Ceratonia /ˌsɛrəˈtoʊniə/,[2] also known as carobs, is a small genus of flowering trees in the pea family, Fabaceae, endemic to the Mediterranean region and the Middle East. Its best known member is the carob tree (Ceratonia siliqua), which is cultivated for its edible pods and has been widely introduced to regions with similar climates. The genus was long considered monotypic, but a second species, Ceratonia oreothauma, was identified in 1979 from Oman and Somalia.[3] The genus is in subfamily Caesalpinioideae and tribe Umtizieae.
| Ceratonia | |
|---|---|
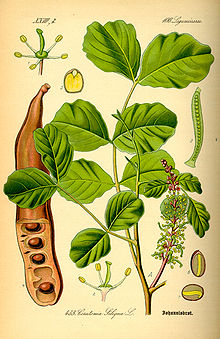
| |
| Carob tree (Ceratonia siliqua) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Genus: | Ceratonia L. (1753) |
| Species[1] | |
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
An obsolete name for Ceratonia was Acalis.
Fossil record
edit†Ceratonia emarginata fossils are known from the Miocene of Switzerland and Hungary.[4]
References
edit- ^ a b Ceratonia L. Plants of the World Online. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ Sunset Western Garden Book, 1995:606–607
- ^ Hillcoat, D.; Lewis, G.; Verdcourt, B. (1980). "A New Species of Ceratonia (Leguminosae-Caesalpinioideae) from Arabia and the Somali Republic". Kew Bulletin. 35 (2): 261–271. Bibcode:1980KewBu..35..261H. doi:10.2307/4114570. JSTOR 4114570.
- ^ Leguminosae species from the territory of Abkhazia by Alexandra K. Shakryl, Advances in Legume Systematics: Part 4, The Fossil Record, Ed. P.S. Herendeen & Dilcher, 1992, The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, ISBN 0 947643 40 0
Images
edit-
Fruit
-
Tree
-
Flowers
-
Fruits