Polygnotus is a crater on Mercury, named by the IAU in 1976, after ancient Greek painter Polygnotus.[1] The crater was first imaged by Mariner 10 in 1974.[2]
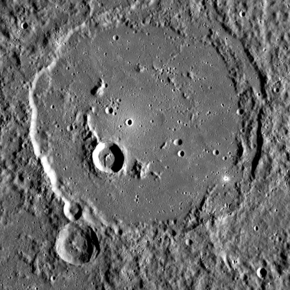 An image of Polygnotus. Its central peak ring has been partially submerged by smooth plains material | |
| Feature type | Peak-ring impact basin |
|---|---|
| Location | Kuiper quadrangle, Mercury |
| Coordinates | 0°08′S 69°16′W / 0.13°S 69.26°W |
| Diameter | 124 km (77 mi) |
| Eponym | Polygnotus |
Polygnotus has a central peak ring which is embayed with smooth plains material, which is very different in texture from the surrounding terrain.[3] It is one of 110 peak ring basins on Mercury.[4]
Boethius crater is west of Polygnotus. Tansen is to the northwest, and Motonobu is to the east.
-
Exaggerated color image with Polygnotus near center
-
Distant oblique view showing Polygnotus at right and Motonobu at top center
References
edit- ^ "Polygnotus". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. IAU/NASA/USGS. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ Davies, M. E.; Dwornik, S. E.; Gault, D. E.; Strom, R. G. (1978). Atlas of Mercury. National Aeronautics and Space Administration. pp. 1–128. ISBN 978-1-114-27448-8. Special Publication SP-423.
- ^ MESSENGER Gathers Unprecedented Data about Mercury's Surface, Release Date: October 7, 2008. Credit: NASA/Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory/Carnegie Institution of Washington
- ^ Chapman, C. R., Baker, D. M. H., Barnouin, O. S., Fassett, C. I., Marchie, S., Merline, W. J., Ostrach, L. R., Prockter, L. M., and Strom, R. G., 2018. Impact Cratering of Mercury. In Mercury: The View After MESSENGER edited by Sean C. Solomon, Larry R. Nittler, and Brian J. Anderson. Cambridge Planetary Science. Chapter 9.

