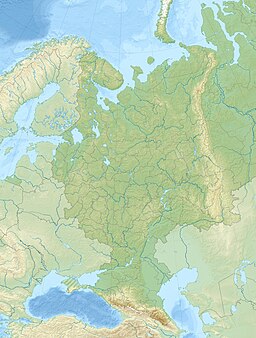
The Pechora Sea (Russian: Печо́рское мо́ре, Pechorskoye More) is an Arctic sea to the north-west of European Russia, forming the south-eastern portion of the Barents Sea. It is bordered to the west by Kolguyev Island; to the east by Vaygach Island's western coasts and the Yugorsky Peninsula; and to the north by the southern end of Novaya Zemlya.
| Pechora Sea | |
|---|---|
| Печо́рское мо́ре (Russian) | |
 Location of the Pechora Sea | |
| Coordinates | 69°45′N 54°00′E / 69.750°N 54.000°E |
| Type | Sea |
| Part of | Barents Sea |
| Primary inflows | Pechora River |
| River sources | Pechora River |
| Primary outflows | Arctic Ocean |
| Ocean/sea sources | Arctic Ocean |
| Catchment area | 330,000 km2 (127,000 sq mi) |
| Basin countries | Russia |
| Surface area | 81,263 km2 (31,376 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 6 m (20 ft) |
| Max. depth | 210 m (690 ft) |
| Water volume | 4,380 km3 (1,050 cu mi) |
| Salinity | 18–34.95 ‰[a] |
| Max. temperature | 8 °C (46 °F) |
| Min. temperature | −1.0 °C (30.2 °F) |
| Frozen | November to late June[1] |
| References | [3][4][2] |
Located in the centre of the East-Atlantic flyway with conditions befitting for benthic life, the Pechora Sea supports about 600 taxa[3] and the Barents Sea's highest total biomass.[3] It is the site of the yearly migration of one of the largest salmon stocks in Northern Europe.[3] Compared to the rest of the Barents Sea, the Pechora Sea is unique for its more continental climate, lower salinity, shallowness, separation from the open sea and large input from rivers,[5][3] as well as a low level of human interference historically.[6] Its temperate characteristics are not typical of the Arctic.[5]
History
editHistorically, before the adjacent Barents Sea was named as such, the Pechora Sea's own name was already established. The rest of the present-day Barents Sea was known then as Sea of Murmansk (Murmanskoye Morye).
The Pechora Sea was used as a starting point of the exploration of the then unknown icy seas lying to the east. The earliest recorded voyage across the Pechora Sea through the Yugorsky Strait was made by early Russian explorer Uleb, from Veliky Novgorod. Uleb's passing into the Kara Sea was recorded in 1032.
Russian Pomors, the coastal dwellers of the White Sea shores, have explored the Sea and the coast of Novaya Zemlya since the 11th century. The Arctic's first shipping line, the Great Mangazea Route, from the White Sea to the Ob River and the Yenisei Gulf began operating in the latter part of the 16th century. This line opened up the way to Siberia's riches and it worked until 1619, when it was closed for military and political reasons, for fear of possible penetration by Europeans into Siberia.
Geography
editThe Pechora Sea is blocked by floating ice from November to June—a relatively short period.[6] The main river entering the Sea is the Pechora. The Sea's salinity ranges from 18 to 34 ‰. At the central part of the Sea, the salinity stays around 34 ‰, and the temperature ranges from 0.5 to 2 °C (32.9 to 35.6 °F).[2]
Bathymetry
editThe Pechora Sea's average depth is 6 m (20 ft), and its deepest point reaches 210 m (690 ft).[4] The mean depth ranges from 11 m (36 ft) in the Bay to 190 m (620 ft) south of Novaya Zemlya.[7] The Atlantic-influenced Kolguyev Current, which influences the temperature and salinity of the central part of the Sea, flows eastwards.[2] There are a few islands[quantify] close to the coast, the largest of which is Dolgiy Island.
The Sea's shallowness makes it distinct from the rest of the Barents Sea. Over its 205,607 km2 (79,385 sq mi) area,[3] the average depth in the Sea is around 50 m (160 ft).[3] This shallowness prevents the upwelling of nutrients from the Atlantic,[3] contributing to the Sea's low pelagic productivity.
Hydrology
editAs with the neighbouring Kara Sea, the Pechora Sea's hydrologic situation is unique for its high input from rivers and heavy continental outflow.[5][3] The Pechora River alone discharges about 130 km3 (31 cu mi) of freshwater into the Pechora Sea from the Pechora River—the Pechora Sea's main source of inflow—supplying the Sea with a sediment load of 6.1×106 tonnes (6.1×109 kg; 1.34×1010 lb) yearly.[2]
Compared to other seas around the world, the Arctic Ocean's river-heavy source of inflow is significant, giving the Pechora Sea less Arctic-like characteristics than would be expected at latitudes so far from the equator. The Pechora Sea together with the bordering Kara Sea (separated by the jet stream) make up more than a third of the Arctic Ocean's total runoff from continental sources[5] (as opposed to mostly saltwater sources like most oceans). This high input from rivers makes this area of the Arctic Ocean unique.[5]
Temperature and salinity
editIce formation is boosted by the Sea's low salinity. The temperature ranges from −1.0 to 1.5 °C (30.2 to 34.7 °F) below 150 m (490 ft); 0.5 to 2 °C (32.9 to 35.6 °F) at the central part of the Sea; and 5 to 8 °C (41 to 46 °F) in summer and autumn at the southern part of the Sea.[2]
Its salinity ranges from 8 to 18 ‰ in the bay, 18 to 26 ‰ in the southern portion, and 34 ‰ in the central part,[2] increasing with distance from the mouth of the Pechora River.[8]
Climate
editThe Pechora Sea has a humid continental climate. Polar bears and Atlantic walrus are threatened by climate change,[3] which exceptionally burdens the Arctic.
Counteracting the Sea's continental position is the influx of nutrients supplied by the Pechora River,[3] which gives the Sea 4,570 km3 (1,100 cu mi) of sediment and 12,500 tonnes (12,500,000 kg; 13,800 short tons) of other suspended matter.[3]
The Sea's cold continental climate,[3] a result of its location in the dead centre of the continent, gives favourable conditions to ice formation.[3] As a result of this continental position and abundance of ice, the Sea's water column is stratified, its sediment is heterogeneous[9] and its pelagic productivity is low.[3]
Seafloor sediment
edit1 km (0.62 mi)-wide fast ice covers the floor of the Sea's coastal zone. On top of it is flaw polynya.[3]
Biogeography and ecology
editIt supports a unique benthic ecosystem. The productive benthic environment fostered by the Pechora River holds more than 600 fauna.[3] At the Kara and Yugorsky Straits, the total biomass is more than 500 mg/m2 (0.00010 lb/sq ft), the highest in the Barents Sea. This benefits benthic organisms such as walruses. The Pechora River, the main input for the Pechora Sea, has an average yearly runoff of 130 km3 (31 cu mi). The Pechora Sea has 70 fish species,[3] the most abundant being Boreogadus saida.[3] This species is important for the cryopelagic ecosystem.
The fisheries of the Barents Sea, in particular the cod fisheries, are of great importance for both Norway and Russia. There is a diversity of benthic fauna on the Pechora Sea floor.[10] In addition, there is a genetically distinct polar bear population associated with the Barents Sea.[11] The Karskaya group of beluga whales migrate into Pechora Sea for wintering.[12] Various species such as walruses are threatened by possible pollutions.[13][14]
Flora and fauna
editThere are about 600 taxa in the Pechora Sea.[3] Various anadromous fishes inhabit the Sea. One of the largest Northern European stocks of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) as well as other fish populations from surrounding areas migrate throughout the Pechora Sea each autumn to spawn, a process which they complete under the ice.[3] Additionally, the only stock of Coregonus autumnalis in Northern Europe, and one of the region's largest, spawns in the Pechora's estuary.[3]
The Pechora Sea is the main 'staging and moulting ground for king eiders. Long-tailed ducks scoters and most other waterfowl species use the Sea as a stopover point.[3]
At the Kara and Yugorsky Straits, the total biomass is more than 500 mg/m2 (0.00010 lb/sq ft), the highest in the Barents Sea.[3] The most abundant phyla are Annelida, Bryozoa, Crustacea, Echinodermata, Mollusca and Sarcomastigophora.[15]
Pollution
editRelative to the rest of the Barents Sea, the water quality of the Pechora Sea is poor.[16]
Economy
editOil and gas
editAs of 2023[update], the Pechora Sea is one of the most developed places in the Arctic with regard to petroleum exploration.[3]
In current times[as of?] there is some oil drilling in the Pechora Sea at the Dolginskoye and Prirazlomnoye oil fields. The negative ecological impact of such industrial exploitation in the Pechora Sea coast is significant.[17] According to Greenpeace[18] and the World Wildlife Fund Gasprom is not prepared to deal adequately with a spill associated with oil production.[19] As such, in September, 2013, Greenpeace staged a confrontation with the Russian Coast Guard in which Greenpeace activists approached and attempted to scale a Gasprom drilling platform.
Notes
editReferences
edit- ^ a b Dahle et al. 1998, p. 184.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Dahle et al. 1998, p. 185.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y Convention on Biological Diversity 2015.
- ^ a b Britannica 1998.
- ^ a b c d e Polyak, Stanovoy & Lubinski 2003, p. 1.
- ^ a b Gebruk et al. 2021, p. 57.
- ^ Dahle et al. 1998, p. 187, Table 2.
- ^ Polyak, Stanovoy & Lubinski 2003, p. 3, 'steady, declerating increase of salinities with distance from the estuaries'.
- ^ Dahle et al. 1998.
- ^ S. Dahle, 2004
- ^ C.M. Hogan, 2008
- ^ Regional Environment Case Study - Barents and Kara Seas
- ^ Pechora Sea pollution causes diseases of the Atlantic walruses
- ^ Reeves R.R., Ewins J.P., Agbayani S., Blijleven J., 2013, Distribution of endemic cetaceans in relation to hydrocarbon development and commercial shipping in a warming Arctic, Marine Policy 44, pp.375-389, DOI: 10.1016/j.marpol.2013.10.005, Retrieved on 29 January 2017
- ^ Dahle et al. 1998, p. 187.
- ^ Politova et al. 2019, Abstract.
- ^ S.A. Ogorodov, 2004
- ^ "Prirazlomnaya oil spill would threaten Russian Arctic with irreparable disaster: study". Greenpeace Russia. 14 August 2012. Retrieved 15 August 2012.
- ^ "Environmentalists warn of risk of oil production in the Russian Arctic". The Washington Post. Associated Press. 14 August 2012. Archived from the original on 3 September 2019. Retrieved 15 August 2012.
Sources
edit- "Pechora Sea". Britannica.com. Encyclopaedia Britannica. 20 July 1998. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- "Ecologically or Biologically Significant Areas: South-eastern Barents Sea (the Pechora Sea)". The Clearing-House Mechanism of the Convention on Biological Diversity: Information Submission Service. Convention on Biological Diversity. 12 June 2015. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- Polyak, Leonid; Stanovoy, Vladimir; Lubinski, David J. (2003). "Stable isotopes in benthic foraminiferal calcite from a river-influenced Arctic marine environment, Kara and Pechora Seas". Paleoceanography. 18 (1): 1003. Bibcode:2003PalOc..18.1003P. doi:10.1029/2001PA000752. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- Dahle, Salve; Denisenko, Stanislav G.; Denisenko, Nina V.; Cochrane, Sabine J. (28 August 1998). "Benthic fauna in the Pechora Sea" (PDF). Sarsia. 83. Bergen: 183–210. ISSN 0036-4827. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- Makarevich, Pavel; Druzhkova, Elena; Larionov, Viktor (2012). "Chapter 16: Primary Producers of the Barents Sea" (PDF). In Ali, Mahamane (ed.). Diversity of Ecosystems. InTech. pp. 367–392. ISBN 978-953-51-0572-5.
- Politova, N. V.; Kravchishina, N. D.; Novigatsky, A. N.; Lokhov, A. S. (2019). "Dispersed Sedimentary Matter of the Barents Sea". Oceanology. 59 (5): 697–714. Bibcode:2019Ocgy...59..697P. doi:10.1134/S0001437019050151. S2CID 211265306. Retrieved 18 September 2023.
- Gebruk, Anna; Zalota, Anna K.; Dgebuadze, Polina; Ermilova, Yulia; Spiridonov, Vassily A.; Shabalin, Nikolay; Henry, Lea-Anne; Henley, Sian F.; Mokievsky, Vadim O. (2021). "Trophic niches of benthic crustaceans in the Pechora Sea suggest that the invasive snow crab Chionoecetes opilio could be an important competitor". Polar Biology. 44 (1): 57–71. Bibcode:2021PoBio..44...57G. doi:10.1007/s00300-020-02775-3. hdl:20.500.11820/b83e5a04-2393-46e4-a4d2-3b94741800c4. S2CID 230533350.
- Benthic fauna: [1]
- C. Michael Hogan (2008) Polar Bear: Ursus maritimus, Globaltwitcher.com, ed. Nicklas Stromberg
- Oil and Gas Resources in North-West Russia (2008) [2]
- S. A. Ogorodov (2004) Human impact on coastal stability in the Pechora Sea [3]
- Leonid Sverdlov, (Member of the Russian Geographic Society), RUSSIAN NAVAL OFFICERS AND GEOGRAPHIC EXPLORATION IN NORTHERN RUSSIA.
- C. Raymond Beazley, The Russian Expansion Towards Asia and the Arctic in the Middle Ages (to 1500). The American Historical Review