The Capture of Oppy Wood was an engagement on the Western Front during the First World War on 28 June 1917.[1] The Battle of Arras of 1917 ended with the Germans in possession of a fortified wood to the west of the village of Oppy, which overlooked British positions. The wood was 1 acre (0.4 ha) in area and contained many German observation posts, machine-gun nests and trench mortars. New German defensive tactics adopted after the Battle of the Somme of defence in depth and rapid counter-attack, had been enforced on the German 6th Army after the disaster of 9 April, the first day of the Battle of Arras. The British attack of the Third Battle of the Scarpe (3–4 May), was defeated everywhere bar Fresnoy, which was captured by the 1st Canadian Division. The attack on Oppy Wood by the 92nd Brigade of the 31st Division, was a costly failure. The area was defended by the 1st Guard Reserve Division and the 15th Reserve Division, which did not need the support of specialist Eingreif (counter-attack) divisions.
| Capture of Oppy Wood | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Battle of Arras (1917) in the First World War | |||||||
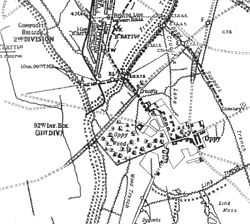 Oppy Wood defences, 1917 | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Sir Douglas Haig Henry Horne |
Ludwig von Falkenhausen Otto von Below Fritz von Lossberg | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 2 divisions | 1 division, 1 regiment | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 452 | c. 566 | ||||||
| British casualties at Oppy Wood on 3 May were 2,417; German casualties at Fresnoy on 8 May were 1,585 | |||||||
A second attack took place on 28 June, as part of a series of feints, intended to simulate a threat to the cities of Lens in the First Army area and Lille in the Second Army area. The attack was conducted by the 15th Brigade, 5th Division and the 94th Brigade, 31st Division, which advanced on a front extending from Gavrelle in the south to the north of Oppy Wood. After a hurricane bombardment, the objectives were captured with few British losses and German counter-attacks were defeated by artillery-fire. An attack at the same time by the 4th Canadian Division and the 46th (North Midland) Division, astride the Souchez river, also succeeded. Operations to continue the encirclement of Lens by an attack by the Canadian Corps on Hill 70 to the north were postponed until August due to a shortage of artillery. The feint attacks failed to divert German attention from Flanders, which included the transfer of ten divisions to the 4th Army, despite claims by the 6th Army command that the British were preparing an offensive towards Lens; the operations did divert German attention from the French front further south.
Background
editStrategic developments
editBefore the Third Battle of the Scarpe, the cancellation of the French part in the Nivelle Offensive seemed certain. A continuation of British attacks towards Cambrai would be pointless in the absence of French operations to the south and Field Marshal Sir Douglas Haig decided to continue operations on the Arras front to reach a good defensive line, then to conduct surprise attacks to keep German troops in the area. Preparations were made to begin operations in Flanders, with the attack at Messines to begin in early June.[2] Despite uncertainty about the French attack on the Aisne, which was due from 4 to 5 May, a plan for an attack by the British Fifth Army, Third Army and the First Army on a 14 mi (23 km) front, went ahead and the First Army objectives were given as Oppy and Fresnoy.[3]
The move of the bulk of the British Expeditionary Force (BEF) to Flanders in late May and June, left the First Army with twelve divisions to hold a 34 mi (55 km) front from Arras northwards to Armentières on the Lys river. During the period needed to prepare the offensive at Ypres after the Battle of Messines (7–14 June), threats to Lens and Lille were planned for the end of June. The First Army was to operate on a three-corps front, in which XIII Corps was to advance 200–500 yd (180–460 m) between Gavrelle and Oppy on a 2,300 yd (2,100 m) front, while to the north the Canadian Corps and I Corps was to attack on both banks of the Souchez river towards Avion.[4]
Tactical developments
editGerman
editExperience of the 1st Army in the Somme Battles, (Erfahrungen der I Armee in der Sommeschlacht) was published by Oberste Heeresleitung (OHL, the supreme command of the German armies) on 30 January 1917. During the Battle of the Somme in 1916, Colonel Fritz von Loßberg (Chief of Staff of the 1st Army) had been able to establish a line of "relief" divisions (Ablösungsdivisionen), with the reinforcements from Verdun which had begun to arrive in September. In his analysis of the battle, Loßberg opposed the granting of discretion to front trench garrisons to retire, as he believed that manoeuvre did not allow the garrisons to evade Allied artillery fire, which could blanket the forward area, making evasion futile and also invite Allied troops to occupy vacated areas unopposed. Loßberg considered that spontaneous withdrawals would disrupt the counter-attack reserves as they deployed and further deprive battalion and division commanders of the ability to conduct an organised defence, which the dispersal of infantry over a wider area had already made difficult. Loßberg and others had severe doubts as to the ability of relief divisions to reach the battlefield in time to conduct an immediate counter-attack (Gegenstoß) from behind the battle zone. Loßberg wanted the Somme practice of fighting in the front line to be retained and authority devolved no further than the battalion, to maintain organisational coherence, in anticipation of a methodical counter-attack (Gegenangriff) by the relief divisions after 24–48 hours. Erich Ludendorff, the Generalquartiermeister (First Quartermaster General) of the German armies was sufficiently impressed by the Loßberg memorandum to add it to the new Manual of Infantry Training for War.[5]
British
editThe British training manual Instructions for the Training of Platoons for Offensive Action (SS 143) of February 1917, marked the end of attacks made by lines of infantry with a few detached specialists.[6] The platoon was divided into a small headquarters and four sections, one with two trained grenade-throwers and assistants, the second with a Lewis gunner and nine assistants, carrying 30 drums of ammunition, the third section comprising a sniper, scout and nine riflemen and a fourth section of nine men with four rifle-grenade launchers.[7] The rifle and hand-grenade sections were to advance in front of the Lewis-gun and rifle-grenade sections, in two waves or in artillery formation, which covered an area 100 yd (91 m) wide and 50 yd (46 m) deep, with the four sections in a diamond pattern, the rifle section ahead, rifle grenade and bombing sections to the sides and the Lewis gun section behind, until resistance was met. German defenders were to be suppressed by fire from the Lewis-gun and rifle-grenade sections, while the riflemen and hand-grenade sections moved forward, preferably by infiltrating round the flanks to overwhelm the defenders from the rear.[8]
Changes in equipment, organisation and formation were elaborated in SS 144 The Normal Formation for the Attack of February 1917, which recommended that the leading troops should push on to the final objective if only one or two had been set. For a greater number of objectives, when artillery covering fire was available for the depth of the intended advance, fresh platoons should "leap-frog" through the leading platoons to the next objective.[9] The new organisation and equipment gave the infantry platoon the capacity for fire and manoeuvre, even in the absence of adequate artillery support against German defences. To bring uniformity in adoption of the methods laid down in the revised manuals and others produced over the winter, Haig established a BEF Training Directorate in January 1917 to issue manuals and oversee training. SS 143 and its companion manuals provided British infantry with off-the-peg tactics, devised from the experience of the Somme and from French Army operations, to go with the new equipment made available by increasing British and Allied war production and better understanding of the organisation necessary to exploit it in battle.[10] For the attack on 3 May, the Fifth Army wanted to make a night assault, to evade German machine-gun fire but the Third and First armies needed to attack in daylight and Haig enforced a compromise zero hour of 3:45 a.m. The moon was close to full and set only sixteen minutes before zero hour; on many parts of the attack front, troops assembling were silhouetted as the moon sank behind them.[11] In XIII Corps the 2nd Division had already had suffered casualties in recent operations and was exhausted; the fresh 31st Division took over the right flank of the 2nd Division front.[12]
Prelude
editBritish plans
editThe First Army plan had assumed a dawn attack and no preparations had been made for an advance at night, such as putting out boards with luminous paint on the German wire, taking compass-bearings or organising intermediate objectives. Sunrise was not until 5:22 a.m. and it would not be possible to distinguish objects at 50 yd (46 m) until 4:05 a.m.[11] An attack on German observation balloons was planned in the First Army area, to be carried out by Nieuport Scout aircraft of the Tenth Wing of the Royal Flying Corps (RFC), which was to be covered by an artillery bombardment; bombing raids further behind the German lines were arranged. The attack of the XIII Corps was to be conducted by two divisions on a front from the south end of Gavrelle northwards to the wood south of Fresnoy.[13]
The depleted and exhausted state of the 2nd Division led to its attack front being reduced to 1,100 yd (1,000 m), from Greenland Hill to Oppy Support Trench and Fresnoy by the extension of the 31st Division front to a width of 3,500 yd (2.0 mi; 3.2 km). The Germans had managed to retain 750 yd (690 m) of the Oppy Line, to the west of Oppy Wood in the Battle of Arleux (28–29 April), which complicated the task of the 31st Division. Oppy Wood was full of fallen trees and tangled branches and a long west to east slope left the British field artillery at extreme range, which reduced its accuracy. The division was supported by nine field artillery brigades and extra machine-guns borrowed from the 63rd (Royal Naval) Division and the 1/1st Northumberland Hussars, the XIII Corps cavalry regiment.[13]
The First Army planned to attack in the first half of July, as part of operations by the First and Second armies to keep German troops away from the Flanders front for as long as possible by feinting towards Lens and Lille. The dispatch of heavy and siege artillery to Flanders led the First Army commander General Henry Horne, to bring forward the attack to 28 June and to limit the attack to the XIII Corps operation against Oppy and Gavrelle. Artillery moving Flanders from the Third Army was diverted, temporarily to increase the weight of the First Army bombardment, which was to take place on a 14 mi (23 km) front, to create the impression of an imminent threat against Lens.[4] XIII Corps had four divisions, with the 31st and 63rd (Royal Naval) divisions alternating in the line on the right and the 2nd Division and 5th Division alternating on the left flank. The 5th Division withdrew the 15th Brigade for a week of training for the attack, which was conducted by all four battalions. The plan required the artillery to cut the German wire but leave the German trenches intact, so that the British infantry could occupy them.[14]
British preparations
editA corps conference was held on 30 April, at which the tired state of the 2nd Division was discussed but it was still required to participate in the attack. A composite brigade was formed from the survivors of the three brigades.[15][a] Three field artillery brigades, corps and army heavy artillery were arranged in support of the composite brigade and the 1st Canadian Brigade was to attack on the northern flank.[16] The 63rd (Royal Naval) Division took over the line from the 31st Division and the right flank sector of the 5th Division on 4–5 July. The division sapped forward down the long slope from the old German Fampoux–Farbus Switch Line, which had become the British "army" line of resistance, by driving forward sap heads and listening posts which were linked laterally overnight.[17] Before the attack, Fresnoy was subjected to an incendiary bombardment by Livens Projectors as a diversion.[18][b]
Raid
editA raid by the 92nd Brigade was planned for 22 June, to inflict casualties on the Germans, study the German defences and note the position of machine-gun nests.[19] Zero hour was set at 10:20 p.m., when the adjacent troops of the 93rd Brigade were to open rapid fire with small arms and to fire German rockets to distract the defenders. On the 92nd Brigade front, the artillery was not to fire until zero hour, at which it would begin 50 yd (46 m) from Cadorna Trench for one minute and then lift onto the trench. Three minutes later, the barrage was to creep forward for 300 yd (270 m), lift one minute later to Windmill Trench for forty minutes and then slowly diminish. The divisions on the flanks were to fire diversionary barrages.[19] Little German return fire from Oppy Wood was encountered but small parties of German troops were found in front of Cadorna Trench, which was discovered to have been destroyed by the bombardment, the raiders passing beyond it without realising. German survivors retreated towards Windmill Trench, were caught by the British barrage and several prisoners were taken. The raiders began to withdraw from Windmill Trench and stopped a German attempt to counter-attack around the northern flank, which was ambushed by a Lewis gun squad. The British suffered 44 casualties.[20]
German preparations
editOn 3 April 1917, German Corps headquarters were detached from their component divisions and given permanent areas to hold under a geographical title.[21] The VIII Reserve Corps holding the area north of Givenchy became Gruppe Souchez, I Bavarian Reserve Corps became Gruppe Vimy and held the front from Givenchy northwards to the Scarpe river with three divisions, Gruppe Arras (IX Reserve Corps) was responsible for the line from the Scarpe to Croisilles and Gruppe Quéant (XIV Reserve Corps) from Croisilles to Mœuvres. Henceforth, divisions moving into the area came under the authority of the corps (Gruppe) for the duration of their stay, to be replaced by fresh divisions.[22] On the Gruppe Vimy front, the 1st Guard Reserve Division, the last of the Eingreif divisions still in the line, had swapped a tired regiment for a fresh one from the 185th Division and held the line from south of Gavrelle north to the Oppy–Bailleul road. The fresh 15th Reserve Division, held the line further north from the road to beyond Fresnoy.[23]
Battle
edit3 May
editOperations on the First Army front began with attacks on German observation balloons, in which four were shot down and another four were damaged. XIII Corps attacked on a 4,600 yd (4,200 m) front, from the south of Gavrelle to the vicinity of Fresnoy, with the 2nd Division, which had been reduced by casualties to a remnant and the fresh 31st Division. The German defenders saw the British infantry forming up in the moonlight, in an assembly trench 250 yd (230 m) from the objective. At midnight a German patrol was seen and at 12:30 a.m. a German bombardment began for twenty minutes and then a second bombardment began from 1:30 a.m. until zero hour. There were few British casualties but the shelling caused considerable confusion and the German bombardment increased, when the British preliminary bombardment began. The British troops advanced in four waves, which were illuminated by German rockets and very lights and engaged by massed small-arms fire; the three battalions of the 93rd Brigade were still able to advance and some units reached the final objective.[24]
On the left, the three attacking battalions of the 92nd Brigade were subjected to a "tremendous" barrage on their assembly-positions, just before zero hour which caused much disorganisation. The darkness in this area was increased by Oppy Wood and the infantry could not see the barrage lift. The right-hand battalion was unable to advance and troops in the centre and left flank battalions found areas of uncut wire and lost many casualties, when they bunched up at the gaps before reaching the wood, which they found to be full of fallen trees covered in barbed wire. The British troops were then cut off and captured or forced back with many casualties. Many of the troops were stranded in no man's land and had to wait all day under fire from snipers, machine-guns and artillery until nightfall, before completing the retirement.[25] A German counter-attack pushed the 92nd Brigade back and retook Gavrelle Windmill for a short time, until forced back by another British attack.[13] It was discovered after the war that the majority of the Hull Commercials who had been taken prisoner during the attack, had advanced as far as Oppy village.[24]
The 2nd Division attacked with a composite brigade only c. 1,800 strong, despite being made up of the least depleted battalions of the division. The first objective was a German trench behind the Arleux Loop, from a wood south of Fresnoy and further to the right; a second objective was set at the Fresnoy–Oppy road.[26] The composite brigade was bombarded as it moved forward to the assembly-positions, which caused many losses and delays in crowded communication trenches, some of the troops failed to reach the jumping-off positions in time. "B" Battalion managed to advance on the left flank, only to be driven back by a German counter-attack from Oppy. "C" Battalion advanced in contact with Canadian troops on the flank, reached the first objective on the right and the final objective on the left, before the German counter-attack from Oppy, which in this area was repulsed by small-arms fire. On the "B" Battalion front, German troops bombed their way northwards and threatened the divisional junction with the 1st Canadian Division, which had captured Fresnoy. Reserves and some Canadian troops managed to form a block, 400 yd (370 m) south of the left flank of the 2nd Division and touch was regained with the 1st Canadian Division south-east of Fresnoy.[27]
28 June
editThe day was dull and humid and at 5:30 p.m., German artillery bombarded the British jumping-off trenches for ten minutes and caused c. 200 casualties in the two attacking brigades. At 7:00 p.m., a British hurricane bombardment began from Gavrelle to Hulluch, along the 14 mi (23 km) front of the XIII Corps and I Corps, as part of a feint against Lens. Howitzers fired smoke-shell to create a screen, to the north of the 5th Division attack and then a thunderstorm began, the infantry advancing at 7:10 a.m. amidst lightning and torrential rain. In the XIII Corps area, the 94th Brigade of the 31st Division advanced north of Gavrelle and the 15th Brigade of the 5th Division attacked Oppy on a 2,300 yd (2,100 m) front. Despite the German bombardment on the jumping-off trenches, the British troops advanced swiftly across no man's land behind a creeping barrage, before the German counter-barrage fell three minutes later. On the 5th Division front, the German trenches were strongly held but the British arrived so quickly that few were able to resist, except on the left flank where the objective was further away. The 15th Brigade took 143 prisoners, several machine-guns and trench mortars and the 94th Brigade took a similar number; 280 German dead were counted on the battlefield. Gavrelle Mill and the other objectives were captured easily but the rain interfered with consolidation, which had begun by 9:00 p.m. The new positions gave a good view to the north and east towards Neuvireuil and Fresnes and to the south-east around Greenland Hill.[28] After the attack, German artillery-fire was concentrated on Fresnoy, which had been subjected to an incendiary bombardment.[18]
German counter-attacks
editThe German front-holding divisions defeated the British attacks all along the front on 3 May and Eingreif divisions were not called upon. Counter-attacks by companies were often all that was needed to repulse British troops, where they had gained footholds in the German defences. Fresnoy was captured by the Canadian Corps and hasty German counter-attacks there were repulsed, the 15th Reserve Division reporting 650 casualties around the village; losses inside Fresnoy were not recorded but were believed to be higher.[29] The 5th Bavarian Division was ordered to prepare a methodical counter-attack (Gegenangriff), to recapture Fresnoy and attacked on 8 May, with all three regiments and the support of 27 field and 17 heavy artillery batteries, plus those of the neighbouring divisions. The right flank brigade was delayed for a short time at Fresnoy Park, then found only a battlefield strewn with dead soldiers and abandoned equipment. The brigade in the centre lost the barrage as it floundered in mud and managed to advance only after the northern brigade reached its objective. The southern brigade managed to push forward and then bomb northwards to roll up the British front but despite rapid success, the division suffered 1,585 casualties.[30]
Air operations
editLosses of British corps aircraft declined after April, which had been the worst in the war and air fighting returned to the German rear areas.[31][c] An attack on German observation balloons was planned during the lull in infantry operations before May and the pilots practised flying at low altitude to exploit the cover of trees, dips in the ground and houses. Observation balloons could be winched down quickly, which made them difficult to shoot down; the commander of the Tenth Wing RFC, Lieutenant-Colonel Wilfrid Freeman, arranged for an artillery barrage on the German trenches as a diversion to cover aircraft from 40 Squadron which made a surprise attack. At 9:00 a.m. on 2 May, the artillery barrage began and six Nieuport pilots attacked the balloons, which were found to be still airborne, at heights up to 2,000 ft (610 m). Four balloons were shot down in flames, four were damaged and all of the Nieuports returned damaged by small arms fire.[32]
On 3 May, British aircraft were set aside for special counter-attack reconnaissance, after the experience of the new German tactics of lightly holding the front line and counter-attacking with reserves and Eingreif divisions. The British aircraft flew low over the battlefield behind captured positions from dawn to dusk, looking for signs of German counter-attacks, to report them immediately to the British artillery. Bombardments from both sides and infantry attacks and counter-attacks, made the battlefield so chaotic that observers were not able to see clearly, except for those of 43 Squadron, who saw German troops massing opposite the XIII Corps front. Five Sopwith 1½ Strutters machine-gunned the German infantry from 50–300 ft (15–91 m) and low-altitude attacks on other bodies of troops were carried out in the afternoon.[33] Tactical bombing took place, with attacks on the railway stations at Don, Busigny Junction, Brebières and the aerodrome at Eswars. After dark, bombing continued on trains; three were hit by low-level attacks by the night-bombing specialists of 100 Squadron, along with railway junctions and Tourmignies airfield.[34]
Aftermath
editAnalysis
editThe British divisions had begun the Arras offensive well trained and equipped but casualties had been replaced by poorly trained men and the British divisions moving north to Flanders received the pick of the replacements. In the Canadian divisions, the new men tended to be older, better built and having had a longer period of training. The Canadians were able to maintain their fighting-power, despite participating in several attacks at short intervals. The German defences between Oppy and Méricourt had proved to be difficult to capture, because the Germans had elaborately fortified the area to protect Fresnoy, which commanded much of the ground on either flank.[35]
The 31st Division headquarters had expected that the attack of 3 May would encounter demoralised troops and that the creeping barrage would neutralise all resistance. On part of the front, the British found that rather than being shaken, the Germans were massing for an attack and that some of the German wire at the south-western corner of the wood was uncut. One company fought their way into the village but the rest were held up despite attacking three times.[36]
The attack on 28 June captured the German first line from Gavrelle to Oppy Wood and advanced the British line about 0.5 mi (0.80 km). The Germans were pushed back to an inferior second position trench and the village of Oppy. With the British in possession of the high ground north of Gavrelle, captured by the 63rd (Royal Naval) Division at the Battle of Arleux on 28 April, a German counter-attack from Oppy village was impossible; the British had consolidated the area by 4–5 July.[17] The attack further north by the Canadian Corps and I Corps was also successful, the 3rd Canadian Division forming a defensive flank on the Arleux–Avion road and linking with the 4th Canadian Division in Avion. Most of Avion, Éleu-dit-Leauwette and the German defences on the east side of Hill 65, were captured by the 4th Canadian and 46th (North Midland) Division.[28]
Casualties
editby John Nash
On 3 May, the 31st Division suffered 1,900 casualties in the attack on Oppy Wood.[37] The 2nd Division composite brigade had 517 casualties, which left the division "bled white" with a "trench strength" of only 3,778 men.[38] On 8 May, the 5th Bavarian Division suffered 1,585 casualties in the counter-attack at Fresnoy.[30] In the attack of 28 June the 31st Division suffered c. 100 casualties and the 5th Division 352.[39]
Subsequent operations
editBy 5 May, the 5th Division had relieved the 2nd Division and the 1st Canadian Division, XIII Corps taking over the front from north of Oppy to beyond Fresnoy. The attack on 3 May had created a sharp salient with the Germans still in the Oppy–Méricourt line between Fresnoy and Oppy. On 7 May, the RFC attacked German observation balloons again and shot down seven for the loss of one aircraft. On 8 May, a German attack recaptured Fresnoy and a British battalion was annihilated as it tried to withdraw from the village. British and Canadian troops nearby were pushed back to the eastern fringe of Arleux and the 5th Division withdrew its left flank to the Arleux–Neuvireuil road. A counter-attack on 9 May reached Fresnoy but was later forced back, midway between Arleux and Fresnoy. No fresh divisions remained in the First Army and artillery was sent northwards to the Second Army on 14 May.[40]
On 18 May, a battalion of the 31st Division attacked near Gavrelle but failed to reach the German front-line trench.[40] On the night of 14/15 July, the 63rd (Royal Naval) Division dug a new front line from Oppy Wood to beyond Gavrelle Windmill and on 20 July, a raid on Gavrelle Trench met feeble resistance and found that the German trenches were in poor condition. The British pushed their lines as close as possible to the German front line to evade German artillery-fire and two artillery batteries were brought forward 2,000 yd (1,800 m), to increase the effect of several hurricane artillery and machine-gun bombardments, which were intended to keep the Germans apprehensive of another attack. The British positions around the windmill were bombarded by German artillery whenever a British operation took place but the infantry positions proved immune to bombardment, which fell on the artillery instead. The gunners frequently changed position but eventually had to be withdrawn.[41]
See also
editVictoria Cross
edit- 2nd Lieutenant Jack Harrison, 11th E. Yorks.[37]
Commemoration
editThe units which attacked Oppy Wood were awarded the battle honour Oppy.[42] A wood on the outskirts of Hull, Yorkshire, is named Oppy Wood in memory of the men of the East Yorkshire Regiment who were killed in the attack of 3 May.[43]
Notes
edit- ^ On 1 May, the fighting strengths of the 2nd Division brigades were: 5th Infantry Brigade, 1,237 men, 6th Infantry Brigade, 1,322 men, 99th Infantry Brigade, 1,028 men.[15]
- ^ "Special Companies" RE filled cylinders with oil and discharged them electrically in salvoes from Livens Projectors. On impact with the ground, they exploded and produced a terrifying effect. Machine-gun and shrapnel-fire were added and sometimes gas was substituted for oil.[18]
- ^ From 30 January 1916, each British army had a Royal Flying Corps brigade attached, which was divided into wings, the "corps wing" contained squadrons responsible for close reconnaissance, photography, artillery observation and contact patrols on the front of each army corps and an "army wing" which by 1917, conducted long-range reconnaissance and bombing, using aircraft types with the highest performance.[31]
Footnotes
edit- ^ James 1990, p. 19.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 427.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 431.
- ^ a b Edmonds 1991, pp. 112–113.
- ^ Wynne 1976, p. 161.
- ^ Bellis 1996, pp. 83–107.
- ^ Griffith 1996, p. 77.
- ^ Corkerry 2001, p. 88.
- ^ Bond 1999, p. 86.
- ^ Sheffield 2011, pp. 209–211.
- ^ a b Falls 1992, p. 432.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 446.
- ^ a b c Falls 1992, pp. 445–446.
- ^ Hussey & Inman 1921, pp. 160, 164.
- ^ a b Wyrall 1921, p. 439.
- ^ Wyrall 1921, p. 440.
- ^ a b Jerrold 2009, p. 245.
- ^ a b c Hussey & Inman 1921, p. 166.
- ^ a b Bilton 2005, p. 131.
- ^ Bilton 2005, p. 132.
- ^ Boff 2018, p. 156.
- ^ Sheldon 2008, p. 40.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 453.
- ^ a b Bilton 2005, p. 94.
- ^ Bilton 2005, pp. 86–87.
- ^ Bilton 2005, p. 115.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 447–448.
- ^ a b Edmonds 1991, p. 114.
- ^ Falls 1992, pp. 453–454.
- ^ a b Falls 1992, p. 523.
- ^ a b Jones 2002, pp. 147–148.
- ^ Jones 2009, p. 371.
- ^ Jones 2009, p. 373.
- ^ Jones 2009, p. 374.
- ^ Falls 1992, p. 451.
- ^ Bilton 2005, p. 95.
- ^ a b Falls 1992, p. 447.
- ^ Wyrall 1921, p. 444.
- ^ Edmonds 1991, pp. 113–114; Hussey & Inman 1921, p. 165.
- ^ a b Falls 1992, pp. 520–522.
- ^ Jerrold 2009, pp. 246–247.
- ^ Rodger 2003, p. 129.
- ^ TWT 2013.
References
edit- Boff, J. (2018). Haig's Enemy: Crown Prince Rupprecht and Germany's War on the Western Front (1st ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-967046-8.
- Bellis, M. (1996) [1916]. Instructions for the Training of Divisions for Offensive Action (repr. ed.). London: Military Press International. ISBN 978-0-85420-195-2.
- Bilton, D. (2005). Oppy Wood. Barnsley: Pen & Sword. ISBN 978-1-84415-248-3.
- Bond, B. (1999). Look To Your Front: Studies in the First World War. Staplehurst: Spellmount. ISBN 978-1-86227-065-7.
- Corkerry, S., ed. (2001) [1916]. Instructions for the Training of Divisions for Offensive Action (repr. ed.). Milton Keynes: Military Press. ISBN 978-0-85420-250-8.
- Edmonds, J. E. (1991) [1948]. Military Operations France and Belgium 1917: 7 June – 10 November. Messines and Third Ypres (Passchendaele). History of the Great War Based on Official Documents by Direction of the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence. Vol. II (facs. repr. Imperial War Museum Department of Printed Books and Battery Press ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 978-0-89839-166-4.
- Falls, C. (1992) [1940]. Military Operations France and Belgium, 1917: The German Retreat to the Hindenburg Line and the Battles of Arras. History of the Great War Based on Official Documents by Direction of the Historical Section of the Committee of Imperial Defence. Vol. I (facs. repr. Imperial War Museum Department of Printed Books and Battery Press ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 978-0-89839-180-0.
- Griffith, P. (1996). Battle Tactics of the Western Front: The British Army's Art of Attack 1916–1918. London: Yale. ISBN 978-0-300-06663-0.
- Hussey, A. H.; Inman, D. S. (1921). The Fifth Division in the Great War (online scan) (facs. repr. ed.). London: Nisbet. OCLC 565246540. Retrieved 28 January 2017 – via Archive Foundation.
- James, E. A. (1990) [1924]. A Record of the Battles and Engagements of the British Armies in France and Flanders 1914–1918 (repr. London Stamp Exchange ed.). Aldershot: Gale & Polden. ISBN 978-0-948130-18-2.
- Jerrold, D. (2009) [1923]. The Royal Naval Division (facs. repr. Naval & Military Press, Uckfield ed.). London: Hutchinson. ISBN 978-1-84342-261-7.
- Jones, H. A. (2002) [1928]. The War in the Air, Being the Story of the Part played in the Great War by the Royal Air Force (online scan). Vol. II (facs. repr. pbk. Imperial War Museum Department of Printed Books and Naval & Military Press ed.). London: Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-1-84342-413-0. Retrieved 5 October 2014 – via Archive Foundation.
- Jones, H. A. (2009) [1931]. The War in the Air, Being the Part played in the Great War by the Royal Air Force (online scan). Vol. III (facs. repr. Imperial War Museum Department of Printed Books and Naval & Military Press ed.). London: Clarendon Press. ISBN 978-1-84342-414-7. Retrieved 5 October 2014 – via Archive Foundation.
- "Oppy Wood". News. The Woodland Trust. 2013. Archived from the original on 24 December 2012. Retrieved 14 September 2013.
- Rodger, A. (2003). Battle Honours of the British Empire and Commonwealth Land Forces. Marlborough: Crowood Press. ISBN 978-1-86126-637-8.
- Sheffield, G. (2011). The Chief: Douglas Haig and the British Army. London: Aurum Press. ISBN 978-1-84513-691-8.
- Sheldon, J. (2008). The German Army on Vimy Ridge 1914–1917. Barnsley: Pen & Sword. ISBN 978-1-84415-680-1.
- Wynne, G. C. (1976) [1939]. If Germany Attacks: The Battle in Depth in the West (Greenwood Press, NY ed.). London: Faber & Faber. ISBN 978-0-8371-5029-1.
- Wyrall, E. (1921). The History of the Second Division, 1914–1918 (online scan). Vol. II. London: Thomas Nelson and Sons. OCLC 565235666. Retrieved 23 November 2016 – via Archive Foundation.
Further reading
edit- Corkerry, S., ed. (2001) [1917]. Instructions for the Training of Platoons for Offensive Action (facs. repr. Pbk. ed.). Milton Keynes: Military Press. ISBN 978-0-85420-250-8.
- Nicholson, G. W. L. (1962). Canadian Expeditionary Force 1914–1919 (online scan). Official History of the Canadian Army in the First World War. Ottawa: Queen's Printer and Controller of Stationery. OCLC 59609928. Retrieved 15 November 2022 – via Canadian Department of National Defence.
External links
edit- The Accrington Pals: Oppy-Gavrelle, May–June 1917
- War diary, 22nd (Service) Battalion Royal Fusiliers Operations in the Battle of Arras and near Oppy Wood