Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma is a cutaneous condition characterized by a solitary, firm skin lesion on the face.[1]: 672 Familial cases have been reported suggesting a possible genetic link.
| Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma | |
|---|---|
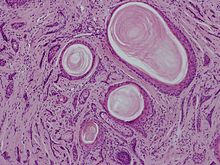 | |
| Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma or sclerosing epithelial hamartoma | |
| Specialty | Dermatology |
The diagnosis is made based on clinical and morphological features. Differential diagnosis includes trichoepithelioma, microcystic adnexal carcinoma, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma, and syringoma.
Surgical excision is the treatment of choice.
Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma is more common in females and usually affects children or adults.
Signs and symptoms
editDesmoplastic trichoepithelioma manifests as a firm, soft, or white to yellowish annular nodule or papule on the cheeks or face with a central indentation.[2]
Causes
editFamilial desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas have been reported suggesting a possible genetic link.[3]
Diagnosis
editDesmoplastic trichoepithelioma can be diagnosed based on clinical and morphological features. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma may resemble other tumors such as conventional trichoepithelioma, microcystic adnexal carcinoma, morpheaform basal cell carcinoma, and syringoma both clinically and histopathologically.[4]
Treatment
editThe preferred course of treatment is surgical excision.[2] Nonetheless, Mohs microscopic surgery is the method of choice for lesions, particularly those on the face.[5]
Epidemiology
editDesmoplastic trichoepithelioma is more common in females. It has a bimodal age distribution and usually affects adults or small children. Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma accounts for less than 1% of all cutaneous tumors.[2]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ a b c Rahman, Jawaria; Tahir, Muhammad; Arekemase, Hassan; Murtazaliev, Salikh; Sonawane, Snehal (2020-08-12). "Desmoplastic Trichoepithelioma: Histopathologic and Immunohistochemical Criteria for Differentiation of a Rare Benign Hair Follicle Tumor From Other Cutaneous Adnexal Tumors". Cureus. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. doi:10.7759/cureus.9703. ISSN 2168-8184. PMC 7486105.
- ^ Lovgren, M.-L.; Rajan, N.; Joss, S.; Melly, L.; Porter, M. (2019). "Inherited desmoplastic trichoepitheliomas". Clinical and Experimental Dermatology. 44 (7). doi:10.1111/ced.13876. ISSN 0307-6938. PMC 6766857. PMID 30697781.
- ^ WANG, QIONGYU; GHIMIRE, DEEPAK; WANG, JUAN; LUO, SUJU; LI, ZHENGXIAO; WANG, HAO; GENG, SONGMEI; XIAO, SHENGXIANG; ZHENG, YAN (2015-07-21). "Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma: A clinicopathological study of three cases and a review of the literature". Oncology Letters. 10 (4). Spandidos Publications: 2468–2476. doi:10.3892/ol.2015.3517. ISSN 1792-1074. PMC 4579987. PMID 26622873.
- ^ Moon, Seong Hun; Choi, Hyun Seok; Kwon, Hyoung Il; Ko, Joo Yeon; Kim, Jeong Eun (2016). "A Case of Multiple Desmoplastic Trichoepithelioma". Annals of Dermatology. 28 (3). Korean Dermatological Association and The Korean Society for Investigative Dermatology: 411. doi:10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.411. ISSN 1013-9087. PMC 4884730. PMID 27274652.
Further reading
edit- Mamelak, Adam J.; Goldberg, Leonard H.; Katz, Tracy M.; Graves, Jeffery J.; Arnon, Ofer; Kimyai-Asadi, Arash (2010). "Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 62 (1). Elsevier BV: 102–106. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2009.06.066. ISSN 0190-9622. PMID 20082889.
- Moynihan, Gavan D.; Skrokov, Robert A.; Huh, Julie; Pardes, Jeffrey B.; Septon, Robin (2011). "Desmoplastic trichoepithelioma". Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 64 (2). Elsevier BV: 438–439. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2010.04.053. ISSN 0190-9622.