Dazoxiben is an orally active thromboxane synthase inhibitor.[1] It has shown a significant clinical improvement in patients with Raynaud's syndrome.[2]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
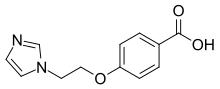
| Preferred IUPAC name
4-[2-(1H-Imidazol-1-yl)ethoxy]benzoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H12N2O3 | |
| Molar mass | 232.239 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Synthesis
editOne convenient synthesis starts with the O-chloroethyl ether of p-hydroxybenzamide and proceeds bydisplacement with imidazole to give 2. Hydrolysis of the amide function completes the synthesis of dazoxiben.
References
edit- ^ Belch, J. J.; Cormie, J.; Newman, P.; McLaren, M.; Barbenel, J.; Capell, H.; Leiberman, P.; Forbes, C. D.; Prentice, C. R. (1983). "Dazoxiben, a thromboxane synthetase inhibitor, in the treatment of Raynaud's syndrome: A double-blind trial". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 15 Suppl 1 (Suppl 1): 113S–116S. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02119.x. PMC 1427695. PMID 6337601.
- ^ Belch, J. J.; Cormie, J.; Newman, P.; McLaren, M.; Barbenel, J.; Capell, H.; Leiberman, P.; Forbes, C. D.; Prentice, C. R. (1983). "Dazoxiben, a thromboxane synthetase inhibitor, in the treatment of Raynaud's syndrome: A double-blind trial". British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology. 15 Suppl 1 (Suppl 1): 113S–116S. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02119.x. PMC 1427695. PMID 6337601.
- ^ DE 2950019, Cross, Peter Edward & Dickinson, Roger Peter, "Imidazolderivate, Verfahren zu ihrer Herstellung und diese enthaltende Arzneimittel [Imidazol derivatives, processes for their production and pharmaceuticals containing them]", published 1980-07-10, assigned to Pfizer Corp.
- ^ Kochergin, P. M.; Palei, R. M.; Balandina, L. V.; Kharitonova, A. E.; Kravchenko, A. N.; Persanova, L. V.; Govorukhina, E. I.; Frolova, M. A. (1995). "Simplified synthesis of dazoxiben". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal. 29 (2): 139. doi:10.1007/BF02226528. S2CID 37387182.
- ^ Iizuka, Kinji; Akahane, Kenji; Momose, Denichi; Nakazawa, Masayuki; Tanouchi, Tadao; Kawamura, Masanori; Ohyama, Isao; Kajiwara, Ikuo; Iguchi, Yohichi (1981). "Highly selective inhibitors of thromboxane synthetase. 1. Imidazole derivatives". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 24 (10): 1139–1148. doi:10.1021/jm00142a005. PMID 7199088.
- ^ Cross, Peter E.; Dickinson, Roger P.; Parry, M. John; Randall, Michael J. (1985). "Selective thromboxane synthetase inhibitors. 1. 1-[(Aryloxy)alkyl]-1H-imidazoles". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 28 (10): 1427–1432. doi:10.1021/jm00148a009. PMID 3930740.