A Phaeozem in the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) is a dark soil with a high base status, but without a secondary carbonates within one metre of the soil surface. Most Phaeozems correlate with the Udolls (Mollisols) of the USDA soil taxonomy.[1][2]

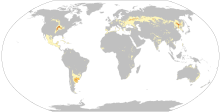
Dominant (more than 50% of soil cover)
Codominant (25-50%)
Associated (5-25%)
These soils are found mainly in humid and sub-humid tall-grass steppes; there are extensive areas of them in the United States, Argentina and China. Phaeozems form from unconsolidated sediments such as loess and glacial till and typically have organic matter contents of about 5% and a pH of 5–7.
Intensive agricultural use is widespread and includes wheat, soybean and cotton production and improved pastures for cattle.
See also
editReferences
edit- IUSS Working Group WRB: World Reference Base for Soil Resources, fourth edition. International Union of Soil Sciences, Vienna 2022. ISBN 979-8-9862451-1-9 ([1]).
- ^ Delvaux, B.; Brahy, V. "Mineral Soils conditioned by a Wet (Sub)Tropical Climate". FAO. Retrieved 14 June 2014.
- ^ "Major Soils of the World. ISRIC Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2001" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2014-06-14.
Further reading
edit- W. Zech, P. Schad, G. Hintermaier-Erhard: Soils of the World. Springer, Berlin 2022, Chapter 5.3.1. ISBN 978-3-540-30460-9
External links
edit- profile photos (with classification) WRB homepage
- profile photos (with classification) IUSS World of Soils