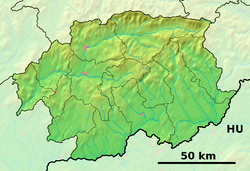
Detva (Hungarian: Gyetva) is a town in central Slovakia with a population of 14,686. It is situated beneath the mountain Poľana.
Detva | |
|---|---|
Town | |
 Panorama of the city | |
Location of Detva in the Banská Bystrica Region | |
| Coordinates: 48°33′05″N 19°25′06″E / 48.55139°N 19.41833°E | |
| Country | Slovakia |
| Region | Banská Bystrica |
| District | Detva |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Ján Šufliarský |
| Area | |
• Total | 68.09 km2 (26.29 sq mi) |
| (2022) | |
| Elevation | 474[2] m (1,555[2] ft) |
| Population | |
• Total | 13,704 |
| • Density | 200/km2 (520/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| Postal code | 962 12[2] |
| Area code | +421 45[2] |
| Car plate | DT |
| Website | www.detva.sk |
Etymology
editThe name means 'youth' in Slovak and was probably motivated by the majority of young people among the first settlers.[4]
History
editDetva was created as a village of bondage in a deep-forested area belonging to Zvolenská Slatina and Očová upon instruction of the owner of the Vígľaš dominion Ladislav Čáky resp. Ladislaus Csáky in 1636-1638. The first settlers were coal producers from Ľubietová, followed by Walachian-type settlers from northern and eastern parts of Slovakia and immigrants from other surrounding villages. In 1787, Ján Vagač founded the first known manufactory producing bryndza cheese. The settlement became an oppidum (market town) in 1811 and a town in 1965. In 1996 the town of Detva became the seat of new Detva district.
It was developed as a large newly cleared land and this character has been preserved up to present, despite the fact that a part of the newly cleared lands were separated from Detva - Hriňová (before 1863), Detvianska Huta (in ?), Korytárky (in 1955; part of Kriváň until 1993) and Kriváň (in 1955). Logging and wood processing, sheep breeding and peasantry had been the main source of bread and butter of the Detvans. Hard living conditions at distant isolated newly cleared lands and self-sufficiency in providing of basic living needs determined the formation of the original material and spiritual culture of local inhabitants and thanks to this Detva had become one of the symbols of the modern Slovak nation.
In 1955 Detva experienced a significant change. A factory for military machinery and strategic constructions was built in the town's woods for security purposes. This factory, called Podpolianske strojárne Detva (PPS) at that time, produced UNC machinery, aka "Universal" on Western European markets. Machinery such as front loaders and skid steer loaders used to reach an annual production of 4,000. The factory enlarged the population of Detva from 3,500 to over 12,000, employing over 70% of Detva's population. However, after the Velvet Revolution and the split of Czechoslovakia, infamous illegal and non-transparent privatization, typical of then Central and Eastern European states, took place. Detva's PPS factory had to put its production on halt and to downsize its workforce from 8,000 in 1993 to 1,000 in 2005.
Demographics
editAccording to the 2001 census, the town had 15,122 inhabitants. 96.11% of inhabitants were Slovaks, 1.75% Roma, and 0.75% Czechs.[5] The religious make-up was 78.03% Roman Catholics, 13.11% people with no religious affiliation and 4.47% Lutherans.[5]
Neighborhoods
edit- Detva (proper)
- Detva - sídlisko
- Kostolná
- Krné
- Piešť I
- Piešť II
- Skliarovo
- Zapriechody
Notability
edit- Folklore festival beneath Poľana
- museum of engraved wood crosses
Twin towns — sister cities
edit- Tuchów, Poland
Gallery
edit-
Church of Francis of Assisi
-
Church of Francis of Assisi
-
Detva in winter
-
Statue of John of Nepomuk
-
Accordionist during folklore festival
-
Folklore group during folklore festival
-
Memorial plaque of Karol Anton Medvecký
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Statistical Office of the Slovak Republic (www.statistics.sk). "Hustota obyvateľstva - obce". www.statistics.sk. Retrieved 2024-02-08.
- ^ a b c d "Základná charakteristika". www.statistics.sk (in Slovak). Statistical Office of the Slovak Republic. 2015-04-17. Retrieved 2022-03-31.
- ^ Statistical Office of the Slovak Republic (www.statistics.sk). "Počet obyvateľov podľa pohlavia - obce (ročne)". www.statistics.sk. Retrieved 2024-02-08.
- ^ Krajčovič, Rudolf (2008). "Z lexiky stredovekej slovenčiny s výkladmi názvov obcí a miest (8)". Kultúra slova (3). Martin: Vydavateľstvo Matice slovenskej: 167.
- ^ a b "Municipal Statistics". Statistical Office of the Slovak republic. Archived from the original on 2007-11-16. Retrieved 2007-12-15.
- ^ "Partnerské mesto". detva.sk (in Slovak). Detva. Retrieved 2019-09-08.
Genealogical resources
editThe records for genealogical research are available at the state archive "Statny Archiv in Banska Bystrica, Slovakia"
- Roman Catholic church records (births/marriages/deaths): 1662-1905 (parish A)