This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
The inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) (also the inferior dental nerve) is a sensory[1][contradictory] branch of the mandibular nerve (CN V3) (which is itself the third branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V)). The nerve provides sensory innervation to the lower/mandibular teeth and their corresponding gingiva as well as a small area of the face (via its mental nerve).
| Inferior alveolar nerve | |
|---|---|
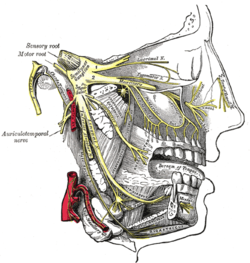 Distribution of the maxillary and mandibular nerves, and the submaxillary ganglion. (Inferior alveolar visible at center left.) | |
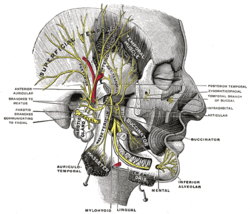 Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve. (Inferior alveolar labeled at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| From | Mandibular nerve |
| To | Mylohyoid, dental, incisive, and mental |
| Innervates | Dental alveolus |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus alveolaris inferior |
| TA98 | A14.2.01.089 |
| TA2 | 6274 |
| FMA | 53243 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
Structure
editOrigin
editThe inferior alveolar nerve arises from the mandibular nerve.[2]: 543
Course
editAfter branching from the mandibular nerve, the inferior alveolar nerve passes posterior to the lateral pterygoid muscle. It issues a branch (the mylohyoid nerve)[contradictory] before entering the mandibular foramen[2]: 543 to come to pass in the mandibular canal within the mandible. Passing through the canal, it issues sensory branches for the molar and second premolar teeth; the branches first form the inferior dental plexus which then gives off small gingival and dental nerves to these teeth themselves.[3]
The nerve terminates distally/anteriorly (near the second lower premolar)[citation needed] within the mandibular canal by splitting into its two terminal branches: the mental nerve, and the incisive branch.[1]
Branches
editMental nerve
editThe mental nerve emerges from the mandibular canal through the mental foramen[1] and provides sensory innervation to the chin and lower lip.[citation needed]
Incisive branch
editThe incisive branch represents the anterior continuation of the inferior alveolar nerve.[citation needed] It continues to course within the mandible in the mandibular incisive canal either as a single nerve or by forming the incisive plexus. It provides sensory innervation to the lower/mandibular premolar, canine, incisor teeth as well as their associated gingiva.[1]
Distribution
editThe inferior alveolar nerves supply sensation to the lower teeth,[2]: 519 and, via the mental nerve, sensation to the chin and lower lip.[citation needed]
The mylohyoid nerve is a motor nerve supplying the mylohyoid and the anterior belly of the digastric.[citation needed][contradictory]
Variation
editRarely, a bifid inferior alveolar nerve may be present, in which case a second mandibular foramen, more inferiorly placed, exists and can be detected by noting a doubled mandibular canal on a radiograph.[4]
Clinical significance
editInjury
editInferior nerve injury most commonly occurs during surgery including wisdom tooth, dental implant placement in the mandible, root canal treatment where tooth roots are close to the nerve canal in the mandible, deep dental local anaesthetic injections or orthognathic surgery. Trauma and related mandibular fractures are also often related to inferior alveolar nerve injuries.
Trigeminal sensory nerve injuries are associated with numbness, pain, altered sensation and usually a combination of all three.[5] This can result in a significant reduction in quality of life with functional difficulties and psychological impact.[6]
The risk associated with wisdom tooth surgery is commonly accepted to be 2% temporary and 0.2% permanent. However, this risk assessment is not concrete as the same source[citation needed] is cited for lingual nerve paresthesia. It is well documented that inferior alveolar nerve injury is more common than lingual nerve injury.[citation needed] The percentage of injury varies significantly in different studies. Furthermore, many factors affect the incidence of nerve injury. For example, the incidence of nerve injury in teens removing third molars is much lower than the incidence in patients 25 and older.[7] This risk increases 10 fold if the tooth is close to the inferior dental canal containing the inferior alveolar nerve (as judged on a dental radiograph).[8] These high risk wisdom teeth can be further assessed using cone beam CT imaging to assess and plan surgery to minimise nerve injury by careful extraction or undertaking a coronectomy procedure in healthy patients with healthy teeth.[9]
The risk of nerve injury in relation to mandibular dental implants is not known but it is a recognised risk requiring the patient to be warned.[10] If an injury occurs urgent treatment is required. The risk nerve injury in relation deep dental injections has a risk of injury in approximately 1:14,000 with 25% of these remaining persistent.[citation needed] Routine preoperative warnings about these injuries should occur before surgery, and represent good practice.[11][12] Inferior alveolar nerve injury secondary to orthodontic treatment is also emerging in the literature in the recent years as a rare complication and manifested as anesthesia, paresthesia, or combination of both; however full recovery was achieved in all of the reported cases when proper management was applied. [13]
Anesthesia
editDuring dental procedures, a local nerve block may be applied. Anaesthetic injected near the mandibular foramen to block the inferior alveolar nerve and the nearby lingual nerve (supplying the tongue). This causes loss of sensation on the same side as the block to:
- the teeth (inferior alveolar nerve block)
- the lower lip and chin (mental nerve block)
- front two-thirds of the tongue (lingual nerve block).
Studies found that oral medications of NSAIDs taken before the dental procedure increases the efficacy of the anesthesia in patients with irreversible pulpitis.[14]
See also
editAdditional images
edit-
Mandible of human embryo 95 mm long. Inner aspect. Nuclei of cartilage stippled.
-
Mandibular division of trifacial nerve, seen from the middle line.
-
Inferior alveolar nerve
-
Mandibular nerve and bone. Deep dissection. Anterior view.
-
Infratemporal fossa. Lingual and inferior alveolar nerve. Deep dissection. Anterolateral view
References
edit- ^ a b c d Caughey, Jennifer A.; Do, Quang; Shen, Daniel; Ohyama, Hiroe; He, Puhan; Tubbs, R. Shane; Iwanaga, Joe (2021-12-31). "Comprehensive review of the incisive branch of the inferior alveolar nerve". Anatomy & Cell Biology. 54 (4): 409–416. doi:10.5115/acb.21.113. ISSN 2093-3665. PMC 8693131. PMID 34620736. S2CID 238474299.
- ^ a b c Standring S, Borley NR, et al., eds. (2008). Gray's Anatomy (40th ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-8089-2371-8.
- ^ Wolf KT, Brokaw EJ, Bell A, Joy A (2016-06-01). "Variant Inferior Alveolar Nerves and Implications for Local Anesthesia". Anesthesia Progress. 63 (2): 84–90. doi:10.2344/0003-3006-63.2.84. PMC 4896047. PMID 27269666.
- ^ Fehrenbach MJ, Herring SW (2011). Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck (4th ed.). Philadelphia, PA: Saunders. p. 59.
- ^ Renton T, Yilmaz Z (2011). "Profiling of patients presenting with posttraumatic neuropathy of the trigeminal nerve". Journal of Orofacial Pain. 25 (4): 333–344. PMID 22247929.
- ^ Smith JG, Elias LA, Yilmaz Z, Barker S, Shah K, Shah S, Renton T (2013). "The psychosocial and affective burden of posttraumatic neuropathy following injuries to the trigeminal nerve". Journal of Orofacial Pain. 27 (4): 293–303. doi:10.11607/jop.1056. PMID 24171179.
- ^ "Recovering from Surgery". Royal College of Surgeons.
- ^ Selvi F, Dodson TB, Nattestad A, Robertson K, Tolstunov L (December 2013). "Factors that are associated with injury to the inferior alveolar nerve in high-risk patients after removal of third molars". The British Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery. 51 (8): 868–873. doi:10.1016/j.bjoms.2013.08.007. PMID 24012054.
- ^ Long H, Zhou Y, Liao L, Pyakurel U, Wang Y, Lai W (July 2012). "Coronectomy vs. total removal for third molar extraction: a systematic review". Journal of Dental Research. 91 (7): 659–665. doi:10.1177/0022034512449346. PMID 22622663. S2CID 21579439.
- ^ Renton T, Dawood A, Shah A, Searson L, Yilmaz Z (June 2012). "Post-implant neuropathy of the trigeminal nerve. A case series". British Dental Journal. 212 (11): E17. doi:10.1038/sj.bdj.2012.497. PMID 22677874. S2CID 21328385.
- ^ "Nerve Damage Associated with Peripheral Nerve Block" (PDF). Information for patients. The Royal College of Anaesthetists. 2013. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-04-16. Retrieved 2014-04-15.
- ^ Tidy G (27 February 2018). Bonsall A (ed.). "Anaesthesia (UK) - Local and General anaesthesia information". Patient. Egton Medical Information Systems Limited.
- ^ AlAli, Ahmad M.; AlAnzi, Talal H. (2021-01-01). "Inferior alveolar nerve damage secondary to orthodontic treatment: A systematic scoping review". International Journal of Risk & Safety in Medicine. 32 (3): 175–191. doi:10.3233/JRS-200098. ISSN 0924-6479. PMID 33579879. S2CID 231910002.
- ^ Shantiaee Y, Javaheri S, Movahhedian A, Eslami S, Dianat O (April 2017). "Efficacy of preoperative ibuprofen and meloxicam on the success rate of inferior alveolar nerve block for teeth with irreversible pulpitis". International Dental Journal. 67 (2): 85–90. doi:10.1111/idj.12272. PMC 9376692. PMID 27933616.
External links
edit- Anatomy figure: 27:03-06 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb3.htm
- lesson4 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (mandibularnerve)
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)