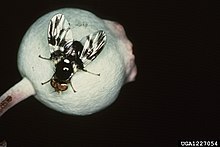
Rhagoletis mendax is a species of tephritid fruit fly known by the common name blueberry maggot. The blueberry maggot is closely related to the apple maggot (R. pomonella), a larger fruit fly in the same genus. It is a major pest of plant species in the Ericaceae family, such as blueberry, cranberry, and huckleberry. The larva is 5 to 8 mm long, apodous, and white with chewing mouthparts. Female adults are 4.75 mm in length, males are slightly smaller. Both adults are mostly black in color with white stripes, orange-red eyes, and a single pair of clear wings with black banding. The adult female fly lays a single egg per blueberry, and when the larva hatches it consumes the fruit, usually finishing the entire berry in under 3 weeks and rendering it unmarketable. The larva then falls to the soil and pupates. Adult flies emerge, mate, and females oviposit when blueberry plants are producing fruit. Each female fly can lay 25 to 100 eggs in their lifetime.
| Rhagoletis mendax | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Diptera |
| Family: | Tephritidae |
| Genus: | Rhagoletis |
| Species: | R. mendax
|
| Binomial name | |
| Rhagoletis mendax Curran, 1932
| |
It is present in regions of the eastern and southern United States and eastern Canada. The spread of infestation is regulated by national and regional plant protection organizations. These include the Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA), the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), the European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO), and smaller regional government organizations.
Blueberry maggot infestations are predominantly controlled with the use of chemical insecticides. Degree day predictive models and monitoring data gathered through sticky card traps are used in an integrated pest management program to make decisions on timing and frequency of control applications. Cultural measures such as removing overripe berries are often paired with chemical insecticide treatments in control programs.
Morphology
editEggs are white and elongate in shape.[1] Full-grown larvae or maggots are 7.75 mm (5⁄16 in) long, off white, with large preoral teeth (in front of the mouth), a cone-shaped distal sensory organ at the head, and large anal lobes and paired spiracles located on the blunt posterior.[2][1][3] The pupa is encased in a brown outer skin known as a puparium. Adults are the most distinguishable of the life stages from other Rhagoletis species - mainly by the ratio of banding on their wings, ovipositor length and other genital features - and can be identified using a taxonomic identification key.[3][4] The female fly is approximately 4.75 mm (3⁄16 in) long with a wingspan of 8 mm (1⁄3 in), with male flies being slightly smaller.[1] The thorax of both males and females is mostly black with a conspicuously white spot covering the scutellum and a white stripe on either side.[1][4] The abdomen of females is pointed and has four horizontal bands of fine white setae separating the sections, while the male abdomen is more rounded and has only three horizontal bands of setae.[1][4] The head is almost entirely covered by the eyes which are red in color, with a protruding pair of aristate antennae. They possess a single set of wings, which are clear with conspicuous dark black bands arranged in an "F" pattern. In many cases, visually distinguishing stages of R. mendax from others in the pomonella species group is not possible and may require the use of biochemical tests such as PCR to conclusively determine the species.[2][3][4]
Life cycle
editThe life cycle of this species is holometabolous, and has four stages of development: egg, larva, pupa and adult. Adults typically have a lifespan of 30–45 days or longer, with females being capable of reproduction starting at 15 days and going to approximately 45 days (weather dependent).[2]
The phenology of the blueberry maggot is varied, and depends on the geographic region the population inhabits.[2] In most regions of North America, populations have a univoltine life cycle. In Maine and potentially other locations however approximately 85% of the population in the state is univoltine, while the rest are semivoltine: 10% spend three winters as pupae, and 5% spend four winters.[2]
In the spring or summer the first wave of adults will emerge from the soil, coinciding with or just before ripening of the host fruit in the region.[2] Adults will continue emerging in groups into the summer.[1] Approximately 90% of the population emerges within a one-month period of each other, however, females will emerge 4–5 days before males at the time of maximum fruit availability.[2] Emergence is delayed to summer in some areas, potentially due to heat-induced quiescence of pupae.[2]
Adults will feed on dew, insect honeydew, and other secretions on foliage until the females become sexually mature.[1] After mating, female flies will lay a single egg per berry using a retractable ovipositor on the end of their abdomen to pierce the fruit and deposit the egg just under the skin.[1] The process leaves behind an oviposition-deterring pheromone to prevent other females from laying their egg in the same fruit for a couple of days.[2][1]
Eggs will hatch in 3–7 days depending upon geographic location and climate, and the larvae will begin consuming the fruit.[3] Larvae will continue to feed and go through three instars of growth in 17–30 days, at which point third instar larvae will emerge from the fruit, drop to the soil, and begin pupating at a depth of one to two inches (25 to 50 mm).[2][1] Pupation can commence in July at the southernmost limits of its distribution and into late September at its northernmost limits.[2]
Distribution
editRhagoletis mendax is native to North America, and is found in the eastern regions of the United States and Canada.[2][3] As of 2015 in the United States its distribution reaches as far south as states such as Georgia and Florida, and as far northwest as states such as Maine and Vermont.[2] In Canada, it is present in all coastal eastern provinces excluding Newfoundland and Labrador ( New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, Quebec, & Ontario), and only in small populations in Quebec and Ontario.[5]
The primary mode of dispersal to new areas is through transport of infected fruit, and secondly through flight, as R. mendax adults can only fly short distances.[3] Pupae can also be transported in contaminated growing media.[3]
Hosts and feeding behavior
editRhagoletis mendax adults are attracted to a wide range of species in their host genus Ericaceae, and prefer them to the hosts of other Rhagoletis species.[2][3]
Of the Ericaceae genera, many hosts are commercial crops and wild species of the genus Vaccinium, such as highbush and lowbush blueberries (V. corymbosum & angustifolia respectively), cranberries (V. macrocarpon), lingonberries (V. vitis-idaea), and huckleberries (Vaccinium sp. & Gaylussacia sp).[3][6]
Some research shows that adults are also attracted to volatiles secreted by Enterobacter (Pantoea) agglomerans, an epiphytic nitrogen-fixing species of bacteria found on the leaves and fruit of plants.[2] This may be due to a symbiotic relationship between the two species, where E. agglomerans provides nitrogen necessary for maturation of the female's ovaries.[2]
Impact
editLarva feeding on berries from within can result in premature fruit drop and loss of structural integrity.[7][8] Additionally, the presence of larvae in commercially grown berries can negatively impact consumer satisfaction. These factors lead to loss of marketability of the fruit and a reduction in profits for the grower.[8]
Controls
editDegree day models
editDegree day predictive modelling based on the temperature of the soil is used to determine the most likely dates of adult emergence in the area.[2][1] The developmental threshold for R. mendax, the minimum temperature required for individuals to continue maturing, is 6.1 °C (43 °F).[1] Degree Day Models from the University of Maine predict that the middle of fly population emergence can be predicted by the accumulation of 971 °F degree days (accumulations period in which the average daily temperature is at or above the developmental threshold) from April 1.[1]
Computer programs that calculate the date of phenological occurrences based on inputted temperature data, such as the middle of R. mendax emergence, are offered by some universities such as the University of Maine as an extension service.[1]
This information is used in combination with monitoring data in integrated pest management programs to determine the timing and effectiveness of control tactics, such as pesticide application, to increase effectiveness.[1]
Monitoring
editYellow sticky cards folded into a v-shape, baited with ammonium acetate on the exterior, and hung between crop plants are most commonly used to detect the presence of R. mendax in a commercial berry field.[7] Traps set in a grid pattern allow for more precise measurements of where in the field populations are located.[1]
Cultural
editRemoving over-ripe fruit from fields can lower the number of adults that will emerge the following spring and reduce the rates of re-infestation.[7]
Chemical
editInsecticides with short environmental persistence are recommended to control the adult stage.[7][8] No pesticides can effectively target the larval or pupal stages,[7][8] as they are protected by a fruiting body and soil respectively. The recommended application time is 5–7 days after catching the first adult fly,[7] with spot and perimeter treatments being effective where there are few but heavily infested areas of the field.[1] Trials conducted by Michigan State University found pesticides with the active ingredient spinosyn were rated good-excellent in controlling populations of blueberry maggot in fields with acute infestations.[7]
Attract-and-kill style traps are being tested for potential use as a control method for R. mendax, having been successfully used to control the apple maggot (R. pomonella).[9] Traps composed of biodegradable and regular plastic, or matted paper are baited with an ammonia-based kairomone lure, an attractive color, or both, and treated with an insecticide. Death results from contact and ingestion of the insecticide. The insecticidal compounds imidacloprid and fipronil yielded the highest rate of R. mendax adult fly death in one study.[9]
Regulation
editThe Canadian Food Inspection Agency (CFIA), the national plant protection organization of Canada, created directive D-02-04 for the use of government agencies such as the United States Department of Agriculture - Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (USDA-APHIS) and Canadian Border Services Agency (CBSA), and private businesses such as growers and importers. It outlines recommended phytosanitary measures to prevent the spread of R. mendax in fresh blueberries and blueberry plants.[6]
Additionally, the CFIA conducts a yearly blueberry maggot survey in non-regulated areas of Canada. Participating commercial blueberry fields are monitored using baited sticky cards in areas where the pest is not present or present in low populations to ensure the "pest-free status" of these areas.[6]
Rhagoletis mendax is regulated as a quarantine pest by the European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO) under the A1 quarantine list category 'non-European Trypetinae' flies.[3] This is used as a trade restriction for imported commodities such as fresh fruit and host plants.
References
edit- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q "201-Monitoring for the Blueberry Maggot (Rhagoletis mendax Curran) - Cooperative Extension: Maine Wild Blueberries - University of Maine Cooperative Extension". Cooperative Extension: Maine Wild Blueberries. Retrieved 2020-04-03.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Rodriguez-Saona, Cesar; Vincent, Charles; Polk, Dean; Drummond, Francis A. (2015-03-01). "A Review of the Blueberry Maggot Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae)". Journal of Integrated Pest Management. 6 (1): 11. doi:10.1093/jipm/pmv010.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Rhagoletis mendax (blueberry fruit fly)". www.cabi.org. Retrieved 2020-04-03.
- ^ a b c d "blueberry maggot - Rhagoletis mendax Curran". entnemdept.ufl.edu. Retrieved 2020-04-03.
- ^ Government of Canada, Canadian Food Inspection Agency (2012-02-03). "Rhagoletis mendax (Blueberry Maggot) - Fact sheet". www.inspection.gc.ca. Retrieved 2020-04-03.
- ^ a b c Government of Canada, Canadian Food Inspection Agency (2011-10-31). "D-02-04: The Blueberry Certification Program and Domestic Phytosanitary Requirements to Prevent the Spread of Blueberry Maggot (Rhagoletis mendax) within Canada". www.inspection.gc.ca. Retrieved 2020-04-06.
- ^ a b c d e f g Wold-Burkness, Suzanne; Hutchison, W.D. (2018-12-11). "Blueberry Maggot". FruitEdge. Archived from the original on 2021-01-28. Retrieved 2020-04-06.
- ^ a b c d "Blueberry Maggot". LSU AgCenter. 2016-01-07. Retrieved 2020-04-06.
- ^ a b Barry, James D.; Polavarapu, Sridhar; Teixeira, Luís A. F. (December 2004). "Evaluation of traps and toxicants in an attract-and-kill system for Rhagoletis mendax (Diptera: Tephritidae)". Journal of Economic Entomology. 97 (6): 2006–2014. doi:10.1093/jee/97.6.2006. ISSN 0022-0493. PMID 15666758.