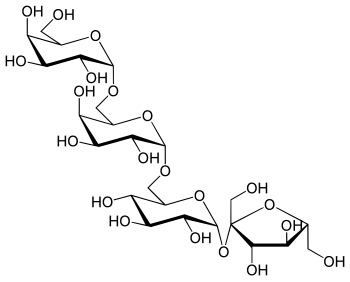
Stachyose is a tetrasaccharide consisting of two α-D-galactose units, one α-D-glucose unit, and one β-D-fructose unit sequentially linked as Gal(α1→6)Gal(α1→6)Glc(α1↔2β)Fruf.[1] Together with related oligosaccharides such as raffinose, stachyose occurs naturally in numerous vegetables (e.g. green beans, soybeans and other beans) and other plants.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
β-D-Fructofuranosyl O-α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→6)-α-D-galactopyranosyl-(1→6)-α-D-glucopyranoside
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(12S,13S,14S,15R,32R,33R,34S,35S,36R,62S,63R,64S,65R,66R,92S,93R,94S,95R,96R)-12,15,96-Tris(hydroxymethyl)-2,5,8-trioxa-3,6(2,6),9(2)-tris(oxana)-1(2)-oxolananonaphane-13,14,33,34,35,63,64,65,93,94,95-undecol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.754 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H42O21 | |
| Molar mass | 666.578 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Stachyose is less sweet than sucrose, at about 28% on a weight basis. It is mainly used as a bulk sweetener or for its functional oligosaccharide properties.[2][additional citation(s) needed] Stachyose is not completely digestible by humans and delivers 1.5 to 2.4 kcal/g (6 to 10 kJ/g).
References
edit- ^ Hanau, Stefania; Almugadam, Shawgi Hago; Sapienza, Eugenia; Cacciari, Barbara; Manfrinato, Maria; Trentini, Alessandro; Kennedy, John (2020). "Schematic overview of oligosaccharides, with survey on their major physiological effects and a focus on milk ones". Carbohydrate Polymer Technologies and Applications. 1: 100013. doi:10.1016/j.carpta.2020.100013. hdl:11392/2426991..
- ^ Nakakuki, T. (2002). "Present status and future of functional oligosaccharide development in Japan" (PDF). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 74 (7): 1245–1251. doi:10.1351/pac200274071245. S2CID 35500606.