Naptumomab estafenatox (ABR-217620) is a drug being developed for the treatment of various types of cancer like non-small cell lung carcinoma[1] and renal cell carcinoma.[2]
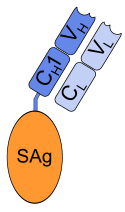 Schematic image of naptumomab estafenatox. VH, VL: variable (antigen binding) domains of antibody fragment | |
| Monoclonal antibody | |
|---|---|
| Type | Fab fragment |
| Source | Mouse |
| Target | 5T4 |
| Clinical data | |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C3255H5025N855O1050S18 |
| Molar mass | 73513.02 g·mol−1 |
| | |
Mechanism of action
editChemically, it is a fusion protein consisting of the antigen-binding fragment (Fab) of a monoclonal antibody with the superantigen staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA/E-120, "estafenatox").[3] The Fab binds to 5T4, an antigen expressed by various tumor cells, and the superantigen induces an immune response by activating T lymphocytes.[4]
See also
edit- Nacolomab tafenatox, a drug with a similar chemical structure and mechanism
References
edit- ^ Borghaei H, Alpaugh K, Hedlund G, Forsberg G, Langer C, Rogatko A, et al. (September 2009). "Phase I dose escalation, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of naptumomab estafenatox alone in patients with advanced cancer and with docetaxel in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 27 (25): 4116–23. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.20.2515. PMC 2734423. PMID 19636016.
- ^ Clinical trial number NCT00420888 for "ABR-217620/Naptumomab Estafenatox With Interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) Compared to IFN-alpha Alone in Patients With Advanced Renal Cell Carcinoma" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ^ "Naptumomabum estafenatoxum" (PDF). WHO Drug Information. 20 (4): 291. 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-02-01.
- ^ Eisen T, Hedlund G, Forsberg G, Hawkins R (February 2014). "Naptumomab estafenatox: targeted immunotherapy with a novel immunotoxin". Current Oncology Reports. 16 (2): 370. doi:10.1007/s11912-013-0370-0. PMC 3918406. PMID 24445502.