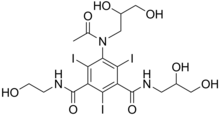
Ioxilan is a diagnostic contrast agent.[1] It is injected intravenously before taking X-ray images to increase arterial contrast in the final image. It was marketed in the US under the trade name Oxilan by Guerbet, L.L.C., but was discontinued in 2017.[2]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Oxilan |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | FDA Professional Drug Information |
| Routes of administration | intravenously |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | N/A |
| Protein binding | negligible |
| Metabolism | none |
| Elimination half-life | 2 hours |
| Excretion | Mostly renal |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H24I3N3O8 |
| Molar mass | 791.116 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Mechanism of action
editIoxilan is an iodinated contrast agent.[2]
References
edit- ^ Cheng KT (December 2007). "Ioxilan carbonate particles". Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). PMID 20641969.
- ^ a b Oxilan FDA Professional Drug Information. Accessed 2021-04-07.