Mount Madeline is a 2,536-metre-elevation (8,320-foot) mountain in Fiordland, New Zealand.
| Mount Madeline | |
|---|---|
 Southeast aspect | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 2,536 m (8,320 ft)[1][2] |
| Prominence | 543 m (1,781 ft)[2] |
| Parent peak | Mount Tūtoko[2] |
| Isolation | 2.87 km (1.78 mi)[2] |
| Listing | New Zealand #62 |
| Coordinates | 44°36′51″S 168°02′45″E / 44.61417°S 168.04583°E[2] |
| Geography | |
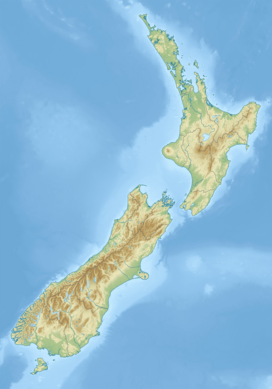
 | |
| Interactive map of Mount Madeline | |
| Location | South Island |
| Country | New Zealand |
| Region | Southland[2] |
| Protected area | Fiordland National Park |
| Parent range | Darran Mountains |
| Topo map(s) | NZMS260 D40[3] Topo50 CA09[4] |
| Geology | |
| Rock age | 136 ± 1.9 Ma |
| Rock type | Gabbronorite, dioritic orthogneiss |
| Climbing | |
| First ascent | 1920 |
Description
editMount Madeline is the second-highest peak of the Darran Mountains. It is situated in the Southland Region of South Island, and set within Fiordland National Park which is part of the Te Wahipounamu UNESCO World Heritage Site.[2] Precipitation runoff from the mountain drains west to the Tūtoko River via Leader Creek, and east to the Hollyford River via Madeline, Cleft, and Glacier creeks. Topographic relief is significant as the summit rises 2,500 metres (8,202 feet) above the Hollyford Valley in four kilometres and 2,100 metres (6,890 feet) above the Tūtoko Valley in four kilometres.
History
editIn 1895, Malcolm Ross, Kenneth Ross, W.J. Hodgkin, and Tom Fyfe climbed the lower west peak (2,516 m) of Madeline.[4] The first ascent of the true summit was made in March 1920 by Alf Cowling and Samuel Turner.[4] The mountain was named in 1921 after Samuel Turner's daughter, Madeline.[3][5]
Climate
editBased on the Köppen climate classification, Mount Madeline is located in a marine west coast climate zone, with a subpolar oceanic climate (Cfc) at the summit.[6] Prevailing westerly winds blow moist air from the Tasman Sea onto the mountain, where the air is forced upward by the mountains (orographic lift), causing moisture to drop in the form of rain and snow. This climate supports unnamed glaciers on the peak's slopes. The months of December through February offer the most favourable weather for viewing or climbing this peak.[7]
Climbing
editClimbing routes with the first ascents:[4]
- South West Face – Samuel Turner, Alf Cowling – (1920)
- North East Ridge from Glacier Creek – R. Offer, G. Mason, A. Witten-Hannah – (1953)
- North West Buttress – Margaret Clark, Jim Clark, G.D. Cowie – (1958)
- North East Ridge – Ian Brown, Tom Williams – (2009)
- Mad Line – Steve Skelton, Justin Venable, Simon Rutherford – (2016)
Gallery
editSee also
editReferences
edit- ^ Mount Madeline, Southland, NZTopoMap, Retrieved 10 January 2025.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g "Mount Madeline, New Zealand". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 10 January 2025.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Mount Madeline, New Zealand Gazetteer, Retrieved 10 January 2025.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d Mt Madeline, New Zealand Alpine Club, Climbnz.org, Retrieved 10 January 2025.
- ^ New Zealand Alpine Journal, Volume 7, New Zealand Alpine Club, 1937, p. 154.
- ^ Te Anau Climate (New Zealand), climate-data.org, Retrieved 10 January 2025.
- ^ The Best Time to Visit the South Island, nzpocketguide.com, Retrieved 10 January 2025.
External links
edit- Mount Madeline: weather
- Mount Madeline: New Zealand Alpine Club