Nicotine polacrilex is nicotine bound to an ion-exchange resin (polymethacrylic acid, such as Amberlite IRP64, Purolite C115HMR or Doshion P551).[4] It is added to gum and hard lozenges used for nicotine replacement therapy in smoking cessation, such as in the Nicorette range of products. The use of the polymer as a delivery system maximizes the amount of nicotine released and absorbed by the oral mucosa. 80 to 90 percent of the nicotine released from the gum is absorbed by the mouth. Side effects of the gum include bad taste, nausea, dyspepsia, and stomatitis.
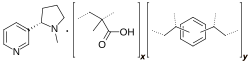 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Nicorette |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| UNII | |
References
edit- ^ "Nicorette 2mg Gum Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". emc. 1 September 2021. Retrieved 17 July 2024.
- ^ "Nicorette 4mg Gum Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". emc. 1 September 2021. Retrieved 17 July 2024.
- ^ "Nicorette White Ice Mint- nicotine polacrilex gum, chewing Nicorette Original- nicotine polacrilex gum, chewing Nicorette Cinnamon Surge- nicotine polacrilex gum, chewing Nicorette Fresh Mint- nicotine polacrilex gum, chewing Nicorette Mint- nicotine polacrilex gum, chewing Nicorette Spearmint Burst- nicotine polacrilex gum, chewing". DailyMed. Retrieved 11 November 2021.
- ^ "Nicotine polacrilex". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2021-11-12. Retrieved 2021-11-12.
External links
edit- Nicotine polacrilex at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)