Propamocarb is a systemic fungicide used for control of soil, root and leaf disease caused by oomycetes. It is used by watering or spraying. Propamocarb is absorbed and distributed through the plant's tissue.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
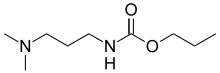
| Preferred IUPAC name
Propyl [3-(dimethylamino)propyl]carbamate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.109.082 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H20N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 188.271 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.957 g/cm3 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Xn |
| Flash point | 109.1 °C (228.4 °F; 382.2 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Use
editPropamocarb has fungicidal activity only against oomycetes.
Safety
editPropamocarb has low general toxicity, and almost no teratogenicity or neurotoxicity for mammals. It is not a carcinogen nor mutagen.[1][2] Propamocarb is not susceptible to formation of resistant diseases. It is fully metabolized by plants and aquatic bacteria in a few weeks, so it is not a major ecological threat. It carries the risk of skin sensitization. Oral LD50 is 2900 mg/kg for male rats and 2000 mg/kg for female rats.[2]
In one study conducted on tobacco, cucumber and spinach, using propamocarb synthesized out of carbon C14 radionuclide, researchers stated that propamocarb is decomposed down to carbon dioxide and then incorporated into the plant's natural compounds,[2] such as amino acids.
References
edit- ^ Propamocarb Hydrochloride, United States Environmental Protection Agency
- ^ a b c Propamocarb Hydrochloride; Notice of Filing a Pesticide Petition to Establish a Tolerance for a Certain Pesticide Chemical in or on Food, Federal Register, Vol. 69, No. 47, March 10, 2004