Penitanzacid F was found as one of the twelve new tanzawaic acid derivatives, which were the secondary metabolites of the fungi Pencillum sp. KWF32 isolated from the tissues of Bathymodiolus sp. collected in the cold spring area of the South China Sea in 2021.[1]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
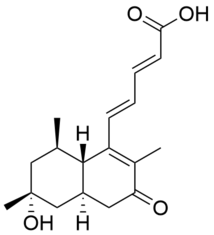
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E,4E)-5-((4aR,6R,8R,8aS)-6-hydroxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-3-oxo-3,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydronaphthalen-1-yl)penta-2,4-dienoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H24O4 | |
| Molar mass | 304.39 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
It may have anticoccidial, cytotoxic, lipid-lowering,[2] superoxide anion production inhibiting, bacterial conjugation inhibiting, and NO production inhibiting properties as a tanzawaic acid derivative.[1]
Structure and biosynthesis
editThe biosynthesis of Penitanzacid F starts from one acetyl-CoA, two methylmalonyl-CoA and three malonyl-CoA molecules with polyketide synthase (PKS). Then the product undergoes Diels-Alder Cyclization, chain elongation with two malonyl-CoA, and is oxidized to penitanzaicacid F.
References
edit- ^ a b Wang, Jiaqi; Li, Taiwei; Wang, Pinmei; Ding, Wanjing; Xu, Jinzhong (2022-05-27). "Tanzawaic Acids from a Deep-Sea Derived Penicillium Species". Journal of Natural Products. 85 (5): 1218–1228. doi:10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c01020. ISSN 0163-3864. PMID 35420798. S2CID 248181547.
- ^ Yu, Guihong; Wang, Shuai; Wang, Lu; Che, Qian; Zhu, Tianjiao; Zhang, Guojian; Gu, Qianqun; Guo, Peng; Li, Dehai (2018-01-12). "Lipid-Lowering Polyketides from the Fungus Penicillium Steckii HDN13-279". Marine Drugs. 16 (1): 25. doi:10.3390/md16010025. ISSN 1660-3397. PMC 5793073. PMID 29329204.