Rubicene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon that consists of two benzene and an anthracene. They are each linked by two carbon–carbon bonds. Dilute solutions of rubicene emit strong yellow fluorescence.[1] It's synthesized from fluorenone by reduction of calcium or magnesium,[1] or it can be obtained by reacting with dihalogenated diphenylanthracene as raw material.[2] It can also be obtained by reacting 9,10-diphenylanthracene and 3 parts of DDQ in dichloromethane in the presence of triflic acid.[2]
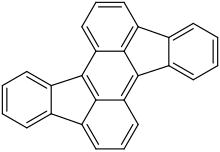 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
rubicene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1914846 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.364 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C26H14 | |
| Molar mass | 326.398 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Red solid |
| Melting point | 306 °C (583 °F; 579 K) [1] |
| Solubility | Insoluble in ethanol and benzene[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ a b c d 化学大辞典編集委員会 (1964). 化学大辞典(縮刷版)9 (in Japanese). 共立出版. p. 855. ISBN 4-320-04015-5. OCLC 990794711.
- ^ a b Masahiko Kawamura, Eiji Tsurumaki, Shinji Toyota (Jan 2018). "Facile Synthesis of Rubicenes by Scholl Reaction". Synthesis. 50 (1): 134–138. doi:10.1055/s-0036-1588570. ISSN 0039-7881. S2CID 103648683. Retrieved 2022-10-06.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Further reading
edit- Pragst, Fritz; Stoesser, Reinhard. Use of bis(1,2,4,6-tetramethyl-1,4-dihydro-4-pyridinyl) as a reducing agent for the generation of organic anion radicals in EPR spectroscopy (in German). Zeitschrift fuer Chemie, 1985. 25 (6): 222. ISSN 0044-2402.
- William C. Herndon (Jan 1982). "Thermal reactivities of polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons and alkyl derivatives". Tetrahedron. 38 (10): 1389–1396. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(82)80218-4. Retrieved 2022-10-06.