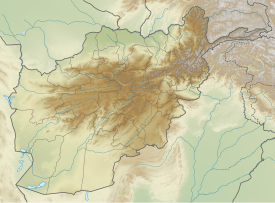
Tepe Fullol (also known as Khush Tepe) is a village in northern Afghanistan where the treasure of Fullol was found, consisting of twenty vessels in gold and silver dated to the Bronze Age. It was accidentally discovered in 1965 by Afghan farmers in a grave cache and provided the first evidence of the Oxus civilization (also known as BMAC) in northern Afghanistan.
Tepe Fullol is situated in Baghlan Province at the junction of the Khost and Sai valleys. On the basis of iconographic comparisons, the treasure has been dated to between 2600 and 1700 BC. There is also a mound, covering an area 14 by 18 metres (46 by 59 ft) and 20 metres (66 ft) high.
The area's wealth probably derived from precious materials extracted from the nearby mountains, in particular lapis lazuli from Badakshan, which were widely traded. The vessel's designs include animal imagery, such as a boar, a stag, snakes and bearded bulls (the latter derived from distant Mesopotamia), indicating that at this early date Afghanistan was already part of an extensive network of trade and cultural exchanges.
Three of these vessels were displayed at the British Museum in 2011.