The house finch (Haemorhous mexicanus) is a North American bird in the finch family. It is native to Mexico and southwestern United States, but has since been introduced to the eastern part of North America and Hawaii; it is now found year-round in all parts of the United States and most of Mexico, with some residing near the border of Canada. There are estimated to be 40 million house finches across North America, making it the second-most populous finch, just behind the American goldfinch. The house finch and the other two American rosefinches (Cassin's and purple finch) are placed in the genus Haemorhous.
| House finch | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Fringillidae |
| Subfamily: | Carduelinae |
| Genus: | Haemorhous |
| Species: | H. mexicanus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Haemorhous mexicanus (Müller, 1776)
| |
| |
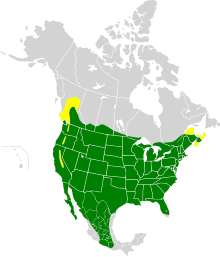
| Range of H. mexicanus Breeding range Year-round range
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Description
editThe house finch is a moderate-sized finch, 12.5 to 15 cm (5 to 6 in) long, with a wingspan of 20 to 25 cm (8 to 10 in). Body mass can vary from 16 to 27 g (9⁄16 to 15⁄16 oz), with an average weight of 21 g (3⁄4 oz). Among standard measurements, the wing chord is 7 to 8.4 cm (2+3⁄4 to 3+1⁄4 in), the tail is 5.7 to 6.5 cm (2+1⁄4 to 2+1⁄2 in), the culmen is 0.9 to 1.1 cm (3⁄8 to 7⁄16 in) and the tarsus is 1.6 to 1.8 cm (5⁄8 to 11⁄16 in).[2]
Adults have a long, square-tipped brown tail and are a brown or dull-brown color across the back with some shading into deep gray on the wing feathers. Breast and belly feathers may be streaked; the flanks usually are. In most cases, adult males' heads, necks and shoulders are reddish.[3][4] This color sometimes extends to the belly and down the back, between the wings. Male coloration varies in intensity with the seasons[5] and is derived from the berries and fruits in its diet.[6] As a result, the colors range from pale straw-yellow through bright orange (both rare) to deep, intense red. Adult females have brown upperparts and streaked underparts.
The house finch's songs typically consist of a series of high-pitched musical jumbles ending with a distinct high note, wheer. Calls from flight include a soft cheet or wheat, with perched birds giving a more drawn-out version.[2][7]
-
Adult male
-
Adult female
-
Yellow variant
Distribution and habitat
editHouse finches are mainly permanent residents throughout their range, some birds migrate to the south, with adult females moving longer distances than males.[8][2] Their breeding habitat is urban and suburban areas across North America, as well as various semi-open areas in the west from southern Canada to the Mexican state of Oaxaca; the population in central Chiapas may be descended from escaped cagebirds.[4] Analyses of nest records from house finches in California spanning more than a century found that egg‐laying occurred significantly earlier in warmer springs.[9]
Originally only a resident of Mexico and the southwestern United States, house finches were introduced to eastern North America in the 1940s. The birds were sold illegally in New York City[6] as "Hollywood finches", a marketing artifice.[5] To avoid prosecution under the Migratory Bird Treaty Act of 1918, vendors and owners released the birds. They have since become naturalized; in largely unforested land across the eastern U.S. they have displaced the native purple finch and even the non-native house sparrow.[10] Sometime in the 19th century, they were introduced to Hawaii and are now abundant on all its major islands.[11]
According to the Partners in Flight database, there are estimated to be 40 million house finches across North America.[12]
Instances of naturalization originating in escapes or releases of cage birds have been recorded in Europe, such as in 2020 in Murcia, (Spain).[13]
Feeding
editHouse finches forage on the ground or in vegetation normally. They primarily eat grains, seeds and berries, being voracious consumers of weed seeds such as nettle and dandelion;[14] included are incidental small insects such as aphids. They are frequent visitors to bird feeders throughout the year, particularly if stocked with sunflower or nyjer seed, and will congregate at hanging nyjer sock feeders. The house finch is known to damage orchard fruit and consume commercially grown grain, but is generally considered an annoyance rather than a significant pest.[15]
Breeding
editNests are made in cavities, including openings in buildings, hanging plants, and other cup-shaped outdoor decorations. Sometimes nests abandoned by other birds are used. Nests may be re-used for subsequent broods or in following years. The nest is built by the female, sometimes in as little as two days.[16] It is well made of twigs and debris, forming a cup shape, usually 1.8 to 2.7 m (5 ft 11 in to 8 ft 10 in) above the ground.[16]
During courtship, the male will touch bills with the female. He may then present the female with choice bits of food, and if she mimics the behavior of a hungry chick, he may feed her. The male also feeds the female during breeding and incubation of the eggs, and raising of the young,[17] and the male is the primary feeder of the fledglings (who can be differentiated from the females by the pin feathers remaining on their heads). Females are typically attracted to the males with the deepest pigment of red to their head, more so than the occasional orange or yellowish-headed males that sometimes occur.[6]
The female lays clutches of eggs from February through August, two or more broods per year with 2 to 6 eggs per brood, most commonly 4 or 5. The egg laying usually takes place in the morning, at one egg per day.[17] The eggs are pale bluish-green with few black spots and a smooth, somewhat glossy surface. In response to mite infestation, which has a more deleterious effect on male chicks than on females, the mother finch may lay eggs containing females first, to reduce the length of time male chicks are exposed to mites. This strategy increases the likelihood that representative numbers of both sexes will survive.[18] The female incubates the eggs for 12 to 14 days. Shortly after hatching, she removes the empty eggshells from the nest.[19][20] The hatchlings are pink with closed eyes and tufts of fluffy down.[21] The female always feeds the young. The male usually joins in.[17] The young are silent for the first seven or eight days, and subsequently start peeping during feedings.[16] Initially, the mother carries fecal sacs out of the nest, but when the young become older, she no longer carries them all away, allowing droppings to accumulate around the edge of the nest.[16] Before flying, the young often climb into adjacent plants and usually fledge at about 11 to 19 days after hatching.[16] Dandelion seeds are among the preferred seeds for the young.[19] Contrary to the way most birds, even ones with herbivorous leanings as adults, tend to feed their nestlings animal matter to give them the protein necessary to grow, house finches are one of the few birds who feed their young only plant matter.[6]
House finches are aggressive enough to drive other birds away from places such as feeders.[22]
-
Male house finch feeding a female as part of the courtship ritual
-
Nest and eggs
-
Same nest with young nestlings
-
Older nestlings in nest in a tree cholla
-
Male house finch feeds a fledgling, who cheeps loudly and flaps its wings.
Threats
editThe house finch may be infected by several parasites including Plasmodium relictum[23] and Mycoplasma gallisepticum, which caused the population of house finches in eastern North America to crash during the 1990s.[24]
The mite Pellonyssus reedi is often found on house finch nestlings, particularly for nests later in the season.[25]
The brown-headed cowbird, a brood parasite, will lay its eggs in house finch nests, although the diet house finches feed their young is inadequate for the young cowbirds, which rarely survive.[26]
In 2012, house finches positive for West Nile virus were found in northwestern Riverside County, CA.[27]
References
edit- ^ BirdLife International (2018). "Haemorhous mexicanus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2018: e.T22720563A132001810. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2018-2.RLTS.T22720563A132001810.en. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ^ a b c Clement, Peter; Harris, Alan; Davis, John (1993). Finches and Sparrows: an Identification Guide. Princeton, New Jersey: Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-03424-9.
- ^ Sibley, David (2000). The Sibley Guide to Birds. Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 978-0-679-45122-8.
- ^ a b Howell, Steve N. G.; Webb, Sophie (1995). A Guide to the Birds of Mexico and Northern Central America. Oxford University Press. pp. 757–758. ISBN 978-0-19-854012-0.
- ^ a b Caldwell, Eldon R. "IV Birds – House Finch". Archived from the original on September 29, 2007. Retrieved April 19, 2008.
- ^ a b c d "House Finch". All About Birds. Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology. Retrieved April 19, 2008.
- ^ Dunn, Jon L.; Alderfer, Jonathan K.; Lehman, Paul E., eds. (2008). National Geographic field guide to the birds of eastern North America. Washington, D.C.: National Geographic. ISBN 978-1-4262-0330-5. OCLC 183926577.
- ^ Belthoff, James R.; Gauthreaux, Sidney A. (1991). "Partial Migration and Differential Winter Distribution of House Finches in the Eastern United States" (PDF). The Condor. 93 (2): 374–382. doi:10.2307/1368953. JSTOR 1368953.
- ^ Watts, Heather E.; Jimenez, Daniela; Pacheco, Veronica; Vilgalys, Tauras P. (2019). "Temperature-correlated shifts in the timing of egg-laying in house finches Haemorhous mexicanus". Ibis. 161 (2): 428–434. doi:10.1111/ibi.12676. ISSN 1474-919X.
- ^ Wootton, JT. (1987). "Interspecific Competition between Introduced House Finch Populations and Two Associated Passerine Species". Oecologia. 71 (3): 325–331. Bibcode:1987Oecol..71..325W. doi:10.1007/BF00378703. PMID 28312977. S2CID 24504742.
- ^ Caum, E.L. (1933). "The exotic birds of Hawaii". Bishop Museum Occasional Papers. 10 (9). Bernice P. Bishop Museum.
- ^ "Population Estimates – Partners in Flight Databases". Retrieved 2024-04-05.
- ^ "Alertan de la reproducción del ave exótica camachuelo mejicano en Murcia". EfeVerde (in Spanish). 30 January 2020.
- ^ "House Finch | Audubon Field Guide". Audubon. Retrieved 2024-04-20.
- ^ Montana state government. "House finch detailed information". Archived from the original on 2009-12-20. Retrieved 2007-08-14.
- ^ a b c d e Evanden, Fred G. (1957). "Observations on Nesting Behavior of the House Finch" (PDF). The Condor. 59 (2). University of California Press/Cooper Ornithological Society: 112–117. doi:10.2307/1364571. JSTOR 1364571. Retrieved June 28, 2008.
- ^ a b c Thompson, William L (1960). "Agonistic Behavior in the House Finch. Part I: Annual Cycle and Display Patterns" (PDF). The Condor. 62 (4). University of California Press, Cooper Ornithological Society: 245–271. doi:10.2307/1365516. JSTOR 1365516. Retrieved June 28, 2008.
- ^ Badyaev, Alexander V.; Hamstra, Terri L.; Oh, Kevin P.; Acevedo Seaman, Dana A. (September 26, 2006). "Sex-biased maternal effects reduce ectoparasite-induced mortality in a passerine bird". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 103 (39). National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America: 14406–11. Bibcode:2006PNAS..10314406B. doi:10.1073/pnas.0602452103. PMC 1599976. PMID 16983088.
- ^ a b Bergtold, W.H. (1913). "A Study of the House Finch" (PDF). The Auk. Retrieved May 23, 2008.
- ^ Woods, Robert S. (1968). "Life Histories of Familiar North American Birds: House Finch". Smithsonian Institution United States National Museum Bulletin (237): 290–314.
- ^ "House Finch Nest Survey" (PDF). Cornell Laboratory of Ornithology.
- ^ "Backyard Birds of Winter in Nova Scotia". Museum.gov.ns.ca. Retrieved August 18, 2009.
- ^ Hartup, Barry K.; Oberc, A.; Stott-Messick, B.; Davis, A. K.; Swarthout, E. C. (April 2008). "Blood Parasites of House Finches (Carpodacus mexicanus) from Georgia and New York" (PDF). Journal of Wildlife Diseases. 44 (2): 469–74. doi:10.7589/0090-3558-44.2.469. PMID 18436682. S2CID 34120031.
- ^ Nolan, Paul M.; Hill, Geoffrey E.; Stoehr, Andrew M. (7 June 1998). "Sex, Size, and Plumage Redness Predict House Finch Survival in an Epidemic". Proceedings: Biological Sciences. 265 (1400). The Royal Society: 961–965. doi:10.1098/rspb.1998.0384. PMC 1689154.
- ^ Stoehr, Andrew M.; Nolan, Paul M.; Hill, Geoffrey E.; McGraw, Kevin J. (2000). "Nest mites (Pellonyssus reedi) and the reproductive biology of the house finch (Carpodacus mexicanus)" (PDF). Canadian Journal of Zoology. 78 (12): 2126–2133. doi:10.1139/b98-207.
- ^ Kozlovic, Daniel R.; Knapton, Richard W.; Barlow, Jon C. (1996). "Unsuitability of the House Finch as a Host of the Brown-Headed Cowbird" (PDF). The Condor. 96 (2): 253–258. doi:10.2307/1369143. JSTOR 1369143.
- ^ Williams, G., B. Van Dyke, B. Haynes, T. Hallum, N. McConnell, J. Allred, R. Reneau, V. Strode, L.S. Mian and M.S. Dhillon. 2013. Mosquito and West Nile Virus Surveillance at Northwest Mosquito and Vector Control District during 2012. Proc. Calif. Mosq. Vector Control Assoc. 81:147-153.
External links
edit- Florida's Introduced Birds: House Finch (Carpodacus mexicanus) Archived 2010-10-07 at the Wayback Machine – University of Florida fact sheet
- House Finch - Carpodacus mexicanus - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- House Finch Sound Archived 2011-05-15 at the Wayback Machine
- "House Finch media". Internet Bird Collection.
- "House Finch Bird Sound". Florida Museum of Natural History. 27 April 2017. from Hardy, J. W. (1998), Sounds of Florida's Birds
- House Finch photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
