Proligestone, sold under the brand names Covinan and Delvosteron, is a progestin medication which is used in veterinary medicine.[1][2][3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Covinan, Delvosteron |
| Other names | 14α,17α-Propylidenedioxyprogesterone; 14α,17α-Dihydroxyprogesterone cyclic acetal with propionaldehyde; 14α,17α-Dihydroxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione cyclic acetal with propionaldehyde |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Progestin |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.041.733 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H34O4 |
| Molar mass | 386.532 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Uses
editVeterinary
editProligestone is used to control estrus in dogs and cats and has also been used to treat hypersexuality in dogs and cats.[4]
Pharmacology
editPharmacodynamics
editProligestone is a progestogen, or an agonist of the progesterone receptor (PR).
Chemistry
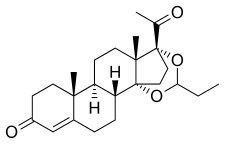
editProligestone, also known as 14α,17α-propylidenedioxyprogesterone or as 14α,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone cyclic acetal with propionaldehyde, as well as 14α,17α-propylidenedioxypregn-4-ene-3,20-dione, is a synthetic pregnane steroid and a derivative of progesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone.[1][2] It is a C14α,17α cyclic ketal of 14α,17α-dihydroxyprogesterone.[5][6][7]
History
editProligestone was described as early as 1968 and was introduced for veterinary use in 1975.[1][8][9]
Society and culture
editGeneric names
editProligestone is the generic name of the drug and its INN and BAN.[1][2][3]
Brand names
editProligestone is marketed under the brand names Covinan and Delvosteron.[1][2][3]
Availability
editProligestone is or has been available for veterinary use in Argentina, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Czechoslovakia, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, the Netherlands, New Zealand, Poland, South Africa, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom.[2][3]
References
edit- ^ a b c d e Elks J (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 1025–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ^ a b c d e Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Taylor & Francis. January 2000. pp. 882–. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1.
- ^ a b c d "List of Progestins". Drugs.com.
- ^ Mundt S (22 April 1981). "Indications for proligestone (Delvosteron) in dogs and cats". Praktische Tierarzt. 62 (12).
- ^ Marler EE (1976). Pharmacological and Chemical Synonyms: A Collection of Names of Drugs, Pesticides and Other Compounds Drawn from the Medical Literature of the World. Excerpta Medica. p. 376. ISBN 978-90-219-0298-2.
- ^ Negwer M, Scharnow HG (4 October 2001). Organic-chemical drugs and their synonyms: (an international survey). Wiley-VCH. p. 2569. ISBN 978-3-527-30247-5.
- ^ "Proligestone". Medical Subject Headings: Supplementary chemical records. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Official Gazette of the United States Patent and Trademark Office: Trademarks. U.S. Department of Commerce, Patent and Trademark Office. 1984. p. 30.
- ^ Vanos JL, Oldenkamp EP (September 1978). "Oestrus control in bitches with proligestone, a new progestational steroid". The Journal of Small Animal Practice. 19 (9): 521–529. doi:10.1111/j.1748-5827.1978.tb05534.x. PMID 567718.