The ROX Desktop is a discontinued[2] graphical desktop environment for the X Window System. It is based on the ROX-Filer which is a drag and drop spatial file manager. It is free software released under the GNU General Public License. The environment was inspired by the user interface of RISC OS (not to be confused with RISC/os).[3] The name "ROX" comes from "RISC OS on X". Programs can be installed or removed easily using Zero Install, a decentralized software installation system.
 | |
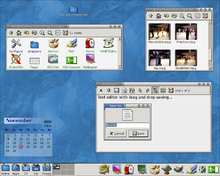 A screenshot of the ROX desktop | |
| Final release | 2.11[1] |
|---|---|
| Repository | github |
| Written in | C, Python, GTK |
| Operating system | Unix-like |
| Type | Desktop environment |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | rox |

The project was started by Thomas Leonard as a student at University of Southampton in 1999[4][5] and was still led by him in 2012.
Software components
editThe ROX Desktop is a desktop environment based on the ROX-Filer file manager. Files are loaded by applications by using drag and drop from the filer to the application, and saved by dragging back to the filer. Applications are executable directories, and are thus also installed (copied), uninstalled (deleted), and run through the filer interface. ROX has a strong link with Zero Install, a method of identifying and executing programs via a URL, to make software installation completely automatic.
The desktop uses the GTK toolkit, like the GNOME and Xfce desktops. The design focuses on small, simple programs using drag-and-drop to move data between them. For example, a user might load a compressed file into a spreadsheet from the web by dragging the data from the web browser to the archiver, and from there into the spreadsheet. A program would be installed in the same way, by dragging the archive from the web to the archiver, and from there to the applications directory in the filer.
Drag-and-drop saving allows the user to save the text file to any directory they please, or directly to another application, such as the archiver on the panel.
ROX Filer
edit| Screenshot of ROX-Filer | |
| Original author(s) | Thomas Leonard |
|---|---|
| Repository | |
| Operating system | Unix-like |
| Type | File manager |
| License | GPL-2.0-or-later |
| Website | rox |
ROX-Filer is a graphical spatial file manager for the X Window System. It can be used on its own as a file manager, or can be used as part of ROX Desktop. It is the file manager provided by default in certain Linux distributions such as Puppy Linux and Dyne:bolic, and was used in Xubuntu until Thunar became stable.
ROX-Filer is built using the GTK+ toolkit. Available under the terms of the GPL-2.0-or-later license, ROX-Filer is free software.[6]
Zero Install
edit| Zero Install ready to run a downloaded program | |
| Developer(s) | Thomas Leonard |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 2.17[7]
/ May 4, 2020 |
| Repository | |
| Written in | OCaml |
| Operating system | Linux, Unix, macOS, Windows |
| Type | Package manager |
| License | LGPLv2.1 |
| Website | 0install |
Zero Install (or 0install) is a multi-platform (Windows, Linux, macOS) system for running applications that allows publishing applications in a decentralized way (without using central repositories, directly on the project websites).[8] Unlike the xcopy mechanism[original research?], 0install retains the advantages of repositories: shared libraries, automatic updates, validation of digital signatures.[9]
Zero Install uses the metadata (sometimes called the feed format) written in XML. Like with xcopy deployment,[original research?] each application gets its own directory and there are no side effects inflicted upon the OS, so no administrative rights are needed and different versions of the same application can be run side-by-side without special modifications.[9]
To run an application, the user needs to use a launcher in ROX-Filer, that will ask the system to run an application with the given URL in the script inside the launcher. At the first time launching it, the URL will be used to download the program and save it in the system. The next times the program is launched, the system will not download it again. This is the reason why it is called Zero Install: the launcher tries to run the program, and not install it.[10][non-primary source needed]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ http://rox.sourceforge.net/desktop/node/962.html.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Kenlon, Seth (16 December 2019). "Relive Linux history with the ROX desktop | Opensource.com". opensource.com. Retrieved 16 June 2024.
- ^ "ROX founder: Why I brought RISC OS to Unix". Archived from the original on 20 November 2007.
- ^ "RISC O-X?". Acorn User. No. 214. December 1999. p. 10. Retrieved 16 August 2013.
- ^ "comp.sys.acorn.misc – Re: ROX desktop".
- ^ "COPYING". Archived from the original on 23 July 2012.
- ^ "Releases · 0install/0install". GitHub.
- ^ Khurshid, Usman (12 September 2013). "Run Windows Programs Without Having to Install Them". Make Tech Easier. Retrieved 15 June 2024.
- ^ a b Eicher 2011, p. 8.
- ^ "Zero Install and AddApp | ROX Desktop". ROX Desktop. 20 November 2007. Archived from the original on 20 November 2007. Retrieved 21 June 2024.
Sources
edit- Eicher, Bastian (2011). Desktop Integration Management for Portable, Zero-Install and Virtualized Applications (PDF). Department of Computer Science (BS thesis). Karlsruhe Institute of Technology.
Notes
edit- Bruce Byfield (7 February 2007) ROX Desktop provides light, quirky alternative to GNOME and KDE[permanent dead link], Linux.com
- (in German) Jo Moskalewski (July 2002) ' RISC rocks. Jo´s alternativer Desktop: ROX LinuxUser
External links
edit