Tagbina, officially the Municipality of Tagbina, is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Surigao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 41,051 people.[3]
Tagbina | |
|---|---|
| Municipality of Tagbina | |
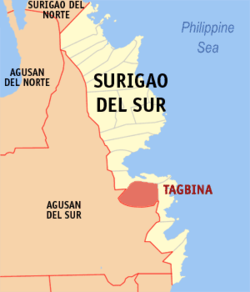 Map of Surigao del Sur with Tagbina highlighted | |
Location within the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 8°27′28″N 126°09′28″E / 8.4578°N 126.1578°E | |
| Country | Philippines |
| Region | Caraga |
| Province | Surigao del Sur |
| District | 2nd district |
| Barangays | 25 (see Barangays) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Sangguniang Bayan |
| • Mayor | Generoso L. Naraiso |
| • Vice Mayor | Antonio N. Adlao |
| • Representative | Johnny T. Pimentel |
| • Electorate | 28,026 voters (2022) |
| Area | |
• Total | 343.49 km2 (132.62 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 44 m (144 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 180 m (590 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 17 m (56 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[3] | |
• Total | 41,051 |
| • Density | 120/km2 (310/sq mi) |
| • Households | 9,686 |
| Economy | |
| • Income class | 2nd municipal income class |
| • Poverty incidence | 31.06 |
| • Revenue | ₱ 185.7 million (2020), 81.66 million (2012), 85.2 million (2013), 98.97 million (2014), 112.6 million (2015), 156.4 million (2016), 160.6 million (2017), 151.3 million (2018), 167.9 million (2019), 199.3 million (2021), 268.7 million (2022) |
| • Assets | ₱ 319.8 million (2020), 114.4 million (2012), 169.6 million (2013), 140.8 million (2014), 135.4 million (2015), 194.9 million (2016), 216 million (2017), 263.5 million (2018), 315.3 million (2019), 336.7 million (2021), 386.3 million (2022) |
| • Expenditure | ₱ 159.2 million (2020), 72.66 million (2012), 70.28 million (2013), 90.6 million (2014), 84.63 million (2015), 107.3 million (2016), 126.8 million (2017), 118.9 million (2018), 147 million (2019), 166.4 million (2021), 210.8 million (2022) |
| • Liabilities | ₱ 99.4 million (2020), 42.78 million (2012), 44.02 million (2013), 37.08 million (2014), 42.9 million (2015), 44.23 million (2016), 63.53 million (2017), 96.46 million (2018), 145.5 million (2019), 70.6 million (2021), 77.2 million (2022) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ZIP code | 8308, 8319 (Malixi only) |
| PSGC | |
| IDD : area code | +63 (0)86 |
| Native languages | Surigaonon Agusan Cebuano Tagalog Kamayo |
| Website | www |
It is one of the only two landlocked municipalities in the province along with San Miguel.
Geography
editBarangays
editTagbina is politically subdivided into 25 barangays. Each barangay consists of puroks while some have sitios.
- Batunan
- Carpenito
- Doña Carmen
- Hinagdanan
- Kahayagan
- Lago
- Maglambing
- Maglatab
- Magsaysay
- Malixi
- Manambia
- Osmeña
- Poblacion
- Quezon
- San Vicente
- Santa Cruz
- Santa Fe
- Santa Juana
- Santa Maria
- Sayon
- Soriano
- Tagongon
- Trinidad
- Ugoban
- Villaverde
Climate
edit| Climate data for Tagbina | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 29.0 (84.2) |
29.1 (84.4) |
30.0 (86.0) |
30.9 (87.6) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.5 (88.7) |
31.6 (88.9) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.4 (88.5) |
30.6 (87.1) |
29.7 (85.5) |
30.8 (87.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 25.3 (77.5) |
25.4 (77.7) |
25.9 (78.6) |
26.6 (79.9) |
27.3 (81.1) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.1 (80.8) |
27.2 (81.0) |
27.1 (80.8) |
26.9 (80.4) |
26.4 (79.5) |
25.8 (78.4) |
26.5 (79.7) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 21.7 (71.1) |
21.7 (71.1) |
21.9 (71.4) |
22.4 (72.3) |
23.0 (73.4) |
22.7 (72.9) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.6 (72.7) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.5 (72.5) |
22.3 (72.1) |
22.0 (71.6) |
22.3 (72.2) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 653 (25.7) |
489 (19.3) |
412 (16.2) |
309 (12.2) |
272 (10.7) |
237 (9.3) |
210 (8.3) |
201 (7.9) |
216 (8.5) |
223 (8.8) |
321 (12.6) |
548 (21.6) |
4,091 (161.1) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[5] | |||||||||||||
Tagbina has a tropical rainforest climate (Af) with heavy to very heavy rainfall year-round.
Demographics
edit| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 13,040 | — |
| 1975 | 20,204 | +9.18% |
| 1980 | 22,572 | +2.24% |
| 1990 | 28,976 | +2.53% |
| 1995 | 32,295 | +2.05% |
| 2000 | 34,057 | +1.15% |
| 2007 | 36,595 | +1.00% |
| 2010 | 34,812 | −1.80% |
| 2015 | 38,833 | +2.10% |
| 2020 | 41,051 | +1.10% |
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[6][7][8][9] | ||
Tourism & Economy
Tagbina is a major robusta coffee producer in the province. It also home to Libuacan Cold Spring a natural blueish green water lagoon.
Tourism
RP Botanical Park, is a hotel and resort that is inspired from a forest and garden. It offers affordable hotel rooms, exclusive accommodation, venue for events such as weddings and seminars. The hotel room price ranges from P300-3,500 Pesos only. It serves as a major tourism destination and accommodation in the municipality of Tagbina.
RP Botanical Park is open to public daily from 10:AM to 5:PM you are advised to make a reservation prior to your arrival. Guests with room bookings however can visit anytime. For more information please visit the hotels website on their Facebook page.
References
edit- ^ Municipality of Tagbina | (DILG)
- ^ "2015 Census of Population, Report No. 3 – Population, Land Area, and Population Density" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. Quezon City, Philippines. August 2016. ISSN 0117-1453. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 25, 2021. Retrieved July 16, 2021.
- ^ a b Census of Population (2020). "Caraga". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ "PSA Releases the 2021 City and Municipal Level Poverty Estimates". Philippine Statistics Authority. April 2, 2024. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
- ^ "Climate: Tagbina". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved October 25, 2020.
- ^ Census of Population (2015). "Caraga". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). "Caraga" (PDF). Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. National Statistics Office. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- ^ Censuses of Population (1903–2007). "Caraga". Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Province/Highly Urbanized City: 1903 to 2007. National Statistics Office.
- ^ "Province of Surigao del Sur". Municipality Population Data. Local Water Utilities Administration Research Division. Retrieved December 17, 2016.
External links
edit- Tagbina Profile at PhilAtlas.com
- Tagbina Profile at the DTI Cities and Municipalities Competitive Index
- Philippine Standard Geographic Code
- Philippine Census Information
- Local Governance Performance Management System