Modern evolution of Palestine
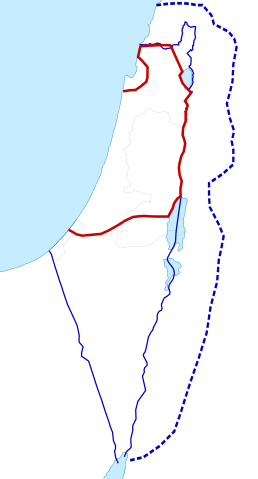
1916–1922 various proposals: Three proposals for the post World War I administration of Palestine. The red line is the "International Administration" proposed in the 1916 Sykes–Picot Agreement, the dashed blue line is the 1919 Zionist Organization proposal at the Paris Peace Conference, and the thin blue line refers to the final borders of the 1923–48 Mandatory Palestine.
1947 UN proposal: Proposal per the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine (UN General Assembly Resolution 181 (II), 1947), prior to the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. The proposal included a Corpus Separatum for Jerusalem, extraterritorial crossroads between the non-contiguous areas, and Jaffa as an Arab exclave.
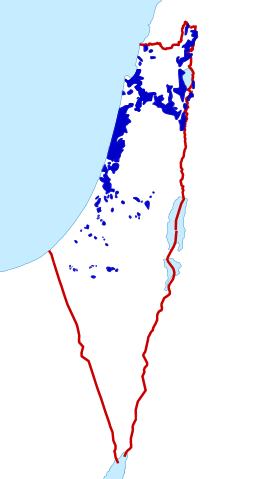
1947 Jewish private land ownership: Jewish-owned lands in Mandatory Palestine as of 1947 in blue, constituting 7.4% of the total land area, of which more than half was held by the JNF and PICA. White is either public land or Palestinian-Arab-owned lands including related religious trusts.
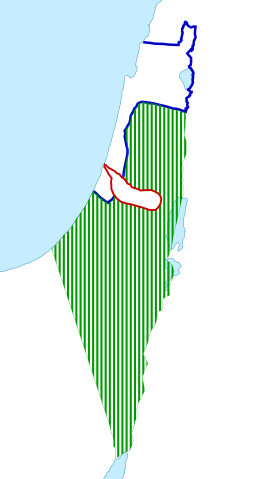
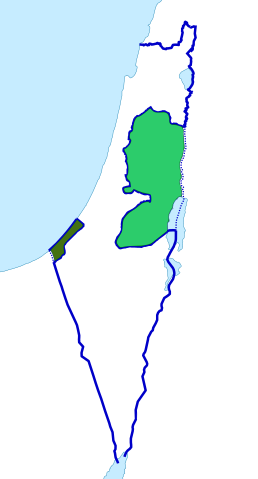
1949 armistice lines: The Jordanian-annexed West Bank (light green) and Egyptian client state All-Palestine Protectorate (dark green), after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, showing 1949 armistice lines.
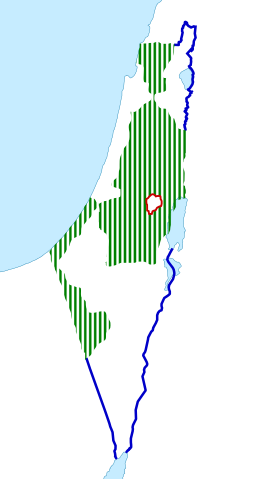
1967 territorial changes: During the Six-Day War, Israel captured the West Bank, the Gaza Strip, and the Golan Heights, together with the Sinai Peninsula (later traded for peace after the Yom Kippur War). In 1980–81 Israel annexed East Jerusalem and the Golan Heights.
Neither Israel's annexation nor the PLO claim over East Jerusalem gained international recognition.
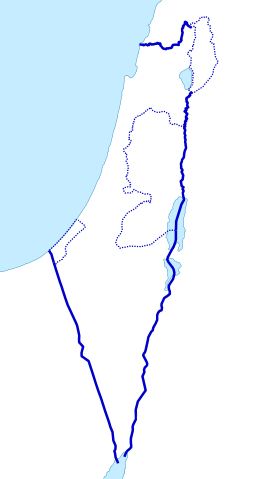
1995 Oslo II Accord: Under the Oslo Accords, the Palestinian National Authority was created to provide a Palestinian interim self-government in the West Bank and the interior of the Gaza Strip. Its second phase envisioned "Palestinian enclaves".
2005–present: After the Israeli disengagement from Gaza and clashes between the two main Palestinian parties following the Hamas electoral victory, two separate executive governments took control in the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and Gaza.
Ethnic majority by settlement (present): The map indicates the ethnic majority of settlements (cities, villages and other communities).