A Maxwell coil is a device for producing a large volume of almost constant (or constant-gradient) magnetic field. It is named in honour of the Scottish physicist James Clerk Maxwell.

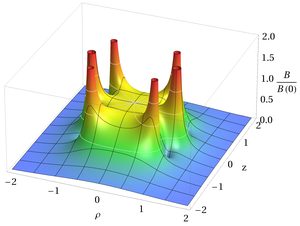
A Maxwell coil is an improvement of a Helmholtz coil: in operation it provides an even more uniform magnetic field (than a Helmholtz coil), but at the expense of more material and complexity.
Description
editA constant-field Maxwell coil set consists of three coils oriented on the surface of a virtual sphere.[1] According to Maxwell's original 1873 design:[2] each of the outer coils should be of radius , and distance from the plane of the central coil of radius .
Maxwell specified the number of windings as 64 for the central coil and 49 for the outer coils. Though Maxwell did not specifically state that current for the coils came from the same source, his work was specifically describing the construction of a sensitive galvanometer designed to detect a single current source. It follows that the ampere-turns for each of the smaller coils must be exactly of the turns of the larger.
Gradient-field Maxwell coil
editA gradient-field Maxwell coil has essentially the same geometry of the 3-coil configuration above, but the central coil is removed to leave only the smaller two coils, and the current in one of these is reversed.[3] This produces a uniform-gradient magnetic field near the centre of the two coils. Maxwell describes the use of the 2-coil configuration for the generation of a uniform force on a small test coil.[4] A Maxwell coil of this type is similar to a Helmholtz coil with the coil distance increased from coil radius to and the coils fed with opposite currents.
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Garrett, Milan Wayne (1967). "Thick Cylindrical Coil Systems for Strong Magnetic Fields with Field or Gradient Homogeneities of the 6th to 20th Order". Journal of Applied Physics. 38 (6): 2563–2586. Bibcode:1967JAP....38.2563G. doi:10.1063/1.1709950.
- ^ Clerk-Maxwell, James (1873). Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism. Vol. 2. Oxford: The Clarendon Press. p. 319. ISBN 978-0-486-60636-1.
- ^ R. Pascone, Manhattan College, T. Vullo and P. T. Cahill (1993) Theoretical and experimental analysis of magnetic field gradients for MRI from IEEE Explore.
- ^ Clerk-Maxwell, James (1873). Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism. Vol. 2. Oxford: The Clarendon Press. p. 333. ISBN 978-0-486-60636-1.