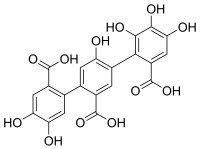
Flavogallonic acid is a hydrolysable tannin that can be found in valonea oak (Quercus macrolepis)[1] in chestnut wood[2] or in Terminalia myriocarpa.[3]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
14,15,25,34,35,36-Hexahydroxy[11,21:24,31-terphenyl]-12,22,32-tricarboxylic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H14O12 | |
| Molar mass | 458.32 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Molecular investigation of valonea tannin. Hasan Özgunay and Özcan Sari, The Journal of the American Leather Chemists Association, 2007, vol. 102, no5, pp. 154-157, INIST 18744048, text
- ^ Considerations on the macromolecular structure of chestnut ellagitannins by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Pasch H and Pizzi A, Journal of applied polymer science, 2002, vol. 85, no2, pp. 429-437, INIST 14185517
- ^ Pharmacologically Active Ellagitannins from Terminalia myriocarpa. Mohamed S.A. Marzouk, Sayed A.A. El-Toumy, Fatma A. Moharram, Nagwa M.M. Shalaby and Amany A.E. Ahmed, Planta Med, 2002, 68(6), pages 523-527, doi:10.1055/s-2002-32549