Grand-Îlet (officially in French: Grand-Îlet des Saintes) is an island in the Îles des Saintes archipelago, in the Lesser Antilles. It belongs to the commune (municipality) of Terre-de-Haut into the French department of Guadeloupe.
 View of Grand-Îlet from Terre-de-Haut Island | |
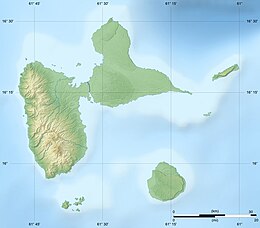
 Grand-Îlet lies to the south of Terre-de-Haut Island | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Caribbean Sea |
| Coordinates | 15°50′15″N 61°35′30″W / 15.83750°N 61.59167°W |
| Archipelago | Îles des Saintes |
| Area | 0.84 km2 (0.32 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 165 m (541 ft) |
| Highest point | Morne Grosse Pointe |
| Administration | |
France | |
| Overseas department | Guadeloupe |
| Canton | Trois-Rivières |
| commune | Terre-de-Haut |
| Mayor | Louis Molinié |
| Demographics | |
| Population | uninhabited |
| Additional information | |
| Natural Reserve of Conservatoire du littoral.[1] Catégorie IV IUCN.[2] | |
Geography
editGrand-Îlet is located, 1,200 m (0.75 mi) south of Terre-de-Haut Island.
Of triangular shape, It ends by three headlands: Grosse Pointe in the east is an abrupt cliff which plunges into Dominica Passage, Basse Pointe in the north of the island overlooking la Redonde, in front of which is located a series of sharpened rocks called les Quilles and Pointe des Colibris on the west, forming with the eastern headland of la Coche, the dangerous passage called Passe des Dames. The island is about 900 m (0.56 mi) from east to west and 1,200 m (0.75 mi) from north to south. The official size is 84 hectares (although some mistakes appear with a calculated 48 hectares) . Its highest mount, Morne Grosse Pointe hill culminates at 165 m (540 ft). It contain two coves: Anse du Grand Etang, a rocky inlet characterized by its large pond and Anse des Colibris, on the west side of the island.
Grand-Îlet Passage is formed by Basse Pointe headland and la Redonde.[3]
Fauna
editThe island is frequented by sea turtles, which come to reproduce there, but it is the home of the seabirds: magnificent frigatebird (Fregata magnificens), brown booby, masked booby, terns, double-crested cormorant (Phalacrocorax auritus), pelican, petrels nest on the cliff of the island. Red-footed booby (Sula sula) and blue-footed booby (Sula nebouxii) are only observable on Grand-Îlet, among the islands of Guadeloupe department. The waste of these birds results in a strong concentration of guano on the rocks and beaches.
The beaches of the island are rich in crabs, in particular the blue land crabs, the blackback land crabs and the sand fiddler crab.
The wading birds of Lesser Antilles live in the large pond of the island.
Natural reserve and diving
editSince 1994,[4] the island is the property of Conservatoire du littoral and is placed under the protection of the agency even if the municipality of Terre-de-Haut and the National Forests Office of Guadeloupe stay the administrators. It is a space protected and classified category IV IUCN.[5]
The xerophile forest of all the islands of the archipelago of les Saintes is also protected, in particular woodlands of Eugenia axillaris, an important species among the Lesser Antilles.
Grand Îlet is included in the area of the natural reserve of the islands of les Saintes.[6] It is a remarkable site of submarine observation, due to the presence of a diving sec in full swell. It is a submarine mountain which the base is at less 25 m (82 ft) and the top at less 5 m (16 ft) below sea level. The place abounds in an incredible variety of sponges, gorgonians, corals and fishes of the Antilles, attracting the divers.[7]
Notes and references
edit- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-10. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-10. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Monographie sur les Saintes (Dépendance de la Guadeloupe) / Sauzeau de Puyberneau. 1901.
- ^ "Conservatoire du littoral". Archived from the original on 2012-04-15. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2012-03-10. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Conservatoire du littoral". Archived from the original on 2012-04-15. Retrieved 2011-12-17.
- ^ "Sec Grand Ilet - Fonds sous-marins - les Saintes".
- Conservatoire du littoral (2010), Dacota (ed.), La Guadeloupe entre terre et mer
- Sylvestre, Richard (2010), Association génération découverte avec la participation du Parc national et la Région Guadeloupe (ed.), Sept trésors des Antilles, vol. tome 1