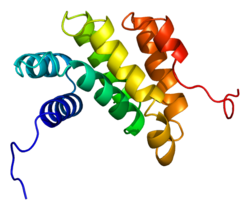
Programmed cell death protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDCD4 gene.[5][6] It is one of the targets of an oncomiR, MIRN21.[7]
Function
editThis gene encodes a protein localized to the nucleus in proliferating cells. Expression of this gene is modulated by cytokines in natural killer and T cells. The gene product is thought to play a role in apoptosis but the specific role has not yet been determined. Two transcripts encoding different isoforms have been identified.[6]
Interactions
editPDCD4 has been shown to interact with RPS13,[8] ribosomal protein L5,[8] p62, LC3 and Ubiquitin [9]
References
edit- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000150593 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024975 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Azzoni L, Zatsepina O, Abebe B, Bennett IM, Kanakaraj P, Perussia B (1998). "Differential transcriptional regulation of CD161 and a novel gene, 197/15a, by IL-2, IL-15, and IL-12 in NK and T cells". Journal of Immunology. 161 (7): 3493–500. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.161.7.3493. PMID 9759869. S2CID 21776266.
- ^ a b EntrezGene 27250
- ^ Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A, Lindow M, Krogh A, Lund AH (2008). "Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 283 (2): 1026–33. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707224200. PMID 17991735.
- ^ a b Kang MJ, Ahn HS, Lee JY, Matsuhashi S, Park WY (2002). "Up-regulation of PDCD4 in senescent human diploid fibroblasts". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 293 (1): 617–21. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00264-4. PMID 12054647.
9. Manirujjaman M, Ozaki I, Murata Y, Guo J, Xia J, Nishioka K, Perveen R, Takahashi H, Anzai K, Matsuhashi S (2020). "Degradation of the Tumor Suppressor PDCD4 Is Impaired by the Suppression of p62/SQSTM1 and Autophagy". Cells. 9(1): 218. doi.org/10.3390/cells9010218.
Further reading
edit- Göke R, Gregel C, Göke A, Arnold R, Schmidt H, Lankat-Buttgereit B (2004). "Programmed Cell Death Protein 4 (PDCD4) Acts As a Tumor Suppressor in Neuroendocrine Tumor Cells". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1014 (1): 220–1. Bibcode:2004NYASA1014..220G. doi:10.1196/annals.1294.024. PMID 15153438. S2CID 9284462.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (1994). "Oligo-capping: A simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Shibahara K, Asano M, Ishida Y, Aoki T, Koike T, Honjo T (1995). "Isolation of a novel mouse gene MA-3 that is induced upon programmed cell death". Gene. 166 (2): 297–301. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(95)00607-9. PMID 8543179.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5′-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Yoshinaga H, Matsuhashi S, Fujiyama C, Masaki Z (1999). "Novel human PDCD4 (H731) gene expressed in proliferative cells is expressed in the small duct epithelial cells of the breast as revealed by an anti-H731 antibody". Pathology International. 49 (12): 1067–77. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1827.1999.00995.x. PMID 10632927. S2CID 968499.
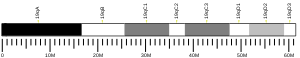
- Soejima H, Miyoshi O, Yoshinaga H, Masaki Z, Ozaki I, Kajiwara S, Niikawa N, Matsuhashi S, Mukai T (1999). "Assignment1 of the programmed cell death 4 gene (PDCD4) to human chromosome band 10q24 by in situ hybridization". Cytogenetic and Genome Research. 87 (1–2): 113–4. doi:10.1159/000015408. PMID 10640828. S2CID 34560093.
- Kang MJ, Ahn HS, Lee JY, Matsuhashi S, Park WY (2002). "Up-regulation of PDCD4 in senescent human diploid fibroblasts". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 293 (1): 617–21. doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00264-4. PMID 12054647.
- Chen Y, Knösel T, Kristiansen G, Pietas A, Garber ME, Matsuhashi S, Ozaki I, Petersen I (2003). "Loss of PDCD4 expression in human lung cancer correlates with tumour progression and prognosis". The Journal of Pathology. 200 (5): 640–6. doi:10.1002/path.1378. PMID 12898601. S2CID 25899458.
- Yang HS, Cho MH, Zakowicz H, Hegamyer G, Sonenberg N, Colburn NH (2004). "A Novel Function of the MA-3 Domains in Transformation and Translation Suppressor Pdcd4 is Essential for Its Binding to Eukaryotic Translation Initiation Factor 4A". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 24 (9): 3894–906. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.9.3894-3906.2004. PMC 387765. PMID 15082783.
- Brill LM, Salomon AR, Ficarro SB, Mukherji M, Stettler-Gill M, Peters EC (2004). "Robust Phosphoproteomic Profiling of Tyrosine Phosphorylation Sites from Human T Cells Using Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography and Tandem Mass Spectrometry". Analytical Chemistry. 76 (10): 2763–72. doi:10.1021/ac035352d. PMID 15144186.
- Göke R, Barth P, Schmidt A, Samans B, Lankat-Buttgereit B (2004). "Programmed cell death protein 4 suppresses CDK1/cdc2 via induction of p21Waf1/Cip1". AJP: Cell Physiology. 287 (6): C1541–6. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00025.2004. PMID 15317660. S2CID 83565566.
- Rush J, Moritz A, Lee KA, Guo A, Goss VL, Spek EJ, Zhang H, Zha XM, Polakiewicz RD, Comb MJ (2004). "Immunoaffinity profiling of tyrosine phosphorylation in cancer cells". Nature Biotechnology. 23 (1): 94–101. doi:10.1038/nbt1046. PMID 15592455. S2CID 7200157.
- Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, et al. (2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein–protein interaction network". Nature. 437 (7062): 1173–8. Bibcode:2005Natur.437.1173R. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514. S2CID 4427026.
- Palamarchuk A, Efanov A, Maximov V, Aqeilan RI, Croce CM, Pekarsky Y (2005). "Akt Phosphorylates and Regulates Pdcd4 Tumor Suppressor Protein". Cancer Research. 65 (24): 11282–6. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3469. PMID 16357133.
- Yang HS, Matthews CP, Clair T, Wang Q, Baker AR, Li CC, Tan TH, Colburn NH (2006). "Tumorigenesis Suppressor Pdcd4 Down-Regulates Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Kinase Kinase Kinase 1 Expression to Suppress Colon Carcinoma Cell Invasion". Molecular and Cellular Biology. 26 (4): 1297–306. doi:10.1128/MCB.26.4.1297-1306.2006. PMC 1367180. PMID 16449643.