A filter graph is used in multimedia processing - for example, to capture video from a webcam. Filters take input, process it (or change the input), and then output the processed data. For example: a video codec takes raw uncompressed video and compresses it using a video standard such as H.264. To compress a multimedia stream a filter graph could have two inputs:
- Audio
- Video
Usually these are expressed as file sources. The file sources would feed compression filters, the output of the compression filters would feed into a multiplexer that would combine the two inputs and produce a single output. (An example of a multiplexer would be an MPEG transport stream creator.) Finally the multiplexer output feeds into a file sink, which would create a file from the output.
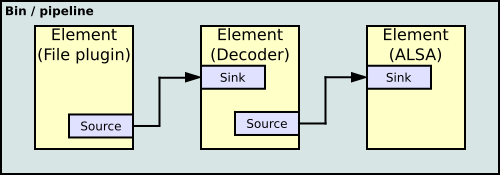
A filter graph in multimedia processing is a directed graph. Edges represent one-way data flow and vertices represent a data-processing step. Pins or pads identify the connection points between vertices and edges.
Example of programs that use filter graphs
edit- GStreamer - Linux based multimedia framework. In Gstreamer a filter is called an element. Filter graphs can be built with the GStreamer Editor.
- GraphEdit - Microsoft tool for building filter graphs
- GraphStudioNext - an open source tool to build and debug DirectShow filter graphs, replacement for GraphEdit
- DirectShow - Windows based multimedia framework.
- GraphEditPlus - a free tool for building DirectShow filter graphs and generating C++ source code for them.
- Harpia - a graphic interface for learning, implementation and management of vision systems
See also
editExplanation of filter graph in DirectShow article: DirectShow#Architecture
External links
editDirectShow
edit- Explanation of filter graph manager [1]
- Filters what they are
- Example of filter graph usage
- Data Flow in the Filter Graph