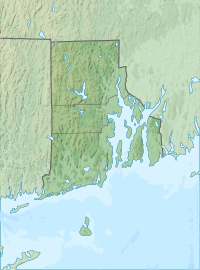
Jerimoth Hill (812 ft, 247 m) is the highest point in the U.S. state of Rhode Island. It is the lowest state highpoint in New England. Located in the town of Foster in the northwest of the state, the site is used as an observatory. It is also a popular destination for highpointers, and prior to 2005 was known for being difficult to access due to a local landowner who prohibited entry.
| Jerimoth Hill | |
|---|---|
 Jerimoth Hill Summit | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 811 ft (247 m) NGVD 29[1] |
| Prominence | 192 ft (59 m)[1] |
| Listing | U.S. state high point 46th |
| Coordinates | 41°50′58″N 71°46′43″W / 41.8495431°N 71.778681°W[2] |
| Geography | |
| Location | Foster, Rhode Island, US |
| Topo map(s) | USGS East Killingly, CT |
| Climbing | |
| Easiest route | Highway (RI 101) |
Location
editThe hill is located on Route 101 in Foster, a half mile from the Connecticut line. To ascend the summit, for which there is a sign, there is a .3-mile (480 m) long trail that has a mere 10-foot (3.0 m) elevation gain. The hill is 812 feet (247 m) high and is located 15 miles (24 km) west of Providence, Rhode Island, and 35 miles (56 km) east of Willimantic, Connecticut.
History
editThe hill was named after Jerimoth Brown (1783–1830), an early settler.[3]
The high point was donated to Brown University by Walter Raymond Turner, a Brown alumnus of the class of 1911. In 1938, he purchased the saltbox house to the west and the surrounding 360 acres (150 ha). Turner provided a right of way, straight north from the high point to Route 101, though eventually, it became overgrown.
Brown University has used Jerimoth Hill as an astronomy observatory location for decades, because the university has easy access to this land-locked parcel where they have a view of the skies without light pollution from Providence. The high ground has been cleared of pine trees over an area of about 200 square feet (19 m2). The high point is a rocky outcrop in the woods on the northwest edge of the clearing. A summit register is located in a mailbox for visitors to sign.[4]
As the highest point in Rhode Island, Jerimoth Hill is a destination for highpointers—hikers who try to reach the highest peak in various areas. For many years, hikers could not access the hill, because the only path to the summit crossed the driveway of a private property owner, Henry Richardson, who prohibited entry.[5] Richardson posted "no trespassing" signs and installed a security system that alerted him whenever people entered his property. Richardson's attitude toward hikers made him something of a legend in the community. Eventually, Richardson's son worked out a plan to allow access to the path four times a year.[5] After Richardson's death, his property was purchased in 2005 by the Mosley family, who permitted daily access and eventually ceded the land to the state. In 2014, Brown sold the summit itself to the state, though the university reserves the right to build an observatory there in the future.[6][4]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ a b "Jerimoth Hill, Rhode Island". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 2010-04-08.
- ^ "Jerimoth Hill". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved 2010-04-05.
- ^ Book Notes: Consisting of Literary Gossip, Criticisms of Books and Local Historical Matters Connected with Rhode Island. S. S. Rider. 1906. p. 150.
- ^ a b "Jerimoth Hill: Climbing, Hiking & Mountaineering". SummitPost. 21 October 2014. Retrieved 2016-09-18.
- ^ a b O'Neill, Helen (September 28, 2000). "Why R.I.'s Jerimoth Hill Is Nation's Toughest Summit". Albuquerque Journal. Associated Press. Archived from the original on February 15, 2019. Retrieved February 14, 2019.
- ^ Naylor, Donita (2014-10-20). "You, too, can make it to the top in R.I.: Jerimoth Hill access to open". Providence Journal. Retrieved 2016-09-18.
- Glickman, Joe (text); Akerlund, Nels (photography) (2003). To the Top: Reaching for America's 50 State Summits. Chanhassen, Minn.: NorthWord Press. ISBN 9781559718714. OCLC 990532182.
,