The Battle of Arras, also known as the Second Battle of Arras, was a British offensive on the Western Front during the First World War. From 9 April to 16 May 1917, British troops attacked German defences near the French city of Arras on the Western Front. The British achieved the longest advance since trench warfare had begun, surpassing the record set by the French Sixth Army on 1 July 1916. The British advance slowed in the next few days and the German defence recovered. The battle became a costly stalemate for both sides and by the end of the battle, the British Third Army and the First Army had suffered about 160,000 casualties and the German 6th Army about 125,000.
| Battle of Arras | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Western Front of the First World War | |||||||
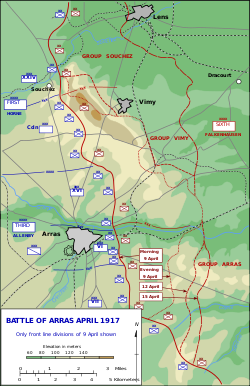 The Battle of Arras, April 1917[image reference needed] | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
First day:
|
First day:
| ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 158,000 | 120,000–130,000 | ||||||
For much of the war, the opposing armies on the Western Front were at stalemate, with a continuous line of trenches from the Belgian coast to the Swiss border.[1] The Allied objective from early 1915 was to break through the German defences into the open ground beyond and engage the numerically inferior German Army (Westheer) in a war of movement. The British attack at Arras was part of the Anglo-French Nivelle Offensive, the main part of which was the Second Battle of the Aisne 50 mi (80 km) to the south.[2] The aim of the French offensive was to break through the German defences in forty-eight hours.[3] At Arras the Canadians were to capture Vimy Ridge, dominating the Douai Plain to the east, advance towards Cambrai and divert German reserves from the French front.[4]
The British effort was an assault on a relatively broad front between Vimy in the north-west and Bullecourt to the south-east. After a long preparatory bombardment, the Canadian Corps of the First Army in the north fought the Battle of Vimy Ridge, capturing the ridge. The Third Army in the centre advanced astride the Scarpe River and in the south, the Fifth Army attacked the Hindenburg Line (Siegfriedstellung) but made few gains. The British armies then conducted smaller attacks to consolidate the new positions. Although these battles were generally successful in achieving limited aims, they came at considerable cost.[4]
When the battle officially ended on 16 May, the British had made significant advances but had been unable to achieve a breakthrough.[4] New tactics and the equipment to exploit them had been used, showing that the British had absorbed the lessons of the Battle of the Somme and could mount set-piece attacks against field fortifications. After the Second Battle of Bullecourt (3–17 May), the Arras sector became a quiet front, typical of most of the war in the west, except for attacks on the Hindenburg Line and around Lens, culminating in the Canadian Battle of Hill 70 (15–25 August).
Background
editAt the beginning of 1917, the British and French were still searching for a way to achieve a strategic breakthrough on the Western Front.[5] The previous year had been marked by the costly success of the Anglo-French offensive astride the River Somme, while the French had been unable to take the initiative because of intense German pressure at Verdun until after August 1916.[6] The battles consumed enormous quantities of resources while achieving virtually no strategic gains on the battlefield.[5] The cost to Germany of containing the Anglo-French attacks had been enormous and given that the material preponderance of the Entente and its allies could only be expected to increase in 1917, Field Marshal Paul von Hindenburg and General Erich Ludendorff decided on a defensive strategy on the Western Front for that year.[7] This impasse reinforced the French and British commanders' belief that to end the stalemate they needed a breakthrough; while this desire may have been the main impetus behind the offensive, the timing and location were influenced by political and tactical considerations.[5][3]
Home fronts
editThe mid-war years were momentous times. Governing politicians in Paris and London were under great pressure from the press, the people and their parliaments to win the war.[8] Hundreds of thousands of casualties had been suffered at the battles of Gallipoli, the Somme and Verdun, with little prospect of victory in sight. The British Prime Minister, H. H. Asquith, resigned in early December 1916 and was succeeded by David Lloyd George.[8] In France, Prime Minister Aristide Briand, along with Minister of Defence Hubert Lyautey were politically diminished and resigned in March 1917, following disagreements over the prospective Nivelle Offensive.[9] The United States was close to declaring war on Germany; American public opinion was growing increasingly incensed by U-boat attacks upon civilian shipping, which had begun with the sinking of RMS Lusitania in 1915 and culminated in the torpedoing of seven American merchantmen in early 1917. The United States Congress declared war on Imperial Germany on 6 April 1917 but it would be more than a year before a suitable army could be raised, trained and transported to France.[10]
Strategy
editThe French, Russians and British had intended to launch a joint spring offensive in 1917 but this strategy foundered in February when the Russians admitted that they could not meet their commitments. The spring offensive was reduced from attacks on the Eastern and Western fronts to a French assault along the Aisne River. In March, the German army in the west (Westheer), withdrew to the Hindenburg line in Operation Alberich, negating the tactical assumptions underlying the plans for the French offensive. Until French troops advanced into the former Noyon Salient during the Battles of Arras, they encountered no German troops in the assault sector and French doubts over the wisdom of the offensive increased. The French government desperately needed a victory to avoid civil unrest but the British were wary of proceeding, given the rapidly changing tactical situation.[11] In a meeting with Lloyd George, French commander-in-chief General Robert Nivelle persuaded the British Prime Minister, that if the British launched a diversionary assault to draw German troops away from the Aisne sector, the French offensive could succeed. It was agreed in the London Convention of 16 January, that the French assault on the Aisne would begin in mid-April and that the British would make a diversionary attack in the Arras sector approximately one week prior.[11][12]
Tactics: British Expeditionary Force
editThree of the armies of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF, Field Marshal Sir Douglas Haig) were in the Arras sector, the Fifth Army (General Hubert Gough) in the south, the Third Army (General Edmund Allenby) in the centre and the First Army (General Henry Horne) in the north and the plan was devised by Allenby.[13] The British used the lessons of the Somme and Verdun the previous year and planned to attack on an 11 mi (18 km) front, from Vimy Ridge in the north to Neuville-Vitasse, 4 mi (6.4 km) south of the Scarpe river.[14] The preliminary bombardment was planned to last about a week except for a much longer and heavier barrage at Vimy Ridge.[15]
Division attack training
editIn December 1916, the training manual SS 135 replaced SS 109 of 8 May 1916 and marked a significant step in the evolution of the BEF into a homogeneous force, well adapted to its role on the Western Front.[16] The duties of army, corps and divisions in planning attacks were standardised. Armies were to devise the plan and the principles of the artillery component. Corps were to allot tasks to divisions, which would then select objectives and devise infantry plans subject to corps approval. Artillery planning was controlled by corps with consultation of divisions by the corps General Officer Commanding, Royal Artillery (GOCRA) which became the title of the officer at each level of command who devised the bombardment plan, which was coordinated with neighbouring corps artillery commanders by the army GOCRA. Specific parts of the bombardment were nominated by divisions, using their local knowledge and the results of air reconnaissance. The corps artillery commander was to co-ordinate counter-battery fire and the howitzer bombardment for zero hour. Corps controlled the creeping barrage but divisions were given authority over extra batteries added to the barrage, which could be switched to other targets by the divisional commander and brigade commanders. SS 135 provided the basis for the operational technique of the BEF for the rest of 1917.[17]
Platoon attack training
editThe training manual SS 143 of February 1917 marked the end of attacks made by lines of infantry with a few detached specialists.[18] The platoon was divided into a small headquarters and four sections, one with two trained grenade-throwers and assistants, the second with a Lewis gunner and nine assistants carrying 30 drums of ammunition, the third section comprised a sniper, scout and nine riflemen and the fourth section had nine men with four rifle-grenade launchers.[19] The rifle and hand-grenade sections were to advance in front of the Lewis-gun and rifle-grenade sections, in two waves or in artillery formation, which covered an area 100 yd (91 m) wide and 50 yd (46 m) deep, with the four sections in a diamond pattern, the rifle section ahead, rifle grenade and bombing sections to the sides and the Lewis gun section behind, until resistance was met. German defenders were to be suppressed by fire from the Lewis-gun and rifle-grenade sections, while the riflemen and hand-grenade sections moved forward, preferably by infiltrating around the flanks of the resistance, to overwhelm the defenders from the rear.[20]
The changes in equipment, organisation and formation were elaborated in SS 144 The Normal Formation For the Attack of February 1917, which recommended that the leading troops should push on to the final objective, when only one or two were involved but that for a greater number of objectives, when artillery covering fire was available for the depth of the intended advance, fresh platoons should "leap-frog" through the leading platoons to the next objective.[21] The new organisations and equipment gave the infantry platoon the capacity for fire and manoeuvre, even in the absence of adequate artillery support. To bring uniformity in adoption of the methods laid down in the revised manuals and others produced over the winter, Haig established a BEF Training Directorate in January 1917, to issue manuals and oversee training. SS 143 and its companion manuals provided British infantry with "off-the-peg" tactics, devised from the experience of the Somme and from French Army operations, to go with new equipment made available by increasing British and Allied war production and better understanding of the organisation necessary to exploit it in battle.[22]
Tactics: German army
editIn a new manual published on 1 December 1916 by Oberste Heeresleitung (OHL, supreme command of the German army), Grundsätze für die Führung in der Abwehrschlacht im Stellungskrieg (Principles of Command for Defensive Battles in Positional Warfare), the policy of unyielding defence of ground, regardless of its tactical value, was replaced by the defence of positions suitable for artillery observation and communication with the rear, where an attacking force would "fight itself to a standstill and use up its resources while the defenders conserve[d] their strength". Defending infantry would fight in areas, with the front divisions in an outpost zone up to 3,000 yd (1.7 mi; 2.7 km) deep behind listening posts, with the main line of resistance placed on a reverse slope, in front of artillery observation posts, which were kept far enough back to retain observation over the outpost zone. Behind the main line of resistance was a Grosskampfzone (battle zone), a second defensive area 1,500–2,500 yd (0.85–1.42 mi; 1.4–2.3 km) deep, on ground hidden from enemy observation, as far as possible while in view of German artillery observers.[23] A rückwärtige Kampfzone (rear battle zone) further back was to be occupied by the reserve battalion of each regiment.[24]
Allgemeines über Stellungsbau (Principles of Field Fortification) was published by OHL in January 1917 and by April an outpost zone (Vorpostenfeld) held by sentries, had been built along the Western Front. Sentries could retreat to larger positions (Gruppennester) held by Stosstrupps (five men and an NCO per Trupp), who would join the sentries to recapture sentry-posts by immediate counter-attack. Defensive procedures in the battle zone were similar but with bigger units. The front trench system was the sentry line for the battle zone garrison, which was allowed to move away from concentrations of enemy fire and then counter-attack to recover the battle and outpost zones; such withdrawals were envisaged as occurring on small parts of the battlefield which had been made untenable by Allied artillery fire, as the prelude to Gegenstoß in der Stellung (immediate counter-attack within the position). Such a decentralised battle by large numbers of small infantry detachments would present the attacker with unforeseen obstructions. Resistance from troops equipped with automatic weapons, supported by observed artillery fire, would increase the further the advance progressed. A school was opened in January 1917 to teach infantry commanders the new methods.[25]
Given the growing Allied superiority in munitions and manpower, attackers might still penetrate to the second Artillerieschutzstellung (artillery protection line), leaving in their wake German garrisons isolated in resistance nests Widerstandsnester (Widas) still inflicting losses and disorganisation on the attackers. As the attackers tried to capture the Widas and dig in near the German second line, Sturmbattalions and Sturmregimenter of the counter-attack divisions would advance from the rückwärtige Kampfzone into the battle zone, in an immediate counter-attack (Gegenstoß aus der Tiefe). If the immediate counter-attack failed, counter-attack divisions would take their time to prepare a methodical attack if the lost ground was essential to the retention of the main position. Such methods required large numbers of reserve divisions ready to move to the battlefront. The reserve was obtained by creating 22 divisions by internal reorganisation of the army, bringing divisions from the eastern front and by shortening the Western Front, in Operation Alberich. By the spring of 1917, the German army in the west had a strategic reserve of 40 divisions.[26]
German 6th Army
editExperience of the German 1st Army in the Somme Battles, (Erfahrungen der I Armee in der Sommeschlacht) was published on 30 January 1917 by Ludendorff but new defensive methods were controversial. During the Battle of the Somme in 1916 Colonel Fritz von Loßberg (Chief of Staff of the 1st Army) had been able to establish a line of relief divisions (Ablösungsdivisionen), with the reinforcements from Verdun, which began to arrive in greater numbers in September. In his analysis of the battle, Loßberg opposed the granting of discretion to front trench garrisons to retire, as he believed that manoeuvre would not evade Allied artillery fire, which could blanket the forward area and invited French or British infantry to occupy vacant areas. Loßberg considered that spontaneous withdrawals would disrupt the counter-attack reserves as they deployed and further deprive battalion and division commanders of the means to conduct an organised defence, which the dispersal of infantry over a wide area had already made difficult. Loßberg and others had severe doubts as to the ability of relief divisions to arrive on the battlefield in time to conduct an immediate counter-attack (Gegenstoss) from behind the battle zone. Sceptics wanted the tactic of fighting in the front line to continue, with authority devolved no further than battalion, to maintain organizational coherence in anticipation of a methodical counter-attack (Gegenangriff) by the relief divisions after 24–48 hours. Ludendorff was sufficiently impressed by Loßberg's memorandum to add it to the new Manual of Infantry Training for War.[27]
General Ludwig von Falkenhausen, commander of the 6th Army arranged the infantry at Arras for the rigid defence of the front-line, supported by methodical counter-attacks (Gegenangriffe), by the "relief" divisions (Ablösungsdivisionen) on the second or third day. Five Ablösungsdivisionen were placed behind Douai, 15 mi (24 km) away from the front line.[28] The new Hindenburg line ended at Telegraph Hill between Neuville-Vitasse and Tilloy lez Mofflaines, from whence the original system of four lines 75–150 yd (69–137 m) apart, ran north to the Neuville St Vaast–Bailleul-aux-Cornailles road. About 3 mi (4.8 km) behind were the Wancourt–Feuchy and to the north the Point du Jour lines, running from the Scarpe river north along the east slope of Vimy ridge. The new Wotan line, which extended the Hindenburg position, was built around 4 mi (6.4 km) further back and not entirely mapped by the Allies until the battle had begun.[29]
Just before the battle, Falkenhausen had written that parts of the front line might be lost but the five Ablösungsdivisionen could be brought forward to relieve the front divisions on the evening of the second day. On 6 April, General Karl von Nagel, the 6th Army Chief of Staff, accepted that some of the front divisions might need to be relieved on the first evening of battle but that any penetrations would be repulsed with local immediate counter-attacks (Gegenangriffe in der Stellung) by the front divisions. On 7 April, Nagel viewed the imminent British attack as a limited effort against Vimy ridge, preparatory to a bigger attack later, perhaps combined with the French attack expected in mid-April.[30] Construction of positions to fulfil the new policy of area defence had been drastically curtailed by shortages of labour and the long winter, which affected the setting of concrete. The 6th Army commanders had also been reluctant to encourage the British to change their plans if the British detected a thinning of the front line. The Germans were inhibited by the extent of British air reconnaissance, which observed new field works and promptly directed artillery fire on them. The 6th Army failed to redeploy its artillery, which remained in lines easy to see and bombard. Work on defences was also divided between maintaining the front line, strengthening the third line and the new Wotanstellung (Drocourt–Quéant switch line) further back.[31]
Prelude
editBritish preparations
editUnderground
editAfter the Allied conference at Chantilly, Haig issued instructions for army commanders on 17 November 1916, with a general plan for offensive operations in the spring of 1917. The Chief engineer of the Third Army, Major-General E. R. Kenyon, composed a list of requirements by 19 November, for which he had 16 Army Troops companies, five with each corps in the front line and one with XVIII Corps, four tunnelling companies, three entrenching battalions, eight RE labour battalions and 37 labour companies. Inside the old walls of Arras were the Grand Place and Petit Place, under which there were old cellars, which were emptied and refurbished for the accommodation of 13,000 men. Under the suburbs of St Sauveur and Ronville were many caves, some huge, which were rediscovered by accident in October 1916. When cleared out, the caves had room for 11,500 men, one in the Ronville system housing 4,000 men. The 8 ft × 6 ft (2.4 m × 1.8 m) Crinchon sewer followed the ditch of the old fortifications and tunnels were dug from the cellars to the sewer.[32]
Two long tunnels were excavated from the Crinchon sewer, one through the St Sauveur and one through the Ronville system, allowing the 24,500 troops safely sheltered from German bombardment to move forward underground, avoiding the railway station, an obvious target for bombardment. The St Sauveur tunnel followed the line of the road to Cambrai and had five shafts in no man's land but the German retirement to the Hindenburg Line forestalled the use of the Ronville tunnels, when the German front line was withdrawn 1,000 yd (910 m) and there was no time to extend the diggings. The subterranean workings were lit by electricity and supplied by piped water, with gas-proof doors at the entrances; telephone cables, exchanges and testing-points used the tunnels, a hospital was installed and a tram ran from the sewer to the St Sauveur caves. The observation post for the VI Corps heavy artillery off the St Sauveur tunnel, had a telephone exchange with 750 circuits; much of the work in this area being done by the New Zealand Tunnelling Company.[33][a]
On the First Army front German sappers also conducted underground operations, seeking out Allied tunnels to assault and counter-mine, in which 41 New Zealand tunnellers were killed and 151 wounded.[35] The British tunnellers had gained an advantage over the German miners by the Autumn of 1916, which virtually ended the German underground threat. The British turned to digging 12 subways about 25 ft (7.6 m) down, to the front line, the longest tunnel being 1,883 yd (1.070 mi; 1.722 km) long of the 10,500 yd (6.0 mi; 9.6 km) dug. In one sector, four Tunnelling companies of 500 men each, worked around-the-clock in 18-hour shifts for two months to dig 12 mi (20 km) of subways for foot traffic, tramways with rails for hand-drawn trolleys and a light railway system.[35] Most tunnels were lit by electricity, accommodated telephone cables and some had trams and water supplies. Caverns were dug into the sides for brigade and battalion HQs, first aid posts and store-rooms. The subways were found to be a most efficient way to relieve troops in the line, form up for the attack and then to evacuate wounded. Some of the tunnels were continued into Russian saps with exits in mine craters in no man's land and new mines were laid. Galleries were dug to be opened after the attack for communication or cable trenches, the work being done by the 172nd, 176th, 182nd and 185th Tunnelling companies (Lieutenant-Colonel G. C. Williams, Controller of Mines First Army).[36][b]
War in the air
editAlthough the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) entered the battle with inferior aircraft to the Luftstreitkräfte, this did not deter their commander, General Trenchard, from adopting an offensive posture. Dominance of the air over Arras was essential for reconnaissance and the British carried out many aerial patrols. RFC aircraft carried out artillery spotting, photography of trench systems and bombing.[38][39] Aerial observation was hazardous work as, for best results, the aircraft had to fly at slow speeds and low altitude over the German defences. It became even more dangerous with the arrival of the Red Baron, Manfred von Richthofen in March 1917. The presence of Jasta 11 led to sharply increased losses of Allied pilots and April 1917, became known as Bloody April. A German infantry officer later wrote,
...during these days, there was a whole series of dogfights, which almost invariably ended in defeat for the British since it was Richthofen's squadron they were up against. Often five or six planes in succession would be chased away or shot down in flames.
— Ernst Jünger[40]
The average flying life of a RFC pilot in Arras in April was 18 hours and from 4 to 8 April, the RFC lost 75 aircraft and 105 aircrew. The casualties created a pilot shortage and replacements were sent to the front straight from flying school; during the same period, 56 aircraft were crashed by inexperienced RFC pilots.[38]
Artillery
editTo keep enemy action to a minimum during the assault, a creeping barrage was planned. This required gunners to create a curtain of high explosive and shrapnel shell explosions that crept across the battlefield in lines, about one hundred metres in advance of the assaulting troops. The Allies had previously used creeping barrages at the Battle of Neuve Chapelle and the Battle of the Somme but had encountered two technical problems. The first was accurately synchronising the movement of the troops to the fall of the barrage: for Arras, this was overcome by rehearsal and strict scheduling. The second was the barrage falling erratically as the barrels of heavy guns wore swiftly but at differing rates during fire: for Arras, the rate of wear of each gun barrel was calculated and calibrated accordingly. While there was a risk of friendly fire, the creeping barrage forced the Germans to remain in their shelters, allowing Allied soldiers to advance without fear of machine gun fire. The new instantaneous No. 106 Fuze had been adapted from a French design for high-explosive shells so that they detonated on the slightest impact, vaporising barbed wire. Poison gas shells were used for the final minutes of the barrage.[41]
The principal danger to assaulting troops came from enemy artillery fire as they crossed no man's land, accounting for over half the casualties at the first day of the Somme. A further complication was the location of German artillery, hidden as it was behind the ridges. In response, specialist artillery units were created to attack German artillery. Their targets were provided by 1st Field Survey Company, Royal Engineers,[42] who collated data obtained from flash spotting and sound ranging. (Flash spotting required Royal Flying Corps observers to record the location of telltale flashes made by guns whilst firing.) On Zero-Day, 9 April, over 80 per cent of German heavy guns in the sector were neutralised (that is, "unable to bring effective fire to bear, the crews being disabled or driven off") by counter-battery fire.[42] Gas shells were also used against the draught horses of the batteries and to disrupt ammunition supply columns.[43]
Tanks
editForty tanks of the 1st Brigade were to be used in the attack on the Third Army front, eight with XVIII Corps and sixteen each in VII Corps and VI Corps. When the blue line had been reached, four of the VII Corps tanks were to join VI Corps for its attack on the brown line. The black line (first objective) was not to be attacked by tanks, which were to begin the drive to the front line at zero hour and rendezvous with infantry at the black line two hours later. The tanks were reserved for the most difficult objectives beyond the black line in groups of up to ten vehicles. Four tanks were to attack Neuville Vitasse, four against Telegraph Hill, four against The Harp and another four against Tilloy lez Mofflaines and two were to drive down the slope from Roclincourt west of Bois de la Maison Blanche. Once the blue line had fallen, the tanks still running were to drive to rally points.[44]
Battle
editFirst phase
editThe preliminary bombardment of Vimy Ridge started on 20 March; and the bombardment of the rest of the sector on 4 April.[35] Limited to a front of only 24 mi (39 km), the bombardment used 2,689,000 shells,[45] over a million more than had been used on the Somme.[11] German casualties were not heavy but the men became exhausted by the endless task of keeping open dug-out entrances and demoralised by the absence of rations caused by the difficulties of preparing and moving hot food under bombardment. Some went without food altogether for two or three consecutive days.[45] By the eve of battle, the front-line trenches had ceased to exist and their barbed wire defences were blown to pieces. The official history of the 2nd Bavarian Reserve Regiment describes the front line as "consisting no longer of trenches but of advanced nests of men scattered about". The 262nd Reserve Regiment history writes that its trench system was "lost in a crater field".[45] To add to the misery, for the last ten hours of bombardment, gas shells were added.[46]
Zero-Hour had originally been planned for the morning of 8 April (Easter Sunday) but it was postponed 24 hours at the request of the French, despite reasonably good weather in the assault sector. Zero-Day was rescheduled for 9 April with Zero-Hour at 05:30. The assault was preceded by a hurricane bombardment lasting five minutes, following a relatively quiet night. When the time came, it was snowing heavily; Allied troops advancing across no man's land were hindered by large drifts. It was still dark and visibility on the battlefield was very poor.[46] A westerly wind was at the Allied soldiers' backs blowing "a squall of sleet and snow into the faces of the Germans". The combination of the unusual bombardment and poor visibility meant many German troops were caught unawares and taken prisoner, still half-dressed, clambering out of the deep dugouts of the first two lines of trenches. Others were captured without their boots, trying to escape but stuck in the knee-deep mud of the communication trenches.[45]
First Battle of the Scarpe (9–14 April 1917)
editThe main British assault of the first day was directly east of Arras, with the 12th (Eastern) Division attacking Observation Ridge, north of the Arras–Cambrai road. After reaching this objective, they were to push on towards Feuchy, the second and third German positions. At the same time, elements of the 3rd Division began an assault south of the road, with the Devil's Wood, Tilloy-lès-Mofflaines and the Bois des Boeufs as their initial objectives.[47] The ultimate objective of these assaults was the Monchyriegel, a trench running between Wancourt and Feuchy and an important component of the German defences.[46] Most of these objectives, including Feuchy village, had been achieved by the evening of 10 April though the Germans were still in control of large sections of the trenches between Wancourt and Feuchy, particularly in the area of the fortified village of Neuville-Vitasse.[46]
The following day, troops from the 56th (1/1st London) Division were able to force the Germans out of the village, although the Monchyriegel was not fully in British hands until a few days later.[46] The British were able to consolidate these gains and push forward towards Monchy-le-Preux, although they suffered many casualties in fighting near the village.[48] One reason for the success of the offensive in this sector was the failure of Falkenhausen to employ a defence in depth. In theory, an attacker would be allowed to make initial gains, thus stretching their lines of communication. Reserves held close to the battlefield would be committed once the initial advance had bogged down, before enemy reinforcements could be brought up. The defenders would thus be able to counter-attack and regain any lost territory. In this sector, Falkenhausen kept his reserve troops too far from the front and they were too late for a useful counter-attack on either 10 or 11 April.[49]
Battle of Vimy Ridge (9–12 April 1917)
editAt roughly the same time, in perhaps the most carefully crafted portion of the entire offensive, the Canadian Corps launched an assault on Vimy Ridge. Advancing behind a creeping barrage and making heavy use of machine guns – eighty to each brigade, including one Lewis gun in each platoon – the corps was able to advance through about 4,000 yd (3,700 m) of German defences and captured the crest of the ridge at about 13:00 on 10 April.[50] Military historians have attributed the success of this attack to careful planning by Canadian Corps commander Julian Byng and his subordinate General Arthur Currie,[51] constant training and the assignment of specific objectives to each platoon. By giving units specific goals, troops could continue the attack even if their officers were killed or communication broke down, thus bypassing two major problems of combat on the Western Front.[52] The Canadian troops could see the Germans in retreat across the Douai Plain away from the ridge. There was nevertheless an inflexibility to the plan which prevented the leading troops from continuing the advance and on 10 April the Germans began to stop the gaps with reserves.[53]
Second phase
editAfter the territorial gains of the first two days, a lull followed as British guns, ammunition and transport links were moved forward. Battalions of pioneers built temporary roads across the churned up battlefield; heavy artillery (and its ammunition) was manhandled into position in new gun pits; food for the men and feed for the draught horses was brought up and Casualty Clearing Stations were established in readiness for the inevitable counter-attacks. Allied commanders also faced a dilemma: whether to keep their exhausted divisions on the attack and run the risk of having insufficient manpower or replace them with fresh divisions and lose momentum.[54]
The news of the battle reached General Ludendorff during his 52nd birthday celebrations at his headquarters in Kreuznach who wrote, "I had looked forward to the expected offensive with confidence and was now deeply depressed". He telephoned each of his commanders and "gained the impression that the principles laid down by OHL were sound but the whole art of leadership lies in applying them correctly". (A later court of inquiry found that Falkenhausen had indeed misunderstood the principles of defence in depth.)[55] Ludendorff immediately ordered reinforcements.[52] On 11 April, he sacked Falkenhausen's chief of staff and replaced him with Loßberg.[56] Loßberg went armed with vollmacht (the right to issue orders in the army commander's name) and within hours, Loßberg began to restructure the German defence.[57] The British aimed to consolidate the gains made in the first days of the offensive, to keep the initiative and to break through in concert with the French at Aisne.[53] From 16 April, it was apparent that the French part of the Nivelle Offensive on the Aisne had not achieved a breakthrough. Haig continued to attack at Arras, to divert troops from the French on the Aisne.[citation needed]
Second Battle of the Scarpe (23–24 April 1917)
editAt 04:45 on 23 April, following two days of poor visibility and freezing weather, VI Corps and VII Corps attacked to the east on a 9 mi (14 km) front from Croisilles to Gavrelle, either side of the Scarpe. The 51st (Highland) Division attacked on the northern side in determined fighting on the western outskirts of Roeux Wood and the chemical works. On their left, the 37th Division, attacked the buildings west of Roeux Station and gained the line of their objectives on the western slopes of Greenland Hill, north of the railway. On the left of the main attack, the 63rd (Royal Naval) Division made rapid progress against Gavrelle and secured the village. To the south of the Scarpe and east of Monchy-le-Preux the 29th Division gained the western slopes of Infantry Hill.[58]
The Cojeul river marked a divisional boundary within VI Corps. Guémappe on the north side of the river was the objective of the 15th (Scottish) Division, attacking east from Wancourt towards Vis-en-Artois.[58] The objective was commanded by the higher ground on the south bank and it was not until the 50th (Northumbrian) Division captured the rise on the south side of the Cojeul that the village was taken. Several determined German counter-attacks were made and by the morning of 24 April, the British held Guémappe, Gavrelle and the high ground overlooking Fontaine-lès-Croisilles and Cherisy; the fighting around Roeux was indecisive.[59]
Battle of Arleux (28–29 April 1917)
editThe principal objective of the attack was to tie down German reserves to assist the French offensive against the plateau north of the Aisne traversed by the Chemin des Dames. Haig reported,
With a view to economising my troops, my objectives were shallow and for a like reason and also in order to give the appearance of an attack on a more imposing scale, demonstrations were continued southwards to the Arras-Cambrai Road and northwards to the Souchez River.[60]
Although the Canadian Corps had taken Vimy Ridge, difficulties in securing the south-eastern flank had left the position vulnerable. To rectify this, British and Canadian troops launched an attack towards Arleux on 28 April. The village was captured by Canadian troops with relative ease but the British troops advancing on Gavrelle met stiffer resistance. The village was secured by early evening but when a German counter-attack forced a brief retreat, elements of the 63rd (Royal Naval) Division were brought up as reinforcements and the village was held. Subsequent attacks on 29 April failed to capture more ground. The attacks achieved the limited objective of securing the Canadian position on Vimy Ridge but casualties were high and the result was disappointing.[61]
Third Battle of the Scarpe (3–4 May 1917)
editAfter securing the area around Arleux at the end of April, the British determined to launch another attack east from Monchy to try to break through the Boiry Riegel and reach the Wotanstellung, another German defensive position in the Douai Plain. This was scheduled to coincide with the Australian attack at Bullecourt to present the Germans with a two–pronged assault. British commanders hoped that success in this venture would force the Germans to retreat further to the east. The British launched another attack using regiments from the 4th Division near the Scarpe on 3 May. Neither effort made a significant advance and the attack was called off the following day after incurring many casualties. The British learned important lessons about the need for close liaison between tanks, infantry and artillery, which they used in the Battle of Cambrai, 1917.[62]
Flanking operations (Round Bullecourt, 11 April – 16 June)
editFirst attack on Bullecourt
edit8–10 April
editThe Hindenburg Line defences enclosing the village of Bullecourt formed a re-entrant for about 2,500 yd (2,286 m) to the Balkonstellung (Balcony Trench) around Quéant, defended by the élite German 27th Division.[63][c] On 8 April it was announced that wire cutting, begun on 5 April, would take another eight days.[65][d] At dusk on 9 April, patrols went forward and found that the Hindenburg Line was occupied but that the wire cutting bombardment had made several lanes through the wire. Preparations were made in a rush, the 4th Australian Division to attack with two brigades, the 4th on the right and 12th on the left. The attack had to cover 500 yd (457 m) to the wire and another 100 yd (91 m) to the first trench at 4:30 a.m., about an hour and 48 minutes before the sun rose to evade crossfire in the re-entrant between Quéant and Bullecourt. Artillery-fire would continue as normal until zero hour then maintain barrages on the flanks.[67]
At 1:00 a.m. Bullecourt was subjected to a gas bombardment by Livens projectors and Stokes 4-inch mortars as the Australians assembled and waited for the tanks to arrive. Six battalions were out in the snow of no man's land. The left of the 12th Australian Brigade was only 400 yd (366 m) from Bullecourt and dawn was approaching. Zero hour was put back but the tanks had only reached Noreuil and Holmes ordered the infantry back under cover; snow began to fall again and shielded the retirement.[68][e] Patrols of the 2/7th and 2/8th battalions, West Yorkshire Regiment began to advance from 4:35 p.m. and at 5:10 a.m. the patrols began to retire. The patrols suffered 162 casualties.[70]
11 April
editAt a conference at the 4th Australian Division HQ, it was decided that the infantry would advance fifteen minutes after the tanks, rather than wait on a signal from them. Only four tanks reached their start line by 4:30 a.m. but drowning the sound of their engines with machine-gun fire failed and they were heard in the German defences.[71] The tank on the right flank deviated to the right, suffered mechanical difficulties and returned to the railway. Another tank also veered right and crossed the first trench of the Balkonstellung opposite Grenadier Regiment 123 and was knocked out by machine-guns firing armour-piercing (K bullet) ammunition. The next tank to reach the German lines was snagged by wire, then crossed the first trench before being knocked out. The last tank started late and followed a similar path to the first. The four tanks comprising the left-hand section were late and two were knocked out short of the German trenches; the third tank arrived behind the Australian infantry and silenced a machine-gun in Bullecourt. The tank was hit twice, returned to the railway and was hit again.[f]
The Australian infantry in the German defences were cut off and the 4th Australian Brigade was forced back; many of its troops were taken prisoner and those who tried to retreat suffered many more casualties. In the 12th Australian Brigade, the 46th Australian Battalion in the first trench was forced out and the 48th Australian Battalion further forward was surrounded.[73] The artillery of the 2nd Guard Division and 220th Division added to the barrage in no man's land and prevented another Australian attack. As the Australians were being forced back, they were unable to salvage ammunition and grenades from the dead and wounded.[74] The British and Australian artillery had eventually begun to fire but this fell on the Australian-occupied trenches, making them untenable. At 12:25 p.m. the 48th Australian Battalion, the last in the German trenches, made an orderly retreat over the bullet-swept ground.[73] By noon the German counter-attack had succeeded; few Australians had managed to re-cross no man's land through artillery and machine-gun fire.[74]
German attack on Lagnicourt (15 April 1917)
editObserving that the 1st Australian Division was holding a frontage of 13,000 yd (7.4 mi; 12 km), the local German corps commander General Otto von Moser, commanding Gruppe Quéant (XIV Reserve Corps) planned a spoiling attack to drive back the advanced posts, destroy supplies and guns and then retire to the Hindenburg defences. OHL had added an extra division to his Gruppe and added two more from Gruppe Cambrai to the south, further to strengthen the attack. The four divisions provided 23 battalions for Unternehmen Sturmbock (Operation Battering Ram). The German forces managed to penetrate the Australian front line at the junction on the 1st Australian Division and 2nd Australian Division, occupying the village of Lagnicourt and destroyed six Australian artillery pieces. Counter-attacks from the 9th and 20th Australian battalions restored the front line and the action ended with the Germans having suffered 2,313 casualties and the Australians 1,010.[75]
Battle of Bullecourt (3–17 May 1917)
editAfter the initial assault around Bullecourt failed to penetrate the German lines, British commanders made preparations for a second attempt. British artillery began an intense bombardment of the village, which by 20 April had been virtually destroyed. Although the infantry assault was planned for 20 April, it was postponed several times until early morning of 3 May.[76] At 03:45, elements of the 2nd Australian Division attacked east of Bullecourt village, intending to pierce the Hindenburg Line and capture Hendecourt-lès-Cagnicourt, while British troops from the 62nd (2nd West Riding) Division attacked Bullecourt, which was finally taken by the 7th Division and despite determined counter-attacks was held by the 62nd (2nd West Riding) Division. German resistance was fierce and when the offensive was called off on 17 May, few of the initial objectives had been met. The Australians were in possession of much of the German trench system between Bullecourt and Riencourt-lès-Cagnicourt but had been unable to capture Hendecourt. To the west, British troops managed to push the Germans out of Bullecourt but incurred considerable losses, failing also to advance north-east to Hendecourt.[77]
Aftermath
editAnalysis
editBy the standards of the Western Front, the gains of the first two days were nothing short of spectacular. A great deal of ground was gained for relatively few casualties and a number of tactically significant points were captured, notably Vimy Ridge. The offensive drew German troops away from the French offensive in the Aisne sector.[52] In many respects, the battle might be deemed a victory for the British and their allies but these gains were offset by high casualties after the first two days and the failure of the French offensive at the Aisne. By the end of the offensive, the British had suffered more than 150,000 casualties and gained little ground since the first day. Despite significant early gains, they were unable to break through and the situation reverted to stalemate. Although historians generally consider the battle a British victory, in the wider context of the front, it had very little impact on the strategic or tactical situation.[53][52] Ludendorff later commented "no doubt exceedingly important strategic objects lay behind the British attack but I have never been able to discover what they were".[57] Ludendorff was also "very depressed; had our principles of defensive tactics proved false and if so, what on Earth was to be done?"[78]
Awards
editOn the Allied side, twenty-five Victoria Crosses were awarded. On the German side, on 24 April 1917, Kaiser Wilhelm awarded Loßberg the Oakleaves (similar to a bar for a repeat award) for the Pour le Mérite he had received at the Battle of the Somme the previous September.[79]
Casualties
editThe most quoted Allied casualty figures are those in the returns made by Lieutenant-General Sir George Fowke, the Adjutant-General. Fowkes collated the daily casualty tallies kept by each unit under Haig's command and his findings were endorsed by the official historian Cyril Falls in 1940.[80][g] Third Army casualties were 87,226, the First Army suffered 46,826 (including 11,004 Canadians at Vimy Ridge) and the Fifth Army 24,608 casualtis, a total of 158,660.[81] German losses are more difficult to determine. Gruppe Vimy and Gruppe Souchez suffered 79,418 casualties but the figures for Gruppe Arras are incomplete. Wolfgang Foerster, the editor of the German official history Der Weltkrieg volume for early 1917 (1939), recorded 85,000 German casualties, 78,000 British losses to the end of April and another 64,000 casualties by the end of May, a total of 142,000.[82] German records excluded the "lightly wounded". Captain Cyril Falls, the author of the History of the Great War volume on the battle (1940), estimated that 30 per cent needed to be added to German returns for comparison with the British. Falls made "a general estimate" that German casualties were "probably fairly equal". Nicholls puts them at 120,000 and Keegan at 130,000.[83]
Commanders
editAlthough Haig paid tribute to Allenby for the "great initial success"; Allenby's subordinates "objected to the way he handled the ... attritional stage" and he was sent to command the Egyptian Expeditionary Force in Palestine. He regarded the transfer as a "badge of failure" but "more than redeemed his reputation by defeating" the Ottomans in battles that were fought in the Sinai and Palestine campaign from 1917 to 1918.[84] Haig stayed in his post until the end of the war. When the failures of the 6th Army command became apparent, Ludendorff removed Falkenhausen (who never held a field command again, spending the rest of the war as Governor-General of Belgium) and several staff officers.[56] Ludendorff and Loßberg discovered that although the Allies were capable of breaking through the first position, they could probably not capitalise on their success if they were confronted by a mobile, clever defence. Ludendorff immediately ordered more training in manoeuvre warfare for the Eingreif divisions.[85] Loßberg was soon promoted to general and directed the defensive battle of the 4th Army against the Flanders Offensive of the summer and late autumn; he had become "legendary as the fireman of the Western Front; always sent by OHL to the area of crisis".[86]
Literature and music
editSiegfried Sassoon makes reference to the battle in the poem The General. The Anglo-Welsh lyric poet Edward Thomas was killed by a shell on 9 April 1917, during the first day of the Easter Offensive.[87] Thomas's war diary gives a vivid and poignant picture of life on the Western front in the months leading up to the battle. C. K. Scott Moncrieff, the translator of Proust, was severely wounded on 23 April 1917 leading an assault on the German trenches outside Monchy-le-Preux (for which he was awarded the MC) and the composer Ernest John Moeran was wounded during the attack on Bullecourt on 3 May 1917.[88][89]
Notes
edit- ^ Due to British fears that blowing the mines would churn up the ground too much and the German withdrawal south-east of Arras, the British were to spring only the 1,000 kg (2,200 lb) charge at Blagny, which was blown by the New Zealand Tunnelling Company at zero hour, 5:30 a.m. Two German dugouts, 46 m (50 yd) of trench and a concrete pillbox were destroyed but it also stunned and apparently buried some members of the 13th Royal Scots and impeded their assault temporarily.[34]
- ^ Most of the tunnels and trenches are barred to the public for reasons of safety. A 270 yd (250 m) portion of the Grange Subway at Vimy Ridge is open to the public from May to November and the Wellington tunnel was opened to the public as the Carrière Wellington museum in March 2008.[37]
- ^ In the Report of the Battles Nomenclature Committee (1921), subsidiary operations to the main Battle of Arras were labelled "Flanking Operations to the Arras Offensive".[64]
- ^ Despite transfers, the Fifth Army had 26 batteries of medium and heavy howitzers but traffic jams caused many hold-ups. When the Bapaume railway station opened on 6 April, train delays caused huge traffic jams, made worse because the lorries could carry only half-loads because of the German road demolitions. The heavy guns of the 1st Anzac Corps fired 1,100 rounds on 3 April, 1,695 and from 5 to 8 April averaged 4,000 rounds per day and 6,025 on 9 April.[66]
- ^ IR 120 in Bullecourt spotted the Australians but were distracted by the 2/7th and 2/8th battalions, West Yorkshire Regiment.[69]
- ^ Falls wrote that reports that tanks got into Riencourt and Hendecourt were caused by the foreshortening effect of the rolling down land. An Australian forward observation officer reported that two tanks and 200 infantry penetrated Hendecourt and that Indian cavalry could be seen west of Riencourt; no cavalry of the Sialkot Brigade came within 1.5 mi (2 km) of the village.[72]
- ^ The original records are in The National Archives
Footnotes
edit- ^ Ashworth 2000, pp. 3–4.
- ^ Ashworth 2000, pp. 48–51, 55–56.
- ^ a b Keegan 1999, pp. 348–352.
- ^ a b c Ashworth 2000, pp. 55–56.
- ^ a b c Ashworth 2000, pp. 48–51.
- ^ Doughty 2005, pp. 250–310.
- ^ Wynne 1976, p. 133.
- ^ a b Keegan 1999, pp. 227–231.
- ^ Strachan 2003, pp. 243–244.
- ^ Keegan 1999, pp. 377–379.
- ^ a b c Strachan 2003, p. 243.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 16.
- ^ Nicholls 2005, p. 23.
- ^ Wynne 1976, p. 168.
- ^ Nicholls 2005, pp. 30–32.
- ^ Bellis 1996, pp. 1–81.
- ^ Simpson 2006, pp. 63–70.
- ^ Bellis 1996, pp. 83–107.
- ^ Griffith 1996, p. 77.
- ^ Corkerry 2001, p. 88.
- ^ Bond 1999, p. 86.
- ^ Sheffield 2011, pp. 209–211.
- ^ Wynne 1976, pp. 149–151.
- ^ Samuels 1995, p. 181.
- ^ Wynne 1976, pp. 152–156.
- ^ Wynne 1976, pp. 156–158.
- ^ Wynne 1976, p. 161.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 240, map.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 175–176.
- ^ Wynne 1976, p. 180.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 353–354.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 189, 192–193.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 193.
- ^ Jones 2010, pp. 136–137.
- ^ a b c Nicholls 2005, p. 30.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 309.
- ^ Veterans Affairs Canada website Archived 21 June 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Nicholls 2005, p. 36.
- ^ Levine 2008, pp. 252–253.
- ^ Jünger 2003, p. 133.
- ^ Nicholls 2005, pp. 53–64.
- ^ a b Sheffield 2002, p. 194.
- ^ Wynne 1976, pp. 173–175.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 186–187.
- ^ a b c d Wynne 1976, p. 173.
- ^ a b c d e Oldham 1997, p. 50.
- ^ Oldham 1997, pp. 50–53.
- ^ Oldham 1997, p. 56.
- ^ Keegan 1999, pp. 325–326.
- ^ Strachan 2003, pp. 244–246.
- ^ Berton 1986, pp. 104–105.
- ^ a b c d Strachan 2003, p. 244.
- ^ a b c Keegan 1999, p. 352.
- ^ Buffetaut 1997, p. 84.
- ^ Sheldon 2008, p. 325.
- ^ a b Lupfer 1981, p. 29.
- ^ a b Ludendorff 2005, pp. 421–422.
- ^ a b Stewart & Buchan 2003, pp. 129–133.
- ^ Boraston 1919, pp. 97–98.
- ^ Boraston 1919, p. 99.
- ^ Oldham 1997, pp. 38–40.
- ^ Oldham 1997, pp. 50–56.
- ^ Sheldon 2015, p. 220; Oldham 2000, pp. 66–67.
- ^ James 1990, pp. viii, 19.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 357–359.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 359.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 361.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 361–362.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 362.
- ^ Wyrall 2003, p. 42; Oldham 2000, pp. 66–67.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 363–364.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 366.
- ^ a b Falls 1992, p. 369.
- ^ a b Sheldon 2015, pp. 224–225.
- ^ Bean 1941, pp. 355–403.
- ^ Oldham 1997, p. 69.
- ^ Oldham 1997, pp. 60–71.
- ^ Wynne 1976, p. 183.
- ^ Winkler & Tiedemann 2014.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 556–561.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 556; Nicholls 2005, pp. 210–211.
- ^ Foerster 1939, pp. 272, 276.
- ^ Keegan 1999, pp. 348–352; Nicholls 2005, pp. 210–211.
- ^ Sheffield & Bourne 2005, pp. 495–496.
- ^ Buffetaut 1997, p. 122.
- ^ Lupfer 1981, p. 10.
- ^ Hollis 2011, pp. 332–333.
- ^ Findlay 2014, ch 9.
- ^ "War Composers: E. J. Moeran's War". War Composers. Archived from the original on 19 September 2021. Retrieved 24 April 2021.
Bibliography
edit- Ashworth, Tony (2000) [1980]. Trench Warfare, 1914–1918: The Live and Let Live System (repr. ed.). London: Pan Books. ISBN 978-0-330-48068-0.
- Bean, C. E. W. (1941) [1933]. The Australian Imperial Force in France: 1917. Official History of Australia in the War of 1914–1918. Vol. IV (11th ed.). Sydney: Angus and Robertson. OCLC 9945668. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- Bellis, M. (1996) [1916]. Instructions for the Training of Divisions for Offensive Action (repr. ed.). London: Military Press International. ISBN 0-85420-195-5.
- Berton, Pierre (1986). Vimy. Toronto: McLelland and Stewart. ISBN 0-7710-1339-6.
- Bond, B., ed. (1999). Look To Your Front: Studies in the First World War. Staplehurst: Spellmount. ISBN 1-86227-065-1.
- Boraston, J. H. (1920) [1919]. Sir Douglas Haig's Despatches (repr. ed.). London: Dent. OCLC 633614212.
- Buffetaut, Yves (1997). The 1917 Spring Offensives: Arras, Vimy, Le Chemin des Dames. Paris: Histoire et Collections. ISBN 2-908182-66-1.
- Corkerry, S., ed. (2001) [1916/1917]. Instructions for the Training of Divisions for Offensive Action, Instructions for the Training of Platoons for Offensive Action (1917) (repr. ed.). Milton Keynes: Military Press. ISBN 0-85420-250-1.
- Doughty, R. A. (2005). Pyrrhic Victory: French Strategy and Operations in the Great War. Cambridge, MA: Belknap Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01880-8.
- Falls, C. (1992) [1940]. Military Operations France and Belgium 1917: The German Retreat to the Hindenburg line and the Battles of Arras. History of the Great War Based on Official Documents by Direction of the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence. Vol. I (Imperial War Museum and Battery Press ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 0-89839-180-6.
- Findlay, Jean (2014). "Chapter 9: Wounded Out". Chasing Lost Time: the Life of C. K. Scott Moncrieff. London: Chatto & Windus. ISBN 978-0-374-71401-7.
- Foerster, Wolfgang, ed. (1939). Der Weltkrieg 1914 bis 1918: Die militärischen Operationen zu Lande Zwölfter Band, Die Kriegführung im Frühjahr 1917 [The World War 1914 to 1918, Military Land Operations Twelfth Volume, Warfare in the Spring of 1917]. Vol. XII (online scan ed.). Berlin: Mittler. OCLC 248903245. Archived from the original on 18 December 2018. Retrieved 29 June 2021 – via Die digitale landesbibliotek Oberösterreich.
- Griffith, P. (1996). Battle Tactics of the Western Front: The British Army's Art of Attack 1916–1918. London: Yale. ISBN 0-30006-663-5.
- Hollis, Matthew (2011). Now All Roads Lead to France: The Last Years of Edward Thomas. London: Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-0-571-27608-0.
- James, E. A. (1990) [1924]. A Record of the Battles and Engagements of the British Armies in France and Flanders 1914–1918 (London Stamp Exchange ed.). Aldershot: Gale & Polden. ISBN 978-0-948130-18-2.
- Jones, Simon (2010). Underground Warfare 1914–1918. Pen & Sword Military. ISBN 978-1-84415-962-8.
- Jünger, E. (2003). Storm of Steel. Translated by Hofman, Michael. London: Penguin. ISBN 978-0-14-118691-7.
- Keegan, John (1999). The First World War. London: Pimlico. ISBN 978-0-7126-6645-9.
- Levine, Joshua (2008). On a Wing and a Prayer. London: Collins. ISBN 978-0-00-726945-7.
- Ludendorff, Erich (2005). My War Memoirs. London: Naval & Military Press. ISBN 978-1-84574-303-1.
- Lupfer, T. (1981). The Dynamics of Doctrine: The Change in German Tactical Doctrine During the First World War (PDF). Fort Leavenworth: US Army Command and General Staff College. OCLC 8189258. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2017. Retrieved 8 April 2017.
- New Zealand Defence Force. Arras Tunnellers Memorial (press release) Archived 21 October 2008.
- Nicholls, J. (2005). Cheerful Sacrifice: The Battle of Arras 1917. Barnsley: Pen and Sword Books. ISBN 1-84415-326-6.
- Oldham, Peter (1997). The Hindenburg Line. Barnsley: Pen and Sword Books. ISBN 978-0-85052-568-7.
- Oldham, Peter (2000) [1997]. The Hindenburg Line (2nd ed.). Barnsley: Pen and Sword Books. ISBN 978-0-85052-568-7.
- Samuels, M. (1995). Command or Control? Command, Training and Tactics in the British and German Armies 1888–1918. London: Frank Cass. ISBN 0-7146-4214-2.
- Sheffield, G. (2002). Forgotten Victory: The First World War – Myths and Realities. London: Review (Hodder). ISBN 978-0-7472-6460-6.
- Sheffield, G.; Bourne, J. (2005). Douglas Haig: War Diaries and Letters 1914–1918. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson. ISBN 978-0-297-84702-1.
- Sheffield, G. (2011). The Chief: Douglas Haig and the British Army. London: Aurum Press. ISBN 978-1-84513-691-8.
- Sheldon, J. (2008). The German Army on Vimy Ridge 1914–1917. Barnsley: Pen & Sword. ISBN 978-1-84415-680-1.
- Sheldon, J. (2015). The German Army in the Spring Offensives 1917: Arras, Aisne & Champagne. Barnsley: Pen & Sword Military. ISBN 978-1-78346-345-9.
- Simpson, A. (2006). Directing Operations: British Corps Command on the Western Front 1914–18. Stroud: Spellmount. ISBN 978-1-86227-292-7.
- Stewart, J.; Buchan, J. (2003) [1926]. The Fifteenth (Scottish) Division 1914–1919 (repr. The Naval & Military Press, Uckfield ed.). Edinburgh: Blakwood. ISBN 978-1-84342-639-4.
- Strachan, Hew (2003). The First World War. Vol. I. New York: Viking. OCLC 53075929.
- Winkler, Gretchen; Tiedemann, Kurt M. von (2014). "Pour le Mérite". Pour le Mérite. Archived from the original on 3 November 2015. Retrieved 6 June 2007.
- Wynne, G. C. (1976) [1939]. If Germany Attacks: The Battle in Depth in the West (Greenwood Press, NY ed.). London: Faber & Faber. ISBN 0-8371-5029-9.
- Wyrall, E. (2003) [1924]. The Story of the 62nd (West Riding) Division, 1914–1919. Vol. I (facs, repr. Naval & Military Press, Uckfield ed.). London: The Bodley Head. ISBN 978-1-84342-467-3. Archived from the original on 26 June 2019. Retrieved 11 February 2020.
Further reading
edit- Bechthold, Mike (2013). "Command, Leadership, and Doctrine on the Great War Battlefield: The Australian, British, and Canadian Experience at the Battle of Arras, May 1917". War & Society. 32 (2): 116–137. doi:10.1179/0729247313Z.00000000020. S2CID 159854430.
- Bechthold, Mike (2018). "Bloody April Revisited: The Royal Flying Corps at the Battle of Arras, 1917". British Journal for Military History. 4 (2). ISSN 2057-0422.
- Cowan, Tony (2019). "The Introduction of New German Defensive Tactics in 1916–1917". British Journal for Military History. 5 (2): 81–99. ISSN 2057-0422. Retrieved 5 April 2024.
- Cowan, Tony (2023). Holding Out: The German Army and Operational Command in 1917. Cambridge Military Histories. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-108-83023-2.
- Harvey, Trevor Gordon (2016). 'An Army of Brigadiers' British Brigade Commanders at the Battle of Arras 1917 (PhD thesis). University of Birmingham.
- Jones, Spencer, ed. (2022). The Darkest Year: The British Army on the Western Front 1917. Wolverhampton military Studies (No. 35). Warwick: Helion. ISBN 978-1-914059-98-8.
- Liddell Hart, Basil (1930). The Real War, 1914–1918. Boston: Little, Brown. OCLC 56212202 – via Archive Foundation.
- Reed, P. (2007). Walking Arras. Barnsley: Pen and Sword Books. ISBN 978-1-84415-619-1.
- Smithson, Jim (2017). A Taste of Success: The First Battle of the Scarpe. The Opening Phase of the Battle of Arras, 9–14 April 1917. Wolverhampton Military Studies. Warwick: Helion. ISBN 978-1-911096-40-5.
External links
edit- The Battle of Arras at 1914–1918.net Online history of the battle, accessed 4 April 2007
- The Battle of Arras at the War Chronicle Another online history of the battle, accessed 16 April 2007
- New Zealand Tunnellers Memorial in Arras archived 21 October 2008
- The Arras tunnels – NZHistory.net.nz Archived 1 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine
- France reveals British WWI cave camp BBC News 5 May 2008
- Finding Private Adams Exploring the life of a soldier killed at Oppy-Gavrelle
- Online history of the Worcestershire Regiment General history of a regiment involved in the battle, accessed 24 April 2007
- The South Africans at Delville Wood, General history of the 1st South African Infantry Brigade involved in the battle, accessed 9 February 2017