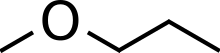
Methoxypropane, or methyl propyl ether, is an ether once used as a general anaesthetic.[1] It is a clear colorless flammable liquid with a boiling point of 38.8 °C.[2]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-Methoxypropane | |
| Other names
Propane, 1-methoxy-
methyl propyl ether Metopryl Neothyl propane, 1-methoxy methyl n-propyl ether | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.327 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 2612 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H10O | |
| Molar mass | 74.12 |
| Density | 0.7356 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 38.8 °C (101.8 °F; 311.9 K) |
| 30.5 g/L | |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.35837 (14.3 °C) |
| Viscosity | 0.3064 cP (0.3 °C) |
| Pharmacology | |
| inhalation | |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | < −20 °C (−4 °F; 253 K) |
| Explosive limits | 1.9-11.8 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Marketed under the trade names Metopryl and Neothyl, methoxypropane was used as an alternative to diethyl ether because of its greater potency. Its use as an anaesthetic has since been supplanted by modern halogenated ethers which are much less flammable.
References
edit
