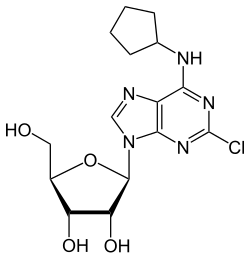
2-Chloro-N6-cyclopentyladenosine (CCPA) is a specific receptor agonist for the Adenosine A1 receptor.[1] It is similar to N6-cyclopentyladenosine. Due to CCPA's high affinity for Adenosine A1 receptors, its tritiated derivative [3H]CCPA can be used as a diagnostic tool for detecting the receptors in tissue with low receptor density.
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-Chloro-N6-cyclopentyladenosine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-[2-Chloro-6-(cyclopentylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | CCPA |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | 2-chloro-N(6)cyclopentyladenosine |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H20ClN5O4 | |
| Molar mass | 369.80 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ Karl-Norbert Klotz; Martin J. Lohse; Ulrich Schwabe; Gloria Cristalli; Sauro Vittori; Mario Grifantini (1989). "2-Chloro-N6-[3H]cyclopentyladenosine ([3HCCPA) — a high affinity agonist radioligand for A1 adenosine receptors". Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology. 340 (6): 679–683. doi:10.1007/BF00717744. PMID 2615857. S2CID 1114190.