Fluo-4 is used to measure calcium (Ca2+) concentrations inside living cells, and is often used for high-throughput screening of receptor ligands and calcium permeable ion channels.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
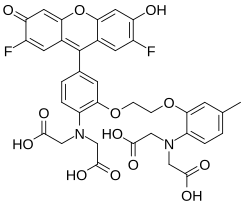
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2′-{[2-(2-{2-[Bis(carboxymethyl)amino]-5-(2,7-difluoro-6-hydroxy-3-oxo-3H-xanthen-9-yl)phenoxy}ethoxy)-4-methylphenyl]azanediyl}diacetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | Fluo-4 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C36H30F2N2O13 | |
| Molar mass | 736.634 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
The green-fluorescent calcium indicator, Fluo-4, is an improved version of the calcium indicator, Fluo-3. It is commonly used as the non-fluorescent acetoxymethyl ester (Fluo-4 AM) which is cleaved inside the cell to give the free, fluorescent Fluo-4. It loads faster, is brighter at equivalent concentrations and is well-excited by the 488 nm line of the argon-ion laser which is often used in biological research laboratories.[1] Fluo-4 and its cell-permeable AM ester are available from a few commercial vendors.
References
edit- ^ Gee KR, Brown KA, Chen WN, Bishop-Stewart J, Gray D, Johnson I (February 2000). "Chemical and physiological characterization of fluo-4 Ca(2+)-indicator dyes". Cell Calcium. 27 (2): 97–106. doi:10.1054/ceca.1999.0095. PMID 10756976.