The C melody saxophone, also known as the C tenor saxophone, is a saxophone pitched in the key of C one whole tone above the common B-flat tenor saxophone.[1] The C melody was part of the series of saxophones pitched in C and F intended by the instrument's inventor, Adolphe Sax, for orchestral use. The instrument enjoyed popularity in the early 1900s, perhaps most prominently used by Rudy Wiedoeft and Frankie Trumbauer, but is now uncommon.
 A Conn C Melody Saxophone. While most C melody saxophones have curved necks (with a similar shape to that of the tenor saxophone), C. G. Conn did make straight-necked C melody instruments (more similar in appearance to the alto). | |
| Woodwind instrument | |
|---|---|
| Classification | Single-reed |
| Hornbostel–Sachs classification | 422.212-71 (Single-reed aerophone with keys) |
| Inventor(s) | Adolphe Sax |
| Developed | 1840s |
| Playing range | |
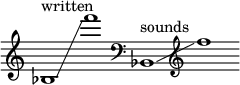 | |
| Related instruments | |
|
Sizes:
Orchestral saxophones: Specialty saxophones: | |
| Musicians | |
| See list of saxophonists | |
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
|
A C melody saxophone is larger than an alto and smaller than a tenor. The bore on most models has a diameter and taper more like a 'stretched' alto than a tenor. When seen in profile, its shape bears some resemblance to a tenor saxophone, though it is smaller and the bell appears longer. Most C melody saxophones have curved necks (with a similar shape to that of the tenor saxophone) though C. G. Conn did make straight-necked C melody instruments (more similar to the alto). C melody saxophones are usually marked with a letter "C" above or below the serial number.
Since 1930, only saxophones in the key of B♭ and E♭ (originally intended by Sax for use in military bands and wind ensembles) have been produced on a large scale. However, in the early years of the 21st century, small-scale production of new C melody saxophones had commenced in China for a company called Aquilasax though production ceased by 2015.[2] Student-quality C melody instruments are, as of 2023, available from Thomann (Germany) and Sakkusu (UK).[3]
Advantages
editA major selling point for the C melody saxophone was the fact that in contrast to other saxophones, it was not a transposing instrument. As a result, the player could read regular printed music (e.g. for flute, oboe, violin, piano, guitar or voice) without having to transpose or read music parts that have been transposed into B♭ or E♭, which most other saxophones would require. This enabled amateur musicians to play along with a friend or family member by reading from the same sheet of music—so long as the music fell within the pitch range of the C melody saxophone itself, that is, was not too high or low. Another selling point was that the C melody produces a more muted tone than the E♭ alto or B♭ tenor, which was useful when playing at home. Many novelty tunes, most influenced by 1920s dance music, were written specifically for the instrument. They were sometimes also used in churches to accompany hymns. Sax players in Irish and Irish-American dance bands of the 1920s and '30s often used the C melody as it made for easier fingering in the keys of G and D commonly used for traditional Irish tunes played by fiddlers, flute players and button accordionists. Similarly, some players prefer the C melody when playing guitar-based blues music in E or A.
Mouthpieces
editDedicated mouthpieces were produced for the C melody saxophone, though these may be hard to find in the 21st century. The C melody has a muted sound when compared to other saxophone types, particularly if an original vintage mouthpiece is used. This made it particularly useful for its originally intended environment of playing in drawing rooms. C melody mouthpieces often give a C melody saxophone a slightly muffled sound, which may or may not be what the player desires. Some players successfully use a modern tenor saxophone mouthpiece, modified by cutting off one centimeter of the mouthpiece if needed to fit, with their C melody saxophone, though depending on which mouthpiece type is chosen (e.g. long shank or short shank) there may be problems regarding the accuracy of intonation, particularly at the upper end of the range. As a result, some experimentation may be required in order to find a tenor mouthpiece which provides accurate intonation across the entire scale. Other players have successfully fitted alto saxophone mouthpieces to their C melody saxophones. As before, some experimentation may be required. With a more modern mouthpiece fitted, a C melody saxophone can lose some of its muted qualities and sound brighter, with more of the sonic power that an alto or tenor saxophone gives. Currently, there are a number of manufacturers producing C melody mouthpieces e.g. Beechler,[4] Ralph Morgan,[5] and Ronald Caravan.
Production history
editA number of high-quality manufacturers produced C melody saxophones (including Buescher, C. G. Conn, Martin,[6] King[7] and Selmer) from 1914 through 1930. Most of these companies also manufactured "stencil" saxophones for other vendors under different names e.g. the 'Harwood Jenkins', 'Lyon & Healy', 'Oliver Ditson' and 'Wurlitzer American' - all of which were actually made by Buescher. Production of C melody saxophones appears to have reached a peak around 1923, with a gradual reduction thereafter. Comparatively few C melody saxophones were made in the late 1920s. The Conn straight-neck Tenor in C is the most common of the actual orchestral saxophones and has a more classical sound and plays in tune throughout the instrument's range. This is one of the few models actually made for professional use. However, the long straight neck means that the saxophone must be held away from the player's body, a posture which some people may find uncomfortable.
Cheaper, novelty C melody saxophones were marketed from the late 1910s through the early 1930s as a version of the saxophone intended for amateur use, in homes, schools, and town bands. It was made with a bore considerably narrower than that of the B♭ tenor saxophone, being more or less a "stretched" version of the alto saxophone bore.
By the late 1920s the popularity of C melody saxophones had faded. Sales of all saxophones fell dramatically after the Wall Street Crash of 1929, and the C melody was one of several models[8] (including the mezzo-soprano saxophone) which were dropped from production soon after. However, it is important to note that production ended for purely financial reasons, and not because of any inherent flaw in the design or poor manufacturing standards. C melody saxophones were as good as the reputation of whichever company manufactured them. The basic problem was that the Great Depression which followed immediately after the stock market crash of 1929 caused extremely harsh economic conditions throughout the world, which affected the production of all leisure-related consumer products. This unusually profound recession hit saxophone manufacturers hard, forcing them to reduce the range of musical instruments they produced down to the most popular models, simply in order for those companies to survive.[9] As a result, production of C melody saxophones ended abruptly. By the time the world economy had recovered sufficiently for C melody saxophones to be economically viable again (around 1935) people's leisure time interests had changed and there was no longer a market for them. Additionally, the "Big Band" era had started in the early 1930s and anyone who wanted to learn the saxophone was interested primarily in soprano, alto, tenor or baritone because this would, potentially at least, allow them to play in a Big Band, and Big Bands did not feature C melody saxophones in their instrument line-up. As a result, there was no consumer demand for C melody instruments, so would-be manufacturers had no incentive to resume production. Not surprisingly, instrument manufacturers concentrated instead on making other types which had strong customer demand and were easy to sell e.g. alto and tenor saxophones.
C.G.Conn made a small number of C melody saxophones during the 1930s which were stamped with the model number "8M". These were almost certainly completed saxophone bodies that had been kept in storage since the 1920s and which were furnished with updated keywork after the Great Depression ended. At least one Conn C melody dating from 1938 has "Transitional" keywork (similar to that found on a Conn 6M alto or Conn 10M tenor) plus a "Lady Face" engraving on the bell front. However, late model Conn C melody saxophones like these are extremely unusual because they are rare exceptions to the general rule that production of C melody saxophones ended in 1930.
During the 1960s, the French woodwind manufacturer Leblanc produced a few C melody saxophones (brand stamped on bell was Vito), though it is thought that they manufactured fewer than 20 examples.
Some early jazz players got their start on the C melody, including Benny Carter and Coleman Hawkins, though Carter eventually moved to the alto, and Hawkins to the B♭ tenor. Among the most famous musicians to perform mainly on C melody sax was Rudy Weidoeft. Although he played alto and soprano saxophones as well (the latter in ensembles with Arnold Brilhart, Alford Evans, and others), he made his most famous recordings on the C melody, and was a significant factor in popularizing the instrument among the general public. Another famous C melody player was Frankie Trumbauer, a jazz player who was known for his superb technical ability on the instrument and influence on later generations. Jack Pettis, a member of the Ben Bernie orchestra and a recording artist under his own name, was another skilled player of the instrument.
A few modern-day saxophonists occasionally perform on C melody instruments, though rarely if ever as a primary instrument. Examples include Anthony Braxton,[10] Kyle Vincent, Scott Robinson, Rick Arbuckle, Rosy McHargue, Dan Levinson, Hayes Greenfield and Joe Lovano.[11] Carla Bley, though mainly a keyboardist, has played the C Melody sax occasionally on recordings led by her daughter Karen Mantler.[12]
Despite the fact that they have not been manufactured in over 75 years, C melody saxophones are readily available today, due to their limited use and the sheer number that were produced in the early 20th century. They can often be found at stores that carry used instruments, tag sales, rummage sales and pawn shops across the United States.
Related and new instruments
edit- Another saxophone pitched in C, called the contralto saxophone, has been produced by California instrument maker Jim Schmidt since the late 1990s.[13] It is a modern design and differs from the vintage C melody instruments in several ways, most notably its linear chromatic fingering system.
- Starting 2007, the New Zealand company Aquilasax began production of a new "C melody tenor saxophone". However, Aquilasax ceased operating June 2015, stating "...our saxes are more popular with customers than with the factory that makes them. We have been unable to solve this problem and have not been able to make the business profitable as a result."[14]
- Beginning in 2012, Thomann, the well-known German instrument manufacturer, started to sell a completely new line of C-Melodies. They sell two versions, one in pure silver plate and one in regular brass lacquer.[15]
- Modern C melody saxes are available (as of 2014) under the Sax.co.uk house label "Sakkusu", as well as on eBay from assorted Chinese manufacturers.[16]
References
edit- ^ Cottrell, Stephen (2012). The Saxophone. Yale Musical Instrument Series. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 84. ISBN 978-0-300100-41-9. LCCN 2012028346. OCLC 844030644. OL 25377233M. Wikidata Q113952716.
- ^ "Aquilasax.com". Aquilasax.com. Archived from the original on 9 March 2018. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
Aquilasax.com has ceased operating since June 2015 (formerly China since 2007) [...] I will keep this website open as an info site as long as funds allow.
- ^ "Jazzfuel.com". 16 January 2021. Retrieved 11 May 2023.
- ^ Prominent Web Design. "Saxophone Mouthpiece Tip Opening Chart". Beechler.com. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ JunkDude Music - Ralph Morgan Mouthpieces Archived 29 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Martin C Melody saxophone review". Shwoodwind.co.uk. 30 September 2005. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "King C Melody saxophone review". Shwoodwind.co.uk. 23 April 2007. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Why are there C melody saxophones ?". Cmelodysax.co.uk. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ c melody » C Melody Archived 16 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ See Braxton's Seven Compositions (Trio) 1989, hatART (1990)
- ^ See Lovano's album Quartets: Live at the Village Vanguard
- ^ See Karen Mantler's Pet Project (Virgin Classics); and Farewell (ECM/XtraWATT)
- ^ "Jim Schmidt'S Contralto". 19 July 2008. Archived from the original on 19 July 2008. Retrieved 19 May 2014.
- ^ "Welcome to Aquilasax!". Aquilasax.com. Archived from the original on 9 March 2018. Retrieved 14 August 2016.
- ^ "Thomann CMS-600 L C- Melody Sax". Musikhaus Thomann. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- ^ "Sakkusu C-Melody Saxophone Review". cafesaxophone.com. 31 August 2014. Retrieved 14 August 2016.