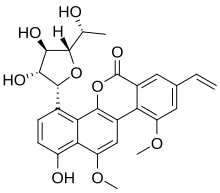
Gilvocarcin V is an antitumor agent and an antibiotic which is active against Gram-positive bacteria with the molecular formula C27H26O9.[3][4] Gilvocarcin V is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces griseoflavus and other Streptomyces bacteria.[3][4][1][5][6] Gilvocarcin V is a strong inhibitor of the DNA synthesis.[6]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-[3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(1-hydroxyethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-8-ethenyl-1-hydroxy-10,12-dimethoxynaphtho[1,2-c]isochromen-6-one[1]
| |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H26O9 | |
| Molar mass | 494.496 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ a b c "Gilvocarcin V". Pubchem.ncbi.NLM.nih.gov.
- ^ a b c "Gilvocarcin V (Anandimycin A, Toromycin B, Antibiotic 1072B), CAS [77879-90-4] | BIOZOL". www.biozol.de.
- ^ a b Comprehensive Natural Products II: Chemistry and Biology. Elsevier. 5 March 2010. p. 257. ISBN 978-0-08-045382-8.
- ^ a b Buckingham, John (1987). Dictionary of Organic Compounds. Taylor & Francis. p. 359. ISBN 978-0-412-17050-8.
- ^ Fischer, Carsten; Lipata, Fredilyn; Rohr, Jürgen (1 July 2003). "The Complete Gene Cluster of the Antitumor Agent Gilvocarcin V and Its Implication for the Biosynthesis of the Gilvocarcins". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 125 (26): 7818–7819. doi:10.1021/ja034781q. PMC 4480634. PMID 12822997.
- ^ a b Progress in Medicinal Chemistry. Elsevier. 1 January 1985. p. 20. ISBN 978-0-08-086270-5.
Further reading
edit- Gillum, Karen D. (1988). Lethal and Mutagenic Effects of Antitumor Agent Gilvocarcin V Photosensitization on Escherichia Coli K-12/343/120. Texas Southern University.
- Publishers, Bentham Science (November 1997). Current Organic Chemistry. Bentham Science Publishers. p. 408.
- Transferases—Advances in Research and Application: 2012 Edition. ScholarlyEditions. 26 December 2012. p. 137. ISBN 978-1-4649-9789-1.
- Diana, Patrizia; Cirrincione, Girolamo (9 February 2015). Biosynthesis of Heterocycles: From Isolation to Gene Cluster. John Wiley & Sons. p. 585. ISBN 978-1-118-02867-4.