 5.7° W | 78 km |
| Q | 20.1° S | 4.2° W | 16 km |
| R | 20.2° S | 4.8° W | 9 km |
| S | 24.8° S | 7.2° W | 16 km |
| T | 20.7° S | 6.0° W | 3 km |
| U | 20.3° S | 5.8° W | 4 km |
Ancient Thebit
editThebit lies on the eastern rim of a much older, 220-km diameter crater informally known as "Ancient Thebit." Its eroded rim is still present to the northwest and southwest of Thebit, and unnamed wrinkle ridges in Mare Nubium may correlate with the western rim that is now buried by mare lava. The Rupes Recta, Birt, and Rima Birt are all within Ancient Thebit.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ The geologic history of the Moon. USGS Professional Paper 1348. By Don E. Wilhelms, John F. McCauley, and Newell J. Trask. U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington: 1987. Table 11.2.
- ^ "Thebit (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763. S2CID 122125855.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.
External links
edit- Thebit at The Moon Wiki
- Wood, Chuck (2006-08-08). "Odd Interiors". Lunar Photo of the Day. Retrieved 2017-01-25.
- Wood, Chuck (August 20, 2009). "Succession". Lunar Photo of the Day.