The Lausberg area is a part of southern Italy, covering much of Basilicata and the northern edge of Calabria, where Southern Italian dialects are spoken that show vowel developments atypical of Italo-Romance. The area is named after Heinrich Lausberg, who brought it to the attention of scholarship in 1939.[1]
Stressed vowel outcomes
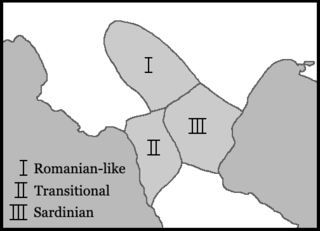
editThere are three main subdivisions, as can be seen on the map to the right.
Romanian-like
editDubbed the Vorposten (“outpost”) by Lausberg, this area encompasses the towns of Castelmezzano, Potenza, and Picerno. Here the Latin vowel /i/ merged with /eː/, while /u/ merged with /uː/. The same asymmetric vowel development characterizes Balkan Romance languages such as Romanian.[1]
Transitional
editThe western part of Lausberg's Mittelzone (“central area”) encompasses the towns of Lauria, Maratea, Scalea, Diamante, and Verbicaro. Here the majority of words show a stressed vowel development similar to that of Sicilian, although many words show Sardinian-like outcomes as well.[2]
Sardinian-like
editThe eastern part of the Mittelzone encompasses the towns of Senise, Tursi, and Oriolo. Here the tonic vowels developed approximately as in Sardinian. There is evidence, however, of an earlier distinction between Latin /eː oː/ and /e o/. In the variety spoken in Senise, for instance, the outcomes of Latin /e/ and /o/ were subject to diphthongization when stressed and followed by a syllable containing a close vowel (namely /i/ or /u/), while the outcomes of /eː/ and /oː/ were not. Cf. Latin /fokum, nepoːteːs/ > */ˈfɔku, neˈpoti/ > [ˈfwokə, nəˈpʊtə].[3]
Selected lexical comparisons
editBelow are the (non-metaphonic) stressed vowel outcomes in the three regions,[2] each represented here by one dialect.
| Latin | ˈfiːlum | ˈniwem | ˈteːlam | ˈpedem | ˈpaːnem | ˈkanem | ˈkor | ˈsoːlem | ˈkrukem | ˈluːnam |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Castelmezzano | ˈfilə | ˈnevə ˈtela ˈperə | ˈpanə ˈkanə | ˈkorə ˈsolə | ˈkrutʃə ˈlunə | |||||
| Verbicaro | ˈfɪlə ˈnɪva ˈtɪla | ˈpɛtra | ˈpanə ˈkanə | ˈkɔrə | ˈsʊlə ˈkrʊtʃa ˈlʊna | |||||
| Senise | ˈfilə ˈnivə | ˈtɛlə ˈpɛrə | ˈpanə ˈkanə | ˈkɔrə ˈsɔlə | ˈkrutʃə ˈlunə | |||||
| English | thread | snow | canvas | foot | bread | dog | heart | sun | cross | moon |
Here is a comparison of the present indicative conjugations of the verb meaning “to die” in the Mittelzone.[4] Asterisks indicate forms that induce syntactic doubling.
| San Chirico | Aliano | Castelluccio | Noepoli | Amendolara | Papasidero | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1SG | ˈmɔrə | ˈmɔrəjə | ˈmɔrəkə | ˈmɔrə~ˈmuərə | ˈmɔrrə | ˈmɔru |
| 2SG | ˈmwerəsə | ˈmɔrəsə | ˈmuːrəsə | ˈmuərəsə | ˈmuːrəsə | ˈmuːrisi |
| 3SG | ˈmwerətə | ˈmɔrətə | ˈmurə* | ˈmuərədə | ˈmuːrədə | ˈmuri* |
| 1PL | muˈriəmə | muˈrɛmə | muˈrimə | muˈriəmə | muˈrimə | muˈrimu |
| 2PL | muˈriəsə | muˈrɛsə | muˈrisə | muˈriətəsə | muˈritəsə | muˈrisi |
| 3PL | ˈmɔrənə | ˈmɔrənə | ˈmɔrənə | ˈmɔrənə | ˈmuːrənə | ˈmɔrunu |
Notes
editReferences
edit- ^ a b Loporcaro 2011, p. 114
- ^ a b Ledgeway 2016, p. 248
- ^ Loporcaro 2011, p. 113
- ^ Trumper 1997, p. 362
Bibliography
edit- Lausberg, Heinrich (1939). Die mundarten Südlukaniens (in German). Halle: Niemeyer.
- Loporcaro, Michele (2011). "Phonological processes". In Maiden, Martin; Smith, John Charles; Ledgeway, Adam (eds.). The Cambridge history of the Romance languages. Vol. 1. Cambridge University Press. pp. 109–154.
- Ledgeway, Adam (2016). "The dialects of southern Italy". In Ledgeway, Adam; Maiden, Martin (eds.). The Oxford guide to the Romance languages. Oxford University Press. pp. 246–269.
- Trumper, John (1997). "Calabria and southern Basilicata". In Maiden, Martin; Parry, Mair (eds.). The dialects of Italy. London: Routledge. pp. 355–364.