The crista galli (Latin: "crest of the rooster") is a wedge-shaped, vertical, midline upward continuation of the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone of the skull,[1] projecting above the cribriform plate[2] into the cranial cavity. It serves as an attachment for the membranes surrounding the brain.[1]
| Crista galli | |
|---|---|
 Ethmoid bone from above. | |
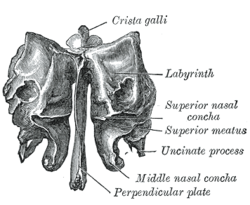 Ethmoid bone from behind. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone |
| System | Skeletal |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | crista galli |
| TA98 | A02.1.07.004 |
| TA2 | 724 |
| FMA | 57442 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Structure
editAttachments
editThe falx cerebri (a fold of the dura mater surrounding the brain) attaches to the crista galli.[citation needed]
Relations
editThe olfactory bulbs of the olfactory nerve lie on either side of the crista galli on top of the cribriform plate.[citation needed]
Variation
editThe base of crista galli varies in height.[2] A bifid crista galli may suggest intracranial extension of a nasal dermoid cyst.[3]
References
edit- ^ a b Fehrenbach, Margaret J.; Herring, Susan W. (2017). Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck (5th ed.). St. Louis: Elsevier. p. 57. ISBN 978-0-323-39634-9.
- ^ a b Hajiioannou, Jiannis; Owens, David; Whittet, Heikki B. (2010). "Evaluation of anatomical variation of the crista galli using computed tomography". Clinical Anatomy. 23 (4): 370–373. doi:10.1002/ca.20957. ISSN 1098-2353. PMID 20196125. S2CID 12865173.
- ^ Clark, W. D.; Bailey, B. J.; Stiernberg, C. M. (February 1985). "Nasal dermoid with intracranial involvement". Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery. 93 (1): 102–104. doi:10.1177/019459988509300121. ISSN 0194-5998. PMID 3920605. S2CID 12407939.
External links
edit- MedEd at Loyola Radio/curriculum/ENT/jay84a.jpg
- Floor of the cranial cavity (close-up)[dead link] - BioWeb at University of Wisconsin System
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2014-01-01.
- Cross section image: skull/x-front—Plastination Laboratory at the Medical University of Vienna