The Rotorua Caldera is a large rhyolitic caldera that is filled by Lake Rotorua. It was formed by an eruption 240,000 years ago that produced extensive pyroclastic deposits. Smaller eruptions have occurred in the caldera since, the most recent less than 25,000 years ago. It is one of several large volcanoes in the Taupō Volcanic Zone on the North Island of New Zealand.
| Rotorua Caldera | |
|---|---|
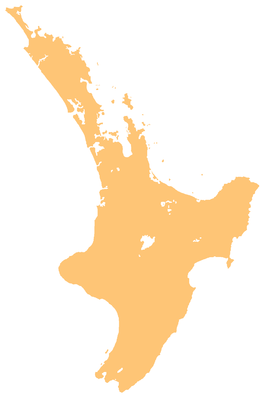
 NASA image of the caldera. The town of Rotorua is south of the lake that fills much of the apparently circular caldera. The caldera is a more complex shape with areas of collapse and the Tikitere Graben at its outlet. Mount Tarawera is in the lower right corner south east of the caldera and it and the lakes to the east are features of the adjacent active Ōkataina Caldera. The eruption products are thickest towards the north east. | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 757 m (2,484 ft) |
| Coordinates | 38°05′S 176°16′E / 38.08°S 176.27°E |
| Dimensions | |
| Width | 22 kilometres (14 mi)[1] |
| Geography | |
| Country | New Zealand |
| Region | Bay of Plenty |
| Geology | |
| Rock age | |
| Mountain type | Caldera |
| Volcanic arc/belt | Taupō Volcanic Zone |
| Last eruption | < 25,000 years ago[3] |
Geography
editThe major regional settlement of Rotorua city is located in the caldera. There is geothermal activity in the city, and the geothermal areas of Tikitere and Whakarewarewa are associated with the caldera. These areas are still associated with small hydrothermal eruptions.[4]
Geology
editEruption history
editThe caldera was formed in a single event paired major eruption, lasting only weeks, that is now dated to 240,000 ± 11,000 years ago.[5] It ejected more than 340 cubic kilometres (82 cu mi) of rhyolitic Mamaku ignimbrite giving it a Volcanic Explosivity Index of 7.[3] The eruption has been reinterpreted as a paired eruption, with a very slightly later, slightly smaller southerly eruption from the same mush body that also feed the Ohakuri Caldera.[2] Ignimbrite, up to 145 metres (476 ft) thick covering about 3,100 km2 (1,200 sq mi), was deposited in the surrounding area, particularly towards the west.[1] A small but rather thick outcrop named Mokai Ignimbrite exposed to the south-west, but beyond the known boundaries of the much thinner at these boundaries, Mamaku ignimbrite, was erupted at close to the same time. This is likely from a different source to either the Mamaku or Ohakuri ignimbrite. A different source would explain interlayered ash not present in northern Mamaku ignimbrite but there is close composition homogeneity, suggesting a similar magma melt source.[1] Perhaps rather than a very directional pyroclastic flow during the eruption events from a southern vent near Rotorua, this formation is explained by more complex pairing with an unknown vent in the area of the Kapenga Caldera. Whatever the Rotorua eruption was definitely paired with an eruption from the Ohakuri Caldera 30 kilometres (19 mi) away, possibly through tectonic coupling, as paired events are being increasingly recognised. The ignimbrite from Ohakuri travelled at least 17 km towards Rotorua.[6][5][2]
The outflow dense-rock equivalent (DRE) of the Mamaku ignimbrite Rotorua eruption alone was up to 145 cubic kilometres (35 cu mi).[2] The maximum DME of the Ohakuri eruption alone is 100 cubic kilometres (24 cu mi).[5]
Caldera collapse occurred particularly during the eruption of middle layer of Mamaku Ignimbrite and in later stages of the eruption as the magma chamber underneath the volcano empted.[1] The circular depression left behind is now filled with Lake Rotorua but the current caldera is more like two ovoids offset from each other, about 22 km (14 mi) in maximum diameter. Mokoia Island, close to the centre of the lake, is a rhyolite dome that later erupted. There are other domes, including Hinemoa Point, Ngongotahā, Pohaturoa and Pukeroa.
The most recent magmatic eruption occurred less than 25,000 years ago, creating some of the smaller lava domes.[3] Mokoia Island has been assigned an age of less than 50,000 years.[1]
240,000 years ago Ohakuri paired eruption
edit{{maplink|frame=yes |frame-
The first major volcanic event 240,000 years ago was the initial Mamaku eruption followed within an hours/days/weeks of a smaller eruption (phase 1) from the same mush body feeding the Ohakuri Caldera about 30 km (19 mi) to the south.[2] Ignimbrite, up to 180 metres (590 ft) thick was deposited in the surrounding area to the south of Rotorua.[1] Between Rotorua and Ohakuri, crosssections of the ash and ignimbrite from the two eruptions have been able to be sequenced completely. The layers have relationships that can only be explained by a sequence of eruptions separated on occasions by days or less (e.g. no rainfall between eruptions).[7] The pairing was possibly through tectonic coupling of separate magma bodies that co-evolved from a lower in the mantle common mush body, as paired events are being increasingly recognised.[5] The maximum outflow dense-rock equivalent (DRE) of the Ohakuri ignimbrite is 100 cubic kilometres (24 cubic miles) which means the combined eruptions produced 245 cubic kilometres (59 cu mi) of material.[2]
It has been postulated that the drainage of the linked deep magma mush body between Rotorua and Ohakuri resulted in more than 250 metres (820 ft) of vertical displacement on the Horohoro Fault scarp. This formed the Paeroa Graben, coincident to the north with the Kapenga Caldera between it and the Paeroa Fault to the east.[7] The formation is known as the Horohoro Cliffs escarpment and displaced Mamaku ignimbrite from the Rotorua Caldera eruption by this amount, presumably shortly after at least the initial the eruption. This fault, in the present day, while active has a much lower displacement rate of the order of 0.14 millimetres (0.0055 in)/year. It has been assigned by some as the outer western fault of the modern Taupō Rift although most think this is further to the east.[8] Understanding that there is volcanotectonic interrelationship lead to a complete reinterpretation of events in the Taupō Volcanic Zone in the last 250,000 years.[5]
See also
edit- Geology of New Zealand
- Geothermal areas in New Zealand
- Geothermal power in New Zealand – Overview of geothermal power in New Zealand
- List of volcanoes in New Zealand
- North Island Volcanic Plateau – Pyroclastic volcanic plateau on the North Island of New Zealand
- Taupō Volcanic Zone
- Taupō Volcano
- Volcanism of New Zealand
References
edit- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f Milner, David M (2001). The structure and eruptive history of Rotorua Caldera, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand (Thesis).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g Bégué, F.; Deering, C. D.; Gravley, D. M.; Kennedy, B. M.; Chambefort, I.; Gualda, G. A. R.; Bachmann, O. (2014). "Extraction, Storage and Eruption of Multiple Isolated Magma Batches in the Paired Mamaku and Ohakuri Eruption, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand". Journal of Petrology. 55 (8): 1653–1684. doi:10.1093/petrology/egu038. hdl:20.500.11850/88102.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Rotorua". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution.
- ^ Klemetti, Erik. "Steam Explosions Rock New Zealand's Rotorua Caldera". Wired.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Gravley, D.M.; Wilson, C.J.N.; Leonard, G.S.; Cole, J.W. (2007). "Double trouble: Paired ignimbrite eruptions and collateral subsidence in the Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand". GSA Bulletin. 119 (1–2): 18–30. Bibcode:2007GSAB..119...18G. doi:10.1130/B25924.1.
- ^ Loame, Remedy Charlotte (2016). Using a tephrostratigraphic framework to determine the past 40,000 yrs of fault rupture and paleohydrothermal activity on the east strand of the Whirinaki Fault, Ngakuru Graben, central Taupo Volcanic Zone (PDF) (Thesis).
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Gravley, Darren MClurg (2004). "The Ohakuri pyroclastic deposits and the evolution of the Rotorua-Ohakuri volcanotectonic depression" (PDF). Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ Zachariasen, Judith; Van Dissen, Russ (2001). "Paleoseismicity of the northern Horohoro Fault, Taupo Volcanic Zone, New Zealand". New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geophysics. 44 (3): 91–40. Bibcode:2001NZJGG..44..391Z. doi:10.1080/00288306.2001.9514946.