The intercostal space (ICS) is the anatomic space between two ribs (Lat. costa). Since there are 12 ribs on each side, there are 11 intercostal spaces, each numbered for the rib superior to it.[1]
| Intercostal space | |
|---|---|
 Intercostal spaces, viewed from the right. | |
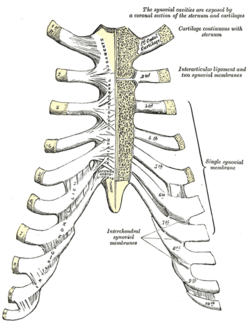 Sternocostal and interchondral articulations. Anterior view. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | spatium intercostale |
| TA98 | A02.3.04.007 |
| TA2 | 1102 |
| FMA | 12243 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Structures in intercostal space
edit- several kinds of intercostal muscle
- intercostal arteries and intercostal veins
- intercostal lymph nodes
- intercostal nerves
Order of components
editMuscles
editThere are 3 muscular layers in each intercostal space, consisting of the external intercostal muscle, the internal intercostal muscle, and the thinner innermost intercostal muscle.[2][3] These muscles help to move the ribs during breathing.[4]
Neurovascular bundles
editNeurovascular bundles are located between the internal intercostal muscle and the innermost intercostal muscle.[3] The neurovascular bundle has a strict order of vein-artery-nerve (VAN), from top to bottom.[2] This neurovascular bundle runs high in the intercostal space, and the smaller collateral neurovascular bundle runs just superior to the lower rib of the space (in the order NAV from superior to inferior). Invasive procedures such as thoracentesis are performed with oblique entry of the instrument, directly above the upper margin of the relevant rib, to avoid damaging the neurovascular bundles.[2]
Nerves
editIn reference to the muscles of the thoracic wall, the intercostal nerves and vessels run posterior to the internal intercostal muscles: therefore, they are generally covered on the inside by the parietal pleura, except when they are covered by the innermost intercostal muscles, innermost intercostal membrane, subcostal muscles or the transversus thoracis muscle.
References
edit- ^ Troyer, A. D., Kelly, S., Macklem, P. T., & Zin, W. A. (1985). Mechanics of intercostal space and actions of external and internal intercostal muscles. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 75(3), 850-857. doi:10.1172/jci111782
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Jacob, S. (January 1, 2008), Jacob, S. (ed.), "Chapter 3 - Thorax", Human Anatomy, Churchill Livingstone, pp. 51–70, doi:10.1016/b978-0-443-10373-5.50006-3, ISBN 978-0-443-10373-5, retrieved November 16, 2020
- ^ Jump up to: a b Rakovich, George; Fréchette, Éric; Deslauriers, Jean (January 1, 2010), Lewis, Michael I.; McKenna, Robert J.; Falk, Jeremy A.; Chaux, George E. (eds.), "8 - Thoracic Surgical Anatomy and Procedures", Medical Management of the Thoracic Surgery Patient, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 95–105, doi:10.1016/b978-1-4160-3993-8.00008-8, ISBN 978-1-4160-3993-8, retrieved November 16, 2020
- ^ Watkins, James; Mathieson, Ian (January 1, 2009), Watkins, James; Mathieson, Ian (eds.), "CHAPTER 3 - The skeleton", The Pocket Podiatry Guide: Functional Anatomy, Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, pp. 67–105, doi:10.1016/b978-0-7020-3032-1.00003-2, ISBN 978-0-7020-3032-1, retrieved November 16, 2020
External links
edit- Anatomy figure: 18:04-00 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Structural organization within an intercostal space."
- Anatomy photo:18:01-0108 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Thoracic Wall: The Anterior Thoracic Wall"