The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred in Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. The eastern half of the Empire survived the conditions that caused the fall of the West in the 5th century AD, and continued to exist until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in the Mediterranean world. The term "Byzantine Empire" was only coined following the empire's demise; its citizens referred to the polity as the "Roman Empire" and to themselves as "Romans".[a] Due to the imperial seat's move from Rome to Byzantium, the adoption of state Christianity, and the predominance of Greek instead of Latin, modern historians continue to make a distinction between the earlier Roman Empire and the later Byzantine Empire.
Byzantine Empire | |
|---|---|
| 330–1453 | |
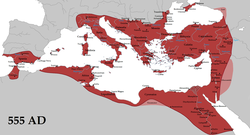 The empire in 555 under Justinian I, its greatest extent since the fall of the Western Roman Empire, with vassals in pink | |
| Capital | Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) |
| Common languages | |
| Religion | Christianity (official) |
| Demonym(s) |
|
| Government | Autocracy |
| Notable emperors | |
• 306–337 | Constantine I |
• 379–395 | Theodosius I |
• 408–450 | Theodosius II |
• 527–565 | Justinian I |
• 610–641 | Heraclius |
• 717–741 | Leo III |
• 976–1025 | Basil II |
• 1081–1118 | Alexios I |
• 1143–1180 | Manuel I |
• 1261–1282 | Michael VIII |
• 1449–1453 | Constantine XI |
| Historical era | Late antiquity to Late Middle Ages |
| Population | |
• 457 | 16,000,000 |
• 565 | 26,000,000 |
• 775 | 7,000,000 |
• 1025 | 12,000,000 |
• 1320 | 2,000,000 |
| Currency | Solidus, denarius, and hyperpyron |
During the earlier Pax Romana period, the western parts of the empire became increasingly Latinised, while the eastern parts largely retained their preexisting Hellenistic culture. This created a dichotomy between the Greek East and Latin West. These cultural spheres continued to diverge after Constantine I (r. 324–337) moved the capital to Constantinople and legalised Christianity. Under Theodosius I (r. 379–395), Christianity became the state religion, and other religious practices were proscribed. Greek gradually replaced Latin for official use as Latin fell into disuse.
The empire experienced several cycles of decline and recovery throughout its history, reaching its greatest extent after the fall of the west during the reign of Justinian I (r. 527–565), who briefly reconquered much of Italy and the western Mediterranean coast. The appearance of plague and a devastating war with Persia exhausted the empire's resources; the early Muslim conquests that followed saw the loss of the empire's richest provinces—Egypt and Syria—to the Rashidun Caliphate. In 698, Africa was lost to the Umayyad Caliphate, but the empire subsequently stabilised under the Isaurian dynasty. The empire was able to expand once more under the Macedonian dynasty, experiencing a two-century-long renaissance. This growth came to an end in 1071 after the defeat by the Seljuk Turks at the Battle of Manzikert. Thereafter, periods of civil war and Seljuk incursion resulted in the loss of most of Asia Minor. The empire recovered during the Komnenian restoration, and Constantinople remained the largest and wealthiest city in Europe until the 13th century.
The empire was largely dismantled in 1204, following the Sack of Constantinople by Latin armies at the end of the Fourth Crusade; its former territories were then divided into competing Greek rump states and Latin realms. Despite the eventual recovery of Constantinople in 1261, the reconstituted empire wielded only regional power during its final two centuries of existence. Its remaining territories were progressively annexed by the Ottomans in perennial wars fought throughout the 14th and 15th centuries. The fall of Constantinople to the Ottomans in 1453 ultimately brought the empire to an end. Many refugees who had fled the city after its capture settled in Italy and throughout Europe, helping to ignite the Renaissance. The fall of Constantinople is sometimes used to mark the dividing line between the Middle Ages and the early modern period.
Nomenclature
The inhabitants of the empire, now generally termed Byzantines, thought of themselves as Romans (Romaioi). Their Islamic neighbours similarly called their empire the "land of the Romans" (Bilād al-Rūm), but the people of medieval Western Europe preferred to call them "Greeks" (Graeci), due to having a contested legacy to Roman identity and to associate negative connotations from ancient Latin literature.[1] The adjective "Byzantine", which derived from Byzantion (Latinised as Byzantium), the name of the Greek settlement Constantinople was established on, was only used to describe the inhabitants of that city; it did not refer to the empire, which they called Romanía—"Romanland".[2]
After the empire's fall, early modern scholars referred to the empire by many names, including the "Empire of Constantinople", the "Empire of the Greeks", the "Eastern Empire", the "Late Empire", the "Low Empire", and the "Roman Empire".[3] The increasing use of "Byzantine" and "Byzantine Empire" likely started with the 15th-century historian Laonikos Chalkokondyles, whose works were widely propagated, notably by Hieronymus Wolf. "Byzantine" was used adjectivally alongside terms such as "Empire of the Greeks" until the 19th century.[4] It is now the primary term, used to refer to all aspects of the empire; however, some modern historians believe that, as an originally prejudicial and inaccurate term, it should not be used.[5]
History
As the historiographical periodizations of "Roman history", "late antiquity", and "Byzantine history" significantly overlap, there is no consensus on a "foundation date" for the Byzantine Empire, if there was one at all. The growth of the study of "late antiquity" has led to some historians setting a start date in the seventh or eighth centuries.[6] Others believe a "new empire" began during changes in c. 300 AD.[7] Still others hold that these starting points are too early or too late, and instead begin c. 500.[8] Geoffrey Greatrex believes that it is impossible to precisely date the foundation of the Byzantine Empire.[9]
Early history (pre-518)
In a series of conflicts between the third and first centuries BC, the Roman Republic gradually established hegemony over the eastern Mediterranean, while its government ultimately transformed into the one-person rule of an emperor. The Roman Empire enjoyed a period of relative stability until the third century AD, when a combination of external threats and internal instabilities caused the Roman state to splinter as regional armies acclaimed their generals as "soldier-emperors".[10] One of these, Diocletian (r. 284–305), seeing that the state was too big to be ruled by one man, attempted to fix the problem by instituting a Tetrarchy, or rule of four, and dividing the empire into eastern and western halves. Although the Tetrarchy system quickly failed, the division of the empire proved an enduring concept.[11]
Diocletian's reforms significantly altered governmental structure, reach and taxation, and these reforms also had the effect of downgrading the first capital, Rome.[12] Constantine I (r. 306–337) secured sole power in 324. Over the following six years, he rebuilt the city of Byzantium as a capital city, which was renamed Constantinople. Rome was further from the important eastern provinces and in a less strategically important location; it was not esteemed by the "soldier-emperors" who ruled from the frontiers or by the empire's population who, having been granted citizenship, considered themselves "Roman".[13] Constantine extensively reformed the empire's military and civil administration and instituted the gold solidus as a stable currency.[14] He favoured Christianity, which he had converted to in 312.[15]
Constantine's dynasty fought a lengthy conflict against Sasanid Persia and ended in 363 after the death of his son-in-law Julian.[16] The short Valentinianic dynasty, occupied with wars against barbarians, religious debates, and anti-corruption campaigns, ended in the East after the death of Valens at the Battle of Adrianople in 378.[17]
Valens's successor, Theodosius I (r. 379–395), restored political stability in the east by allowing the Goths to settle in Roman territory;[18] he also twice intervened in the western half, defeating the usurpers Magnus Maximus and Eugenius in 388 and 394 respectively.[19] He actively condemned paganism, confirmed the primacy of Nicene Christianity over Arianism, and established Christianity as the Roman state religion.[20] He was the last emperor to rule both the western and eastern halves of the empire;[21] after his death, the West was destabilised by a succession of "soldier-emperors", unlike the East, where administrators continued to hold power. Theodosius II (r. 408–450) largely left the rule of the east to officials such as Anthemius, who constructed the Theodosian Walls to defend Constantinople, now firmly entrenched as Rome's capital.[22]
Theodosius' reign was marked by the theological dispute over Nestorianism, which was eventually deemed heretical, and by the formulation of the Codex Theodosianus law code.[23] It also saw the arrival of Attila's Huns, who ravaged the Balkans and exacted a massive tribute from the empire; Attila however switched his attention to the rapidly-deteriorating western empire, and his people fractured after his death in 453.[24] After Leo I (r. 457–474) failed in his 468 attempt to reconquer the west, the warlord Odoacer deposed Romulus Augustulus in 476, killed his titular successor Julius Nepos in 480, and the office of western emperor was formally abolished.[25]
Through a combination of luck, cultural factors, and political decisions, the Eastern empire never suffered from rebellious barbarian vassals and was never ruled by barbarian warlords—the problems which ensured the downfall of the West.[26] Zeno (r. 474–491) convinced the problematic Ostrogoth king Theodoric to take control of Italy from Odoacer, which he did; dying when the empire was at peace, Zeno was succeeded by Anastasius I (r. 491–518).[27] Although his Monophysitism brought occasional issues, Anastasius was a capable administrator and instituted several successful financial reforms including the abolition of the chrysargyron tax. He was the first emperor, since Diocletian, who did not face any serious problems affecting his empire.[28]
518–717
The reign of Justinian I was a watershed in Byzantine history.[29] Following his accession in 527, the law-code was rewritten as the influential Corpus Juris Civilis and Justinian produced extensive legislation on provincial administration;[30] he reasserted imperial control over religion and morality through purges of non-Christians and "deviants";[31] and having ruthlessly subdued the 532 Nika revolt he rebuilt much of Constantinople, including the original Hagia Sophia.[32] Justinian took advantage of political instability in Italy to attempt the reconquest of lost western territories. The Vandal Kingdom in North Africa was subjugated in 534 by the general Belisarius, who then invaded Italy; the Ostrogothic Kingdom was destroyed in 554.[33]
In the 540s, however, Justinian began to suffer reversals on multiple fronts. Taking advantage of Constantinople's preoccupation with the West, Khosrow I of the Sasanian Empire invaded Byzantine territory and sacked Antioch in 540.[34] Meanwhile, the emperor's internal reforms and policies began to falter, not helped by a devastating plague that killed a large proportion of the population and severely weakened the empire's social and financial stability.[35] The most difficult period of the Ostrogothic war, against their king Totila, came during this decade, while divisions among Justinian's advisors undercut the administration's response.[36] He also did not fully heal the divisions in Chalcedonian Christianity, as the Second Council of Constantinople failed to make a real difference.[37] Justinian died in 565; his reign saw more success than that of any other Byzantine emperor, yet he left his empire under massive strain.[38]
Financially and territorially overextended, Justin II (r. 565–578) was soon at war on many fronts. The Lombards, fearing the aggressive Avars, conquered much of northern Italy by 572.[39] The Sasanian wars restarted that year, and continued until the emperor Maurice finally emerged victorious in 591; by that time, the Avars and Slavs had repeatedly invaded the Balkans, causing great instability.[40] Maurice campaigned extensively in the region during the 590s, but although he managed to re-establish Byzantine control up to the Danube, he pushed his troops too far in 602—they mutinied, proclaimed an officer named Phocas as emperor, and executed Maurice.[41] The Sasanians seized their moment and reopened hostilities; Phocas was unable to cope and soon faced a major rebellion led by Heraclius. Phocas lost Constantinople in 610 and was soon executed, but the destructive civil war accelerated the empire's decline.[42]
Bottom: the Theodosian Walls of Constantinople, critically important during the 717–718 siege.
Under Khosrow II, the Sassanids occupied the Levant and Egypt and pushed into Asia Minor, while Byzantine control of Italy slipped and the Avars and Slavs ran riot in the Balkans.[43] Although Heraclius repelled a siege of Constantinople in 626 and defeated the Sassanids in 627, this was a pyrrhic victory.[44] The early Muslim conquests soon saw the conquest of the Levant, Egypt, and the Sassanid Empire by the newly-formed Arabic Rashidun Caliphate.[45] By Heraclius' death in 641, the empire had been severely reduced economically as well as territorially—the loss of the wealthy eastern provinces had deprived Constantinople of three-quarters of its revenue.[46]
The next seventy-five years are poorly documented.[47] Arab raids into Asia Minor began almost immediately, and the Byzantines resorted to holding fortified centres and avoiding battle at all costs; although it was invaded annually, Anatolia avoided permanent Arab occupation.[48] The outbreak of the First Fitna in 656 gave Byzantium breathing space, which it used wisely: some order was restored in the Balkans by Constans II (r. 641–668),[49] who began the administrative reorganisation known as the "theme system", in which troops were allocated to defend specific provinces.[50] With the help of the recently rediscovered Greek fire, Constantine IV (r. 668–685) repelled the Arab efforts to capture Constantinople in the 670s,[51] but suffered a reversal against the Bulgars, who soon established an empire in the northern Balkans.[52] Nevertheless, he and Constans had done enough to secure the empire's position, especially as the Umayyad Caliphate was undergoing another civil war.[53]
Justinian II sought to build on the stability secured by his father Constantine but was overthrown in 695 after attempting to exact too much from his subjects; over the next twenty-two years, six more rebellions followed in an era of political instability.[54] The reconstituted caliphate sought to break Byzantium by taking Constantinople, but the newly crowned Leo III managed to repel the 717–718 siege, the first major setback of the Muslim conquests.[55]
718–867
Leo and his son Constantine V (r. 741–775), two of the most capable Byzantine emperors, withstood continued Arab attacks, civil unrest, and natural disasters, and reestablished the state as a major regional power.[56] Leo's reign produced the Ecloga, a new code of law to succeed that of Justinian II,[57] and continued to reform the "theme system" in order to lead offensive campaigns against the Muslims, culminating in a decisive victory in 740.[58] Constantine overcame an early civil war against his brother-in-law Artabasdos, made peace with the new Abbasid Caliphate, campaigned successfully against the Bulgars, and continued to make administrative and military reforms.[59] However, due to both emperors' support for the Byzantine Iconoclasm, which opposed the use of religious icons, they were later vilified by Byzantine historians;[60] Constantine's reign also saw the loss of Ravenna to the Lombards, and the beginning of a split with the Roman papacy.[61]
In 780, Empress Irene assumed power on behalf of her son Constantine VI.[62] Although she was a capable administrator who temporarily resolved the iconoclasm controversy,[63] the empire was destabilized by her feud with her son. The Bulgars and Abbasids meanwhile inflicted numerous defeats on the Byzantine armies, and the papacy crowned Charlemagne as Roman emperor in 800.[64] In 802, the unpopular Irene was overthrown by Nikephoros I; he reformed the empire's administration but died in battle against the Bulgars in 811.[65] Military defeats and societal disorder, especially the resurgence of iconoclasm, characterised the next eighteen years.[66]
Stability was somewhat restored during the reign of Theophilos (r. 829–842), who exploited economic growth to complete construction programs, including rebuilding the sea walls of Constantinople, overhaul provincial governance, and wage inconclusive campaigns against the Abbasids.[67] After his death, his empress Theodora, ruling on behalf of her son Michael III, permanently extinguished the iconoclastic movement;[68] the empire prospered under their sometimes-fraught rule. However, Michael was posthumously vilified by historians loyal to the dynasty of his successor Basil I, who assassinated him in 867 and who was given credit for his predecessor's achievements.[69]
867–1081
Basil I (r. 867–886) continued Michael's policies.[70] His armies campaigned with mixed results in Italy but defeated the Paulicians of Tephrike.[71] His successor Leo VI (r. 886–912)[b] compiled and propagated a huge number of written works. These included the Basilika, a Greek translation of Justinian I's law-code which included over 100 new laws created by Leo; the Tactica, a military treatise; and the Book of the Eparch, which codified Constantinople's trading regulations.[73] In non-literary contexts Leo was less successful: the empire lost in Sicily and against the Bulgarians,[74] while he provoked theological scandal by marrying four times in an attempt to father a legitimate heir.[75]
The early reign of that heir, Constantine VII, was tumultuous, as his mother Zoe, his uncle Alexander, the patriarch Nicholas, the powerful Simeon I of Bulgaria, and other influential figures jockeyed for power.[76] In 920, the admiral Romanos I used his fleet to secure power, crowning himself and demoting Constantine to the position of junior co-emperor.[77] His reign, which brought peace with Bulgaria and successes in the east under the general John Kourkouas, was ended in 944 by the machinations of his sons, whom Constantine soon usurped in turn.[78] Constantine's ineffectual sole rule has often been construed as the zenith of Byzantine learning, but while several works were compiled, they were largely intended to legitimise and glorify the emperor's Macedonian dynasty.[79] His son and successor died young; under two soldier-emperors, Nikephoros II (r. 963–969) and John I Tzimiskes (r. 969–976), the Roman army claimed numerous military successes, including the conquest of Cilicia and Antioch, and a sensational victory against Bulgaria and the Kievan Rus' in 971. John in particular was an astute administrator who reformed military structures and implemented effective fiscal policies.[80]
After John's death, Constantine VII's grandsons Basil II and Constantine VIII ruled jointly for half a century, although the latter exercised no real power.[81] Their early reign was occupied by conflicts against two prominent generals, Bardas Skleros and Bardas Phokas, which ended in 989 with the former's death and the latter's submission, and with a power struggle against the eunuch Basileios, who was dismissed in 985.[82] Basil, who for unknown reasons never married or had children, subsequently refused to delegate any authority: he sidelined the military establishment by taking personal command of the army and promoting officers loyal to him.[83] His reign was preoccupied with the decades-long campaign against Bulgaria, which ended in total Byzantine victory at the Battle of Kleidion in 1018.[84] Diplomatic efforts, critical for that success,[85] also contributed to the annexation of several Georgian provinces in the 1020s and coexistence with the new Fatimid Caliphate.[86] When he died in 1025, Basil's empire stretched from the Danube and Sicily in the west to the Euphrates in the east; his swift expansion was, however, unaccompanied by administrative reforms.[87]
After Constantine VIII's death in 1028, his daughters, the empresses Zoe (r. 1028–1052) and Theodora (r. 1042–1056), held the keys to power: four emperors (Romanos III, Michael IV, Michael V, and Constantine IX) ruled only because of their connection to Zoe, while Michael VI (r. 1056–1057) was selected by Theodora.[88] This political instability, regular budget deficits, a string of expensive military failures, and other problems connected to over-extension led to substantial issues in the empire;[89] its strategic focus moved from maintaining its hegemony to prioritizing defence.[90]
The empire soon came under sustained assault on three fronts, from the Seljuk Turks in the east, the Pecheneg nomads in the north, and the Normans in the west. The Byzantine army struggled with confronting these enemies, who did not organise themselves as traditional states and were thus untroubled by defeats in set-piece battles.[91] The year 1071 brought two consequential reverses: Bari, the last remaining Byzantine settlement in Italy, was captured by the Normans, while the Seljuks won a decisive victory at the Battle of Manzikert, taking the emperor Romanos IV Diogenes prisoner.[92] The latter event sparked a decade-long civil war, during which the Seljuks took possession of Anatolia up to the Sea of Marmara.[93]
1081–1204
One prominent general, Alexios I, usurped the throne in 1081. In contrast to the prior turmoil, the three reigns of Alexios (r. 1081–1118), his son John II (r. 1118–1143), and his grandson Manuel I (r. 1143–1180) lasted a century and restored the empire's regional authority for the final time.[94] Alexios immediately faced the Normans under Robert Guiscard, who were repelled through warfare and diplomacy.[95] He then targeted the Pechenegs, who were decisively defeated in 1091 with help from the Cumans, who were in turn defeated three years later.[96] Finally, looking to recover Asia Minor from the Seljuks, he approached Pope Urban II for help c. 1095. He did not anticipate the scale of western Christendom's response—the First Crusade led to the recapture of western Anatolia, although Alexios soon fell out with its leaders.[97] The rest of his reign was spent dealing with the Normans and Seljuks, establishing a new, loyal aristocracy to ensure stability, and carrying out fiscal and ecclesiastical reforms.[98]
Alexios' concentration of power in the hands of his Komnenos dynasty meant the most serious political threats came from within the imperial family—before his coronation, John II had to overcome his mother Irene and his sister Anna, and the primary threat during his reign was his brother Isaac.[99] John campaigned annually and extensively—he fought the Pechenegs in 1122, the Hungarians in the late 1120s, and the Seljuks throughout his reign, notably waging large campaigns in Syria in his final years—but did not achieve large territorial gains.[100] In 1138, John raised the imperial standard over the Crusader Principality of Antioch to intimidate the city into allying with the Byzantines, but chose not to attack, fearing that it would provoke western Christendom to respond.[101]
Manuel I utilised his father's overflowing imperial treasury in pursuit of his ambitions and to secure the empire's position in an increasingly multilateral geopolitical landscape.[102] Through a combination of diplomacy and bribery, he cultivated a ring of allies and clients around the empire: the Turks of the Sultanate of Rum, the Kingdom of Hungary, the Cilician Armenians, Balkan princes, Italian and Dalmatian cities, and most importantly Antioch and the Crusader States, marrying one of their princesses in 1161.[103] Manuel averted the threat of war during the tumultuous passage of the Second Crusade through Byzantine territories in 1147, but the campaign's failure was blamed on the Byzantines by western contemporaries.[104] He was less successful militarily: an invasion of Sicily was decisively defeated by King William I in 1156, leading to tensions with Frederick Barbarossa, the Holy Roman Emperor;[105] two decades later, an invasion of Anatolia was resoundingly defeated at the Battle of Myriokephalon.[106]
Manuel's death left the empire rudderless and it soon came under intense pressure.[107] His son Alexios II was too young to rule, and his troubled regency was soon overthrown by an uncle, who was himself replaced by Isaac II in 1185.[108] Centrifugal forces swirled at the borders as ambitious rulers seized their chance: Hungary and the Turks captured Byzantine territories, an exiled Komnenian prince seized Cyprus; and most injuriously, a revolt in 1185 caused the foundation of a resurrected Bulgarian state.[109] Relations with the west deteriorated further after Constantinople allied with Saladin, the vanquisher of the Third Crusade, whose leaders also conflicted with Byzantium as they passed through its territory.[110] In 1195, Isaac II was deposed by his brother Alexios III; this particular quarrel proved fatal.[111]
The Fourth Crusade was originally intended to target Egypt, but amid strategic difficulties, Isaac II's son Alexios Angelos convinced the crusaders to restore his father to the throne in exchange for a huge tribute.[112] They attacked Constantinople in 1203, reinstating Isaac II and his son to the throne. The new rulers grew swiftly unpopular and were deposed by Alexios V, which the crusaders used as a pretext to sack the city in April 1204, ransacking the wealth it had accumulated over nine centuries.[113]
1204–1453
Byzantine territories fragmented into competing political entities. The crusaders crowned Baldwin I as the ruler of a new Latin Empire in Constantinople; it soon suffered a crushing defeat against the Bulgarians in 1205. It also failed to expand west or east, where three Greek successor states had formed: the Empire of Nicaea and the Empire of Trebizond in Asia Minor, and the Despotate of Epirus on the Adriatic. The Venetians acquired many ports and islands, and the Principality of Achaea emerged in southern Greece.[114] Trebizond lost the key port of Sinope in 1214 and thereafter was unable to affect matters away from the southeastern Black Sea.[115] For a time, it seemed like Epirus was the one most likely to reclaim Constantinople from the Latins, and its ruler Theodore Doukas crowned himself emperor, but he suffered a critical defeat in 1230 and Epirote power waned.[116]
Nicaea, ruled by the Laskarid dynasty and composed of a mixture of Byzantine refugees and native Greeks, blocked the Latins and the Seljuks of Rum from expanding east and west respectively.[117] John III (r. 1221–1254) was a very capable emperor.[118] His protectionist economic policies strongly encouraged Nicaean self-sufficiency,[119] while he made many diplomatic treaties, especially after Mongol armies ravaged Bulgaria and defeated Rum between 1237 and 1243. This chaos was an opportunity for John, who fought numerous successful campaigns against the states which bore the brunt of the Mongol invasions.[120] Soon after his death, his grandson was usurped by Michael VIII, founder of the Palaiologos dynasty, who recaptured Constantinople in 1261.[121]
Michael chose to expand the empire, gaining only short-term success. To avoid another sacking of the capital by the Latins, he forced the Church to submit to Rome, again a temporary solution for which the peasantry hated Michael and Constantinople.[122] The efforts of Andronikos II and later his grandson Andronikos III marked Byzantium's last genuine attempts to restore the glory of the empire. However, the use of mercenaries by Andronikos II often backfired, like the time the Catalan Company ravaged the countryside, which increased public resentment towards Constantinople.[123]
The situation became worse for Byzantium during the civil wars which erupted after Andronikos III died. A six-year-long civil war devastated the empire, allowing the Serbian ruler Stefan Dušan to overrun most of the empire's remaining territory and establish a Serbian Empire.[124] In 1354, an earthquake at Gallipoli devastated the fort, allowing the Ottomans to conquer it and establish themselves in Europe, after originally being hired as mercenaries during the civil war by John VI Kantakouzenos.[125] By the time the Byzantine civil wars ended, the Ottomans had defeated the Serbians and subjugated them as vassals. After the Battle of Kosovo, much of the Balkans became dominated by the Ottomans.[126]
Constantinople at this stage was underpopulated and dilapidated. The population of the city had collapsed so severely that it was now little more than a cluster of villages separated by fields. On 2 April 1453, Sultan Mehmed's army of 80,000 men and large numbers of irregulars laid siege to the city.[127] Despite a desperate last-ditch defence of the city by the massively outnumbered Christian forces (c. 7,000 men, 2,000 of whom were foreign),[128] Constantinople finally fell to the Ottomans after a two-month siege on 29 May 1453. The final Byzantine emperor, Constantine XI Palaiologos, was last seen casting off his imperial regalia and throwing himself into hand-to-hand combat after the walls of the city were taken.[129]
Government
Governance
The patriarch inaugurated emperors from 457 onwards, while the crowds of Constantinople proclaimed their support, thus legitimizing their rule.[130] The senate originally had its own identity but later became a ceremonial extension of the emperor's court.[131] The reign of Phocas (r. 602–610) was the first military coup after the third century, and he was one of 43 emperors violently removed from power.[132] From Heraclius' accession in 610 till 1453, a total of nine dynasties ruled the Empire. During this time, for only 30 of the 843 years were the reigning emperors unrelated by blood or kinship, largely due to the practice of co-emperorship.[133]
Diocletian and Constantine's reforms reorganized the Empire into Praetorian prefectures and separated the army from the civil administration.[134] From the 7th century onward, these prefectures were reorganized into provinces and later divided into districts called themata, governed by military commanders known as strategos, who oversaw both civil and military matters.[135] Before this change, cities were self-governing communities represented by central government and church officials, while emperors focused on defense and foreign relations.[136] However, constant wars and raids by Arab forces drastically changed this structure. City councils declined, as did the local elites who supported them. Through his legal reforms, Leo VI (r. 886–912) centralised power, formally ending city councils' rights and the legislative authority of the senate.[137]
Diplomacy
Diplomacy is often regarded as one of the Empire's lasting contributions to European history, particularly in preserving civilization in Eastern Europe.[138] This reputation stems from its aggressive treaty negotiations, alliances with the enemies of its adversaries, and strategic partnerships.[139] For instance, the Empire supported the Turks against the Persians during the Perso-Turkic War (627–629) and exploited tensions between the Umayyads in Spain and the Aghlabids in Sicily.[140] Diplomacy frequently involved long-term embassies, hosting foreign royals as political pawns, and deliberately displaying wealth and power to ensure such impressions spread widely.[141] Other diplomatic strategies included political marriages, granting titles, bribery, persuasion, and intelligence gathering.[142] Notably, the 'Bureau of Barbarians', established in the 4th century, is considered one of the earliest foreign intelligence agencies.[139]
Diplomacy after the reign of Theodosius I (r. 379–395) shifted significantly from the more conquest-focused policies of the Roman Republic, instead emphasizing peace as a strategic necessity.[143] Even in the 6th century, when the Empire had greater resources and fewer threats, the enormous costs of defense, agricultural self-reliance, and aggressive neighbors made avoiding war a priority.[144] Between the 4th and 8th centuries, diplomats capitalized on the Empire's reputation as the Orbis Romanus and its administrative sophistication to influence new settlements on former Roman territories.[145] Byzantine diplomacy often drew fledgling states into dependency, creating a network of inter-state relations (the oikouménē) dominated by the Empire and leveraging Christianity to strengthen these ties.[146] This network emphasized treaty-making, integrating new rulers into the "family of kings," and assimilating values, institutions, and attitudes.[147] These practices have even been referred to as creating a "Byzantine Caliphate", where religion re-framed the civilised-versus-barbarian dichotomy in classical times.[148] By contrast, diplomatic relations with Muslim states focused primarily on war-related issues, such as negotiating hostages or preventing hostilities.[149]
Peace and survival, rather than conquest, were central objectives. Historians describe this approach as "defensive imperialism," which evolved between the 9th and 10th centuries to include halting and reversing Muslim advances, cultivating alliances with Armenians and Rus, and subjugating the Bulgarians.[150][151] Diplomatic relations with Western states became more challenging after 752–753 and particularly during the Crusades, as shifts in the balance of power undermined the Empire's dominance and its use of the Limitrophe system.[152] By the 11th century, the Empire adopted a principle of diplomatic equality, leveraging the emperor's personal presence to negotiate.[153]
After recovering Constantinople in 1261, the Empire maintained its influence as a great power in the 13th and 14th centuries, despite its declining strength. This success is attributed to its efficient statecraft and strategic use of the Constantinople patriarch.[154]
Law
Roman law originated with the Twelve Tables and evolved primarily through the annual Praetorian Edict and the opinions of educated specialists known as Jurists.[155] Hadrian (r. 117–138) made the Praetorian Edict permanent and established a rule where a legal point jurists unanimously agreed on became law.[156] Over time, conflicting legal sources caused confusion about what the law should be.[157] Efforts to address this included two private collections of imperial constitutions compiled during Diocletian's reign (284–305), the Gregorianus and the Hermogenianus (r. 284–305).[158]
Theodosius II (r. 402–450) formalized Roman law by appointing five jurists as principal authorities and compiling legislation issued since Constantine’s reign into the Codex Theodosianus.[159] This process culminated in the Corpus Juris Civilis under Justinian I (r. 527–565), who commissioned a complete standardization of imperial decrees since Hadrian’s time and resolved conflicting legal opinions.[160] The result became the definitive legal authority. This body of law covered not only civil matters but also public law, including imperial power and administrative organization.[161] After 534, Justinian issued the Novellae (New Laws) in Greek, which marked a transition from Roman to Byzantine law. Legal historian Bernard Stolte distinguishes Roman law as this because Western Europe inherited law through the Latin texts of the Corpus Juris Civilis only.[162]
Zachary Chitwood argues that the Corpus Juris Civilis was largely inaccessible in Latin, particularly in the provinces.[163] Following the 7th-century Islamic conquests, people began questioning the development and application of law, leading to stronger ties between law and Christianity.[164] This context influenced Leo III (r. 717–741) to develop the Ecloga, which emphasized humanity.[165] The Ecloga inspired practical legal texts like the Farmers' Law, Seamen's Law, and Soldiers' Law, which Chitwood suggests were used daily in the provinces as companions to the Corpus Juris Civilis.[166] During the Macedonian dynasty, efforts to reform law began with the Procheiron and the Eisagoge, which aimed to replace the Ecloga due to its association with iconoclasm and to define the emperor's power under prevailing laws.[167] Leo VI (r. 886–912) completed a complete codification of Roman law in Greek through the Basilika, a monumental work of 60 books that became the foundation of Byzantine law.[168] Later, in 1345, Constantine Harmenopoulos compiled the Hexabiblos, a six-volume law book derived from various Byzantine legal sources.[169]
Military
Army
In the 5th century the East was fielding five armies of ~20,000 each in two army branches: stationary frontier units (limitanei) and mobile forces (comitatenses).[170] The historian Anthony Kaldellis claims that the fiscally stretched Empire could only handle one major enemy at a time in the 6th century.[171] The Islamic conquests between 634 and 642 led to significant changes, transforming the 4th-7th centuries field forces into provincial militia-like units which had a core of professional soldiers.[172] The state shifted the burden of supporting the armies onto local populations and during Leo VI (r. 886–912) wove them into the tax system, where provinces evolved into military regions known as themata.[173] Despite many challenges, the historian Warren Treadgold states that the field forces of the Eastern Empire between 284 and 602 were the best in the western world, while the historian Anthony Kaldellis believes that during the conquest period of the Macedonian dynasty (r. 867–1056), they were the best in the empire's history.[174]
The military structure diversified to incorporate militia-like soldiers tied to regions, professional thematic forces (tourmai), and imperial units mostly based in Constantinople (tagmata).[175] Foreign mercenaries also increasingly became employed, including the better-known tagma regiment, the Varangians, that guarded the emperor.[176] The defence-orientated thematic militias were gradually replaced by more specialised offensive field armies, which could also counter the generals who rebelled against the emperor.[177] When the Empire was expanding, the state began to commute thematic military service for cash payments: in the 10th century, there were 6,000 Varangians, another 3,000 foreign mercenaries and when including paid and unpaid citizen soldiers, the army on paper was 140,000 (an expeditionary force was 15,000 soldiers and field armies seldom were more than 40,000).[178]
The thematic forces faded into insignificance—the government relying on the tagmata, mercenaries and allies instead—and which led to a neglect in defensive capability.[179] Mercenary armies further fueled political divisions and civil wars that led to a collapse in the Empire's defence, and resulted in significant losses over territories such as Italy and the Anatolian heartland in the 11th century.[180] Major military and fiscal reforms under the emperors of the Komnenian dynasty after 1081 re-established a modest-sized, adequately compensated and competent army.[181] However, the costs were not sustainable and the structural weaknesses of the Komnenian approach—namely, the reliance on fiscal exemptions called pronoia—unraveled after the end of the reign of Manuel I (r. 1143–1180).[182]
Navy
The navy dominated the eastern Mediterranean and were active also on the Black Sea, the Sea of Marmara, and the Aegean.[183] Imperial naval forces were restructured to challenge Arab naval dominance in the 7th century, and later ceded their own maritime dominance to the Venetians and Genoans in the 11th century.[184] The navy's patrols, as well as the chains of watchtowers and fire signals that warned inhabitants of threats, created the coastal defense for the Empire and were the responsibility of three themes: Cibirriote, Aegean Sea, Samos and an imperial fleet that consisted of mercenaries like the Norsemen and Russians that later became Varangians.[185]
A new type of war galley, the dromon, appeared early in the sixth century.[186][187] A multi-purpose variant, the chelandia, appeared during the reign of Justinian II (r. 685–711) and could be used to transport cavalry.[188] The galleys were oar-driven, designed for coastal navigation, and are estimated to be able to operate for up to four days at a time.[189][190] They were equipped with apparatus to deliver Greek fire in the 670s, and when Basil I (r. 867–886) developed professional marines, this combination kept a check on Muslim raiding through piracy.[191] The dromon was the most advanced galley on the Mediterranean, until the 10th century development of a dromon called a galeai, which superseded dromons after the development of a late 11th century Western (Southern Italian) variant.[192]
Late era (1204–1453)
The rulers of the Empire of Nicaea that retook the capital and the Palaiologos that ruled until 1453, built on the Komnenian foundation initially with four types of military units—the Thelematarii (volunteer soldiers), Gasmouloi and the Southern Peloponnese Tzacones/Lakones (marines), and Proselontes/Prosalentai (oarsmen)—but similarly could not sustain funding a standing force, largely relying on mercenaries as soldiers and fiscal exemptions to pronoiars who provided a small force of mostly cavalry.[193] The Fleet was disbanded in 1284 and attempts were made to build it back later but the Genoese sabotaged the effort.[194] The historian John Haldon claims that over time, the distinction between field troops and garrison units eventually disappeared as resources were strained.[195] The frequent civil wars further drained the Empire, now increasingly instigated by foreigners such as the Serbs and Turks to win concessions, and the emperors were dependent on mercenaries to keep control, all the while dealing with the impact of the Black Death.[196] The strategy of employing mercenary Turks to fight civil wars was repeatedly used by emperors and always led to the same outcome: subordination to the Turks.[197]
Society
Demography
As many as 27 million people lived in the Empire at its peak in 540, but fell to as low as 12 million by 800.[198] Although plague and territorial losses to Arab Muslim invaders weakened the Empire, it eventually recovered and by the near end of the Macedonian dynasty in 1025, the population is estimated to have been as high as 18 million.[199] A few decades after the recapture of Constantinople in 1282, the Empire's population was in the range of 3–5 million; by 1312, the number had dropped to 2 million.[200] By the time the Ottoman Turks captured Constantinople, there were only 50,000 people in the city, which was one-tenth of its population in its prime.[201]
Education
Education was voluntary and required financial means, so the most literate people were often those associated with the church.[202] Primary education focused on teaching foundational subjects like reading, writing, and arithmetic whereas Secondary school focused on the trivium and quadrivium as their curriculum.[203] The Imperial University of Constantinople was formed in 425, and refounded in 1046 as a centre for law.[204][205][206]
Slavery
During the third century, 10–15% of the population was enslaved (numbering around 3 million in the east).[207] Youval Rotman calls the changes to slavery during this period "different degrees of unfreedom".[208] Previous roles fulfilled by slaves became high-demand free market professions (like tutors), and the state encouraged the coloni, tenants bound to the land, as a new legal category between freemen and slaves.[209] From 294, but not completely, the enslavement of children was forbidden; Honorius (r. 393–423) began freeing enslaved people who were prisoners of war, and from the 9th century onward, emperors freed the slaves of conquered people.[210] Christianity as an institution had no direct impact, but by the 6th century it was a bishop's duty to ransom Christians, there were established limits on trading them, and state policies which prohibited the enslavement of Christians shaped Byzantine slave-holding from the 8th century onwards.[211] However, slavery persisted due to a steady source of non-Christians, prices thus remained stable until 1300, when prices for adult slaves, particularly females, started rising.[212][213]
Socio-economic
Agriculture was the main basis of taxation and the state sought to bind everyone to land for productivity.[214] Most land holdings were small and medium-sized lots around villages, with family farms serving as the primary source of agriculture.[215] The coloni, sometimes called proto-serfs, were free citizens, though historians still debate their exact status.[216]
The Ekloge in 741 made marriage a Christian institution and no longer a private contract, where it evolved alongside the increased rights of slaves and the change in power relations.[217] Marriage was considered an institution to sustain the population, transfer property rights, support the elderly of the family; and the Empress Theodora had additionally said that it was needed to restrict sexual hedonism.[218] Women usually married between ages 15 and 20, and the average family had two children.[219] Divorce could be done by mutual consent but was restricted over time, for example, only being allowed if a married person was joining a convent.[220]
Inheritance rights were well developed, including for all women.[221] The historian Anthony Kaldellis claims that these rights may have been what prevented the emergence of large properties and a hereditary nobility capable of intimidating the state.[222] The prevalence of widows (estimated at 20%) meant that women often controlled family assets as heads of households and businesses, contributing to the rise of some empresses to power.[223] Women played significant roles as taxpayers, landowners, and petitioners, often seeking to resolve property disputes in court.[224]
Women
Although women shared the same socio-economic status as men, they faced legal discrimination and had limitations in economic opportunities and vocations.[225] Prohibited from serving as soldiers or holding political office, and restricted from serving as deaconesses in the Church from the 7th century onwards, women were mostly assigned household responsibilities that were "labour-intensive".[226] They worked in professions, such as in the food and textile industry, as medical staff, in public baths, had a heavy presence in retail, and were practicing members of artisan guilds.[227] They also worked in disreputable occupations: entertainers, tavern keepers, and prostitutes; a class where some saints and empresses allegedly originated from.[228] Prostitution was widespread, and attempts were made to limit it, especially during Justinian's reign under the influence of Theodora.[229] Women participated in public life, engaging in social events and protests.[230] Women's rights were not better in comparable societies, Western Europe or America until the 19th century.[231]
Language
Right: The Joshua Roll, a 10th-century illuminated Greek manuscript possibly made in Constantinople (Vatican Library, Rome)
There was never an official language of the Empire, however, Latin and Greek were the main languages.[232] During the early years of the Roman Empire, educated nobles often relied on their knowledge of Greek to meet societal expectations, and knowledge of Latin was useful for a career in the military, government, or law.[233] In the east, Greek was the dominant language, a legacy of the Hellenistic period.[234] Greek was also the language of the Christian Church and trade.[235]
Most early emperors were bilingual but had a preference for Latin in the public sphere for political reasons, a practice that first started during the Punic Wars.[236] Classical languages expert Bruno Rochette claims Latin had experienced a period of spread from the second century BC onwards, and especially so in the western provinces, but not as much in the eastern provinces with a change due to Diocletian's reforms: there was a decline in the knowledge of Greek in the west, and Latin was asserted as the language of power in the east.[237]
Despite this, Greek's influence gradually grew in the government, beginning when Arcadius in 397 AD allowed judges to issue decisions in Greek, Theodosius II in 439 expanded its use in legal procedures, the first law in Greek was issued in 448, and when Leo I legislated in the language in the 460s.[239] Justinian I's Corpus Juris Civilis, a compilation of mostly Roman jurists, was written almost entirely in Latin; however, the laws issued after 534, from Justinian's Novellae Constitutiones onwards, were in both Greek and Latin, which marks the year when the government officially began to use the former language.[240]
Historian Nikolaos Oikonomides states that Greek for a time became diglossic with the spoken language, known as Koine (later, Demotic Greek), used alongside an older written form (Attic Greek) until Koine won out as the spoken and written standard.[241] Latin fragmented into the incipient Romance languages in the 8th century, following the collapse of the Western Empire after the Muslim invasions broke the connection between speakers.[242][243] During the reign of Justinian (r. 527–565), Latin disappeared in the east, though it may have lingered in the military until Heraclius (r. 610–641).[244] Historian Steven Runciman claims contact with Western Europe in the 10th century revived Latin studies, and by the 11th century, knowledge of Latin was no longer unusual in Constantinople.[245]
Many other languages are attested in the Empire, not just in Constantinople but also at its frontiers.[246] They include Syriac, Coptic, Slavonic, Armenian, Georgian, Illyrian, Thracian, and Celtic; these were typically the languages of the lower strata of the population and the illiterate, who were the vast majority.[247] The Empire initially was a multi-lingual state, and although Greek bound everyone, there was a decline in the diversity of its peoples' languages over time.[248]
Economy
The Empire's geographic and maritime advantages reduced the costs of transporting goods and facilitated trade, making it a key driver of economic growth from antiquity and through the post-classical period.[249] Infrastructure, including roads, public buildings, and the legal system, supported trade and other economic activities.[250] Regions like Asia Minor, the Aegean islands, Egypt, the Levant, and Africa thrived as mature economic centres despite political challenges and military insecurities.[251] From the mid-6th century onward, however, plagues, invasions, and wars caused populations and economies to decline significantly, leading to the collapse of the ancient economy.[252] Major cities like Constantinople, Antioch, Alexandria, and Thessaloniki continued to support substantial populations exceeding 100,000, while the countryside transitioned into fortified settlements.[253] These rural areas developed into hamlets and villages, reflecting an economic shift between historical periods toward more efficient land use.[254]
Low population density prompted emperors to encourage migration and resettlement, stimulating agriculture and demographic growth.[255] By the 9th century, the economy began to revive, marked by increased agricultural production and urban expansion.[256] Advances in science, technical knowledge, and literacy gave the Empire a competitive edge over its neighbors.[257] The 11th and 12th centuries saw the continued rapid population growth, marking the peak of this revival.[258] Meanwhile, Italian merchants, particularly Venetians, Genoese, and Pisans, took control of international trade, thus reducing the influence of native merchants.[259] The political system grew increasingly extractive and authoritarian, contributing to the Empire's collapse in 1204.[260]
The fall of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade in 1204 destroyed its wealth, led to the confiscation of large landholdings and the fragmentation of the Empire into smaller rump states, making governance inefficient and increasing the costs of doing business.[261] The state gradually lost its control over trade practices, price regulations, the outflow of precious metals, and possibly even the minting of coins.[262] Italian merchants further dominated trade as the events of 1204 opened the Black Sea to Western merchants, permanently altering the Empire's fortunes.[263] Farmers increasingly produced goods for local use and were affected by the insecurity of constant warfare.[264] Despite these challenges, the Empire's mixed economy—characterised by state interventions, public works, and market liberalisation—remained a model of medieval economic adaptability, even as it deteriorated under external pressures.[265]
Daily life
Clothing
Historical evidence of Byzantine dress is scant. However, it is known that the court had a distinguishable dress, while non-elite men and women observed certain conventions of clothing.[266] Fashion trends started in the provinces, and not in the capital, which was more conservative.[267] The imperial dress was centred around the loros, tzangia and crown which represented the empire and the court.[268] The loros derived from the trabea triumphalis, a ceremonial toga worn by consuls. It was more prominent in the early empire, indicating a continuation of the traditions of the Roman Empire.[269] Historian Jennifer Ball claims that the chlamys cloak was like a modern-day business suit, which originated with the military, and was an evolution of the paludamentum cloak worn by aristocratic men including the emperor during the early empire.[270] In the middle empire, dresses replaced the tunic for women.[271] The late empire saw the larger influence on Byzantine dress of non-Greek cultures like the Italians (Genoese, Venetian), Turks (Ottomans) and Bulgarians.[272]
Cuisine
Feasting was a major part of Byzantine culture and included the use of clean tables and forks. Modern Italian standards of gastronomy are likely to have been influenced by this era.[273] Foods which are contemporary in the modern world are, among others, a cured meat called paston, baklava, Feta cheese, salt roe similar to the modern boutargue, black sea caviar, fermented fish sauce, tiropita, dolmades, and the soup trachanas.[274][275] Fruits unknown from classical times which were added to Byzantine diets included aubergines (eggplants) and oranges.[276] There were famed medieval sweet wines such as the Malvasia from Monemvasia, the Commandaria, and the eponymous Rumney wine that were drunk, as were millet beer (known as boza) and Retsina.[277]
Recreation
Chariot races were held since the early era till 1204, becoming one of the world's longest continuous sporting events.[279] Mimes, the pantomime and some wild-animal shows were prominent until the 6th century.[280] Because Christian bishops and pagan philosophers did not like these activities, the state's funding for them ceased, leading to their decline and a shift to private entertainment and sporting.[281] A Persian version of Polo introduced by the Crusaders called Tzykanion was played by the nobility and urban aristocracy in major cities during the middle and late eras, along with the sport of jousting introduced from the West.[282] Over time, game boards like tavli became increasingly popular.[283]
Religion
The granting of citizenship to all free Roman men in 212 fostered greater societal uniformity, particularly in religious practices.[284][285] Christianity, bolstered by Constantine's support, began shaping all aspects of life.[286] Subsequent emperors encouraged conversion and enacted laws in the late 4th century to restrict pagan activities.[287] In 529, Justinian enforced conversions, specifically targeting polytheists.[288] The confiscation of pagan treasures, diversion of funds, and legal discrimination led to the decline of paganism, resulting in events like the closure of schools of philosophy and the end of the Ancient Olympics.[c][291] Christianity's debates increased the importance of Greek, making the emergent church dependent on branches of Hellenic thought such as Neoplatonism.[d][293] Despite the transition, the historian Anthony Kaldellis views Christianity as "bringing no economic, social, or political changes to the state other than being more deeply integrated into it".[294]
When the Roman state in the West politically collapsed, cultural differences began to divide the Christian churches of the East and West.[296] Internal disputes within the Eastern churches led to the migration of monastic communities to Rome, exacerbating tensions between Rome and Constantinople.[297] These disputes,[e] particularly in Egypt and the eastern Mediterranean, eventually split the church into three branches: Chalcedonian, Monophysite (Coptic), and Nestorian.[300] The Chalcedonian group maintained dominance within the Empire’s territories, while the Monophysite and Nestorian branches largely fell under Muslim rule following the rise of Islam in the 7th century.[301]
Eastern patriarchs frequently sought the Papacy’s mediation in doctrinal and practical matters, but the pope’s authority was not universally acknowledged, even in nearby regions like Northern Italy.[302] By 600, the Slavic settlement of the Balkans disrupted communication between Rome and Constantinople, further widening the divide.[303] The Arab and Lombard invasions, and the increased Frankish presence, deepened this estrangement and intensified disputes over jurisdiction and authority between the two spiritual centres.[304] Differences in ritual and theology, such as the use of unleavened bread and the Filioque clause, along with divergences in ecclesiology — plenitudo potestatis versus the authority of Ecumenical Councils — and issues of mutual respect, contributed to the separation of Western Christianity from Eastern Christianity.[305] This separation began as early as 597 and culminated more definitively in 1054 during the East–West Schism.[306]
In 1439, a proposed reunion between the Eastern and Western churches faced Eastern resistance, delaying its official publication in Constantinople until 1452.[307] This agreement was overturned the following year by the Fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Turks in 1453.[308] The conquest of 1453 marked the destruction of the Church as the central institution of the Christian empire established by Constantine, isolating Greek-speaking Orthodoxy from the West and restricting its influence for nearly 150 years.[309] Despite this, the Church survived in an altered form, and the spiritual and cultural influence of the Eastern Church, Constantinople, and Mount Athos the monastic peninsula has endured.[310]
Arts
Art and architecture
- Christ Pantocrator icon, 6th-century, Sinai Monastery
- Hosios Loukas mosaics, detail, early 11th century
- Barberini ivory, an early 6th-century ivory diptych[311]
- The Hagia Sophia exterior
- Dead Christ and Mourners, c. 1164, Gorno Nerezi[312]
Subjects in Byzantine art were primarily Christian and typically non-naturalistic in their representation.[313] Emerging from both the earliest Christian and Late Antique art,[314] many early examples were lost amid the Roman Persecution; the fragmented mosaics of the 3rd-century Dura-Europos church are a unique exception.[315] Such Byzantine mosaics, known for their gold ground style, became a hallmark of the empire, appearing with both secular and sacred themes in diverse places, including churches (Basilica of San Vitale), the circus (Hippodrome of Constantinople), and the Great Palace of Constantinople.[316] The early 6th-century reign of Justinian I saw systemic developments: religious art came to dominate and once-popular public marble and bronze monumental sculpture fell out of favor due to pagan associations.[317] Justinian commissioned the monumental Hagia Sophia church, influential elements of which became architectural hallmarks for the empire: the immense size, massive dome, innovative use of pendentives and highly decorative interior was imitated as far north as the Cathedral of Saint Sophia in Novgorod and the Saint Sophia Cathedral in Kyiv.[318] The Hagia Sophia's creators, the engineer-architects Isidore of Miletus and Anthemius of Tralles, are uniqely esteemed;[319] most Byzantine artists were unrecorded and typically deemed of little importance.[320]
Smaller-scale art flourished throughout the entire Byzantine period: costly ivory carvings—often as diptychs (Barberini ivory) or triptychs (Harbaville Triptych)—featured imperial commemorations or religious scenes and were particularly esteemed, as were metalwork and enamels.[321] Other costly objects included illuminated manuscripts, which were lavishly illustrated for a wide range of texts, and silks, often including the prized imperial purple, both of which became highly popular in Western Europe.[322] The rise of small, portable icon paintings, used for both public and private religious worship, grew increasingly controversial.[323] During two periods of Byzantine Iconoclasm (726–843), possibly influenced by Islamic prohibitions on religious images,[324] icons faced severe suppression and enormous amounts of figurative religious art was destroyed.[325] Iconoclasts condemned their use, likening them to pagan idolatry and ascribing recent Umayyad defeats as divine retribution for their use, while iconophile supporters eventually prevailed, maintaining their essential use for veneration, considered distinct from worship, and found precedent in Gospel references.[326]
Post-iconoclast Macedonian art (867–1056) saw a cultural Renaissance, from which an unprecedentedly vast amount of artworks survive.[327] Subjects and styles became standardized, particularly cross-in-square churches, and already-existing frontality and symmetry evolved into a dominant artistic aesthetic, observable in the small Pala d'Oro enamel and the large mosaics of Hosios Loukas, Daphni, and Nea Moni monasteries.[328] The subsequent Komnenos-Angelos periods (1081–1204) saw increased imperial patronage, alongside figurative artwork of increased emotional expression (Dead Christ and Mourners, c. 1164; see right).[312] Byzantine artistic influence spread widely to Norman–Sicily (the Madrid Skylitzes) and Venice (mosaics of St Mark's Basilica).[312] Serbian churches flourished in particular, as three successive schools of architecture—Raška (1170–1282), Byzantine Serbia (1282–1355), and Morava (1355–1489)—combined a Romanesque aesthetic with increasingly voluminous decorations and domes.[329] As smaller Palaeologan artworks (1261–1453) gained relic status in Western Europe—many looted in the 1204 Fourth Crusade—they greatly influenced Italo-Byzantine style of Cimabue, Duccio, and later Giotto, who is traditionally regarded by art historians as the inaugurator of Italian Renaissance painting.[330]
Literature
Byzantine literature concerns all Greek literature from the Middle Ages.[331] Although the Empire was linguistically diverse, the vast majority of extant texts are in medieval Greek,[332] albeit in two diglossic variants: a scholarly form based on Attic Greek, and a vernacular based on Koine Greek.[333] Most contemporary scholars consider all medieval Greek texts to be literature,[334] but some offer varying constraints.[335] The literature's early period (c. 330–650) was dominated by the competing cultures of Hellenism, Christianity and Paganism.[336] The Greek Church Fathers—educated in an Ancient Greek rhetoric tradition—sought to synthesize these influences.[331] Important early writers include John Chrysostom, Pseudo-Dionysius the Areopagite and Procopius, all of whom aimed to reinvent older forms to fit the empire.[337] Theological miracle stories were particularly innovative and popular;[337] the Sayings of the Desert Fathers (Apophthegmata Patrum) were copied in practically every Byzantine monastery.[338] During the Byzantine Dark Ages (c. 650–800), production of literature mostly stopped, although some important theologians were active, such as Maximus the Confessor, Germanus I of Constantinople and John of Damascus.[337]
The subsequent cultural Macedonian Renaissance (c. 800–1000; the "Encyclopedism period") saw a renewed proliferation of literature and revived the earlier Hellenic-Christian synthesis.[331] Works by Homer, Ancient Greek philosophers and tragedians were translated, while hagiography was heavily reorganized.[337] After this early flowering of monastic literature, there was a dearth until Symeon the New Theologian in the late 10th-century.[337] A new generation (c. 1000–1250), including Symeon, Michael Psellos and Theodore Prodromos, rejected the Encyclopedist emphasis on order, and were interested in individual-focused ideals variously concerning mysticism, authorial voice, heroism, humor and love.[339] This included the Hellenistic-inspired Byzantine romance and Chivalric approaches in rhetoric, historiography and the influential epic Digenes Akritas.[337] The empire's final centuries saw a renewal of hagiography and increased Western influence, leading to mass Greek to Latin translations.[340] Authors such as Gemistos Plethon and Bessarion exemplified a new focus on human vices alongside the preservation of classical traditions, which greatly influenced the Italian Renaissance.[340]
Music
Byzantine music is eclectically descended from early Christian plainsong, Jewish music, and a variety of ancient music, although its exact connections to ancient Greek music remain uncertain.[342] While it included both sacred and secular traditions, the latter is little known, whereas the former remains the central music of Eastern Orthodox liturgy into the 21st century.[343] The empire's church music, known as Byzantine chant, was exclusively unaccompanied monodic vocal music, sung in Greek.[344] From the 8th century onwards, chant melodies were governed by the Oktōēchos framework, a set of eight modes—echos (ἦχος; lit. 'sound')—each of which provide predetermined motivic formulae for composition.[345] These formulae were chosen for proper text stress and occasionally for text painting, then centonizationally collated into a variety of hymns or psalms.[346]
Byzantine chant was central to the Byzantine Rite; however, the earliest music was not notated,[347] including early monostrophic short hymns like the troparion.[348] While proto-Ekphonetic notation (9th century onwards) marked simple recitation patterns, the neumatic Palaeo-Byzantine notation system emerged in the 10th century, while the Middle Byzantine "Round Notation" from mid-12th century onwards is the first fully diastematic scheme.[349] Several major forms developed alongside well-known composers: the long kontakion (5th century onwards), popularised by Romanos the Melodist; the also-extensive kanōn (late 7th century onwards), developed by Andrew of Crete; and the shorter sticheron (at least 8th century onwards), championed by Kassia.[350] By the Palaiologan period, the dominance of strict compositional rules lessened and John Koukouzeles led a new school which favoured a more ornamental "kalophonic" style that deeply informed post-empire Neo-Byzantine music.[351]
Secular music, often state-sponsored, was ubiquitous in daily life and featured in a variety of ceremonies, festivals, and theatre.[352] Secular vocal music was rarely notated, and extant manuscripts date much later, suggesting the tradition was passed through oral tradition and likely improvised.[353] Prohibited for liturgical use, a wide variety of Byzantine instruments flourished in secular contexts, although notated instrumental music does not survive.[354] It is uncertain to what extent instrumentalists improvised or if they doubled vocalists monophonically or heterphonically.[355] Among the best known instruments are the hydraulic organ, used for both circus and imperial court events; the ancient Greek-descended aulos, a wind instrument; the tambouras, a plucked string instrument; and mostly popularly, the Byzantine lyra.[355] Prominent genres included acclamation chants of laudation or salutation; the celebratory Acritic songs; symposia instrumental banquets, based on ancient symposiums; and dance music.[356]
Science and medicine
Science
Byzantine science played an important and crucial role in the transmission of classical knowledge to the Islamic world and Renaissance Italy.[357][358] Many of the most distinguished classical scholars held high offices in the Eastern Orthodox Church.[359]
The manuscripts of classical antiquity were studied and preserved in Byzantium. Therefore, Byzantine science was, in every era, closely connected t0 ancient philosophy and metaphysics.[360] In the field of engineering, Isidore of Miletus, the Greek mathematician and architect of the Hagia Sophia, produced the first compilation of Archimedes' works c. 530. It is through this manuscript tradition, sustained by the school of mathematics and engineering established c. 850 during the "Byzantine Renaissance" by Leo the Mathematician, that such works are known today, primarily through the school's production, the Archimedes Palimpsest.[361]
Alexandrian philosopher John Philoponus was the first to question Aristotelian physics. Unlike Aristotle, who based his physics on verbal arguments, Philoponus relied on observations. Philoponus' criticism of the Aristotelian principles of physics was an inspiration for Galileo Galilei's refutation of Aristotelian physics during the Scientific Revolution many centuries later, as Galileo cites Philoponus substantially in his works.[362]
Greek fire, an incendiary weapon which could even burn on water, is attributed to the Byzantines. It played a crucial role in the empire's victory over the Umayyad Caliphate during the siege of Constantinople (717–718).[363] The discovery is attributed to Callinicus of Heliopolis, who had fled to the city after the Arab conquest of Syria. However, it has also been argued that no single person invented Greek fire, and that it was instead "invented by the chemists in Constantinople who had inherited the discoveries of the Alexandrian chemical school...".[364]
During the last century of the empire, astronomy and other mathematical sciences were taught in Trebizond; medicine attracted the interest of almost all scholars.[359] The Fall of Constantinople in 1453 fuelled the era later commonly known as the "Italian Renaissance". During this period, refugee Byzantine scholars were principally responsible for transmitting ancient Greek grammatical, literary, mathematical, and astronomical works to early Renaissance Italy, whether personally or through their written works.[358] They also brought classical knowledge and texts on botany, medicine and zoology, as well as the works of Dioscorides and John Philoponus' criticism of Aristotelian physics.[365]
Medicine
The Byzantines pioneered the concept of the hospital as an institution offering medical care and the possibility of a cure for the patients as a reflection of the ideals of Christian charity, rather than merely being a place to die.[366]
Legacy
Political aftermath
By the time of the fall of Constantinople, the Byzantine Empire, already an empire in name only since the Fourth Crusade, had been reduced to three rump states: the Despotate of the Morea, the Empire of Trebizond and the Principality of Theodoro. The Morea was ruled by the brothers of Constantine XI, Thomas Palaiologos and Demetrios Palaiologos. The despotate continued as an independent state by paying an annual tribute to the Ottomans. Incompetent rule, failure to pay the annual tribute, and a revolt against the Ottomans finally led to Mehmed II's invasion of Morea in May 1460.[367]
A few holdouts remained for some time. In the Morea, the island of Monemvasia came under the protection of Pope Pius II before the end of 1460.[368] The Empire of Trebizond, which had split away from the Byzantine Empire just weeks before Constantinople was taken by the Crusaders in 1204, became the last remnant of and de facto successor state to the Byzantine Empire. Efforts by Emperor David to recruit European powers for an anti-Ottoman crusade provoked war between the Ottomans and Trebizond in the summer of 1461. After a month-long siege, David surrendered the city of Trebizond on 14 August 1461. Trebizond's Crimean principality, the Principality of Theodoro (part of the Perateia), lasted another 14 years, falling to the Ottomans in December 1475.[369]
Mehmed II and his successors continued to consider themselves heirs to the Roman Empire. They considered that they had shifted their religious basis as Constantine had done before, and they continued to refer to their conquered Eastern Roman inhabitants (Orthodox Christians) as Rûm. This claim gradually faded away as the Ottoman Empire assumed a more Islamic political identity.[370] Meanwhile, the Danubian Principalities, whose rulers also considered themselves the heirs of the Eastern Roman Emperors,[371] harboured Orthodox refugees, including some Byzantine nobles.
After Constantine's death, the role of the emperor as a patron of Eastern Orthodoxy was claimed by Ivan III, Grand Prince of Muscovy. He had married Andreas' sister, Sophia Palaiologina, whose grandson, Ivan IV, became the first tsar of Russia (tsar, or czar, meaning caesar, is a term traditionally applied by Slavs to the Byzantine emperors). Their successors supported the idea that Moscow was the proper heir to Rome and Constantinople. The idea of the Russian Empire as the successive Third Rome was very much alive in Imperial Russia, but it lost state support after the Russian Revolution.[372]
Cultural aftermath
The historian Averil Cameron notes how Byzantium has often been identified with absolutism, orthodox spirituality, orientalism and exoticism, while the terms "Byzantine" and "Byzantinism" have been used as bywords for decadence, complex bureaucracy, and repression. Both Eastern and Western European authors have often perceived Byzantium as a body of religious, political, and philosophical ideas contrary to those of the West. Even in 19th-century Greece, the focus was mainly on the classical past, while Byzantine tradition was associated with negative connotations.[373]
This traditional approach towards Byzantium has been partially or wholly disputed and revised by modern studies, which focus on the positive aspects of Byzantine culture and legacy. From the ninth to the twelfth centuries, Byzantine Christianity converted and helped establish multiple nations in what is now Eastern Europe.[374][375] Cameron regards this as undeniable, and she and Obolensky both recognize the major role of Byzantium in shaping Orthodoxy, which in turn occupies a central position in the history, societies and culture of Greece, Romania, Bulgaria, Russia, Georgia, Serbia and other countries.[376] Its use of vernacular language, and the development of the first Slavic written script, increased education and literacy and influenced the direction of the spiritual, religious, and cultural development of the entire region.[377][378] The Byzantines also preserved and copied classical manuscripts, and they are thus regarded as transmitters of classical knowledge, as important contributors to modern European civilization, and as precursors of both Renaissance humanism and Slavic-Orthodox culture.[379] The Byzantine law codes form the basis of civil law traditions in much of Europe, Latin America, Ethiopia, other countries that follow common law, and possibly even Islamic countries.[380][381]
As the only stable long-term state in Europe during the Middle Ages, Byzantium isolated Western Europe from newly emerging forces to the East. Constantly under attack, it shielded Western Europe from the Persians, Arabs, Seljuk Turks, and for some time, the Ottomans. From another perspective, since the 7th century, the evolution and constant reshaping of the Byzantine state was directly corelated to the progress of Islamic conquests.[379] Following the conquest of Constantinople by the Ottoman Turks in 1453, Sultan Mehmed II took the title "Kaysar-i Rûm" (the Ottoman Turkish equivalent of Caesar of Rome), since he was determined to make the Ottoman Empire the heir of the Eastern Roman Empire.[382]
See also
References
Notes
- ^ Medieval Greek: Ῥωμαῖοι, romanized: Rhōmaîoi
- ^ Leo VI was officially the son of Basil I, but a persistent rumour alleged that he had been fathered by Michael III, who had previously taken Leo's mother Eudokia Ingerina as his mistress. One of Leo's first acts was to rebury Michael III in Basil's mausoleum in the Church of the Holy Apostles complex, which exacerbated the rumours.[72]
- ^ The historian Sofie Remijsen says there are several reasons to conclude that the Olympic games continued after Theodosius I, as the traditionally known terminal year of 393 AD for the games is linked to his anti-pagan constitution. She argues that the games instead came to an end during the reign of Theodosius II, when a fire burned down the Temple of Olympian Zeus in Athens.[289] The historian Anthony Kaldellis says there is a common misconception that the games were banned by an imperial decree. Kaldellis instead argues that the declining interest in chariot games, lack of funding (due to state policies) and hostility from zealots is what led to their end.[290]
- ^ Greek's importance grew larger, even though Hellenic culture had already influenced Roman identity immensely and the Greek language had been entrenched in the east since the Hellenistic era.[292]
- ^ Arianism, one of the first major controversies, shook the Empire until it was addressed by the Nicene Creed.[298] Other controversies persisted, leading to schisms, such as debates on the fundamental definitions of Christ's nature at the Council of Chalcedon in 451.[299]
Citations
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 2; Aschenbrenner & Ransohoff 2022a, pp. 1–2; Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys 2008, pp. 8–9.
- ^ Kaldellis 2022, pp. 349–351; Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys 2008, p. 4.
- ^ Aschenbrenner & Ransohoff 2022a, p. 2.
- ^ Kaldellis 2022, pp. 352–357.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 2–3; Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys 2008, p. 4.
- ^ Cameron 2002, pp. 190–191; Kaldellis 2015.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 34; Shepard 2009, p. 22.
- ^ Shepard 2009, p. 26.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 232.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 233; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 16–17; Treadgold 1997, pp. 4–7.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, pp. 233–235; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 17–18; Treadgold 1997, pp. 14–18.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 20–21, 34; Treadgold 1997, pp. 39, 45, 85; Rotman 2022, p. 234–235; Greatrex 2008.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 335; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 16–20; Treadgold 1997, pp. 39–40.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, pp. 335–337; Kaldellis 2023, chapter 2; Treadgold 1997, p. 40.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, pp. 336–337; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 81–84; Treadgold 1997, pp. 31–33, 40–47.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, pp. 337–338; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 92–99, 106–111; Treadgold 1997, pp. 52–62.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, pp. 239–240; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 114–118, 121–123; Treadgold 1997, pp. 63–67.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 240; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 128–129; Treadgold 1997, p. 73.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 241; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 129–137; Treadgold 1997, pp. 74–75.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, pp. 240–241; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 126–128; Treadgold 1997, pp. 71–74.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 136.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 242; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 165–167; Treadgold 1997, pp. 87–90.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 242; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 172–178; Treadgold 1997, pp. 91–92, 96–99; Shepard 2009, p. 23.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, pp. 242–243; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 193–196, 200; Treadgold 1997, pp. 94–95, 98.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, pp. 243–244; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 209, 214–215; Treadgold 1997, pp. 153, 158–159.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 243–246.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 244; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 220–221; Treadgold 1997, pp. 162–164.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 244; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 223–226; Treadgold 1997, pp. 164–173.
- ^ Haldon 2008a, p. 250; Louth 2009a, p. 106; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 257–258; Treadgold 1997, p. 174.
- ^ Louth 2009a, pp. 108–109; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 269–271; Sarris 2002, p. 45; Treadgold 1997, pp. 178–180.
- ^ Sarris 2002, pp. 43–45; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 271–274; Louth 2009a, pp. 114–119.
- ^ Louth 2009a, pp. 111–114; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 274–277; Sarris 2002, p. 46.
- ^ Sarris 2002, p. 46; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 279–283, 287–288, 305–307; Moorhead 2009, pp. 202–209.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 297; Treadgold 1997, pp. 193–194; Haldon 2008a, pp. 252–253.
- ^ Sarris 2002, p. 49; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 298–301.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, pp. 196–207; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 298–299, 305–306; Moorhead 2009, pp. 207–208.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, pp. 210–211, 214; Louth 2009a, pp. 117–118; Haldon 2008a, p. 253.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 318–319; Treadgold 1997, p. 217; Sarris 2002, p. 51.
- ^ Sarris 2002, p. 51; Haldon 2008a, p. 254; Treadgold 1997, pp. 220–222.
- ^ Louth 2009a, pp. 124–127; Haldon 2008a, p. 254; Sarris 2002, p. 51.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 336–338; Treadgold 1997, pp. 232–235; Haldon 2008a, p. 254.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 347–350; Haldon 2008a, p. 254; Louth 2009b, pp. 226–227; Treadgold 1997, p. 241.
- ^ Haldon 2008a, pp. 254–255; Treadgold 1997, pp. 287–293; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 351–355.
- ^ Sarris 2002, pp. 56–58; Haldon 2008a, p. 255; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 364–367, 369, 372; Louth 2009b, pp. 227–229; Treadgold 1997, pp. 397–400.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 375; Haldon 2008a, p. 256; Louth 2009b, pp. 229–230.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 387; Haldon 2008a, p. 256; Treadgold 2002, p. 129.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 387.
- ^ Haldon 2008a, p. 257; Kaldellis 2023, p. 387.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 389; Louth 2009b, pp. 230–231.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, pp. 315–316; Louth 2009b, pp. 239–240.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, pp. 323–327; Haldon 2008a, p. 257; Louth 2009b, pp. 232–233.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 403; Haldon 2008a, pp. 257–258; Treadgold 2002, pp. 134–135.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 403; Treadgold 2002, p. 135.
- ^ Treadgold 2002, pp. 136–138; Haldon 2008a, p. 257; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 438–440.
- ^ Treadgold 2002, pp. 137–138; Haldon 2008a, p. 257; Auzépy 2009, p. 265.
- ^ Haldon 2008a, pp. 258–259; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 443, 451–452; Auzépy 2009, pp. 255–260.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 444–445; Auzépy 2009, pp. 275–276.
- ^ Auzépy 2009, pp. 265–273; Kaegi 2009, pp. 385–385; Kaldellis 2023, p. 450.
- ^ Haldon 2008a, p. 260; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 450–454; Treadgold 2002, pp. 140–141.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 443, 447–449, 454–459; Haldon 2008a, pp. 258–261; Auzépy 2009, pp. 253–254.
- ^ Treadgold 2002, pp. 140–141; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 459–561; Auzépy 2009, pp. 284–287.
- ^ Haldon 2008a, p. 261; Treadgold 2002, pp. 141–142; Magdalino 2002, p. 170.
- ^ Haldon 2008a, p. 261; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 464–469.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 470–473; Magdalino 2002, pp. 169–171; Haldon 2008a, p. 261.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 473–474, 478–481.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 265; Auzépy 2009, pp. 257, 259, 289; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 482–483, 485–491.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 491–495; Holmes 2008, p. 265; Auzépy 2009, pp. 273–274.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 498–501; Holmes 2008, p. 266.
- ^ Holmes 2008, pp. 265–266; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 504–505; Auzépy 2009, p. 254; Tougher 2009, pp. 292–293, 296.
- ^ Tougher 2009, pp. 292, 296; Holmes 2008, p. 266.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 266; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 522–524; Treadgold 1997, pp. 455–458.
- ^ Tougher 2009, p. 296; Kaldellis 2023, p. 526.
- ^ Shepard 2009b, pp. 493, 496–498; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 429–433; Holmes 2008, p. 267.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 267; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 534–535.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 537–539; Holmes 2008, p. 267; Shepard 2009b, p. 503.
- ^ Shepard 2009b, p. 505; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 540–543; Holmes 2008, p. 267.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 543–544; Shepard 2009b, pp. 505–507.
- ^ Shepard 2009b, pp. 508–509; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 546–552; Holmes 2008, p. 268.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 553–555; Holmes 2008, p. 268.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 563–573; Holmes 2008, p. 268–269; Magdalino 2002, p. 176.
- ^ Holmes 2008, pp. 268.
- ^ Shepard 2009b, pp. 522–526; Magdalino 2002, p. 202; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 573–578.
- ^ Shepard 2009b, pp. 526, 531; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 578–579; Holmes 2008, p. 269.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 269; Shepard 2009b, pp. 526–29; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 579–582.
- ^ Shepard 2009b, p. 529; Holmes 2008, p. 271.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 584; Holmes 2008, pp. 270–271; Magdalino 2002, p. 180.
- ^ Shepard 2009b, pp. 531–536; Holmes 2008, p. 271.
- ^ Magdalino 2002, pp. 202–203; Holmes 2008, pp. 271–272; Angold 2009, pp. 587–588; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 588–589.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 590, 593; Magdalino 2002, pp. 181–182; Angold 2009, pp. 587–598.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 602.
- ^ Holmes 2008, pp. 272–273; Magdalino 2002, p. 182; Kaldellis 2023, p. 636.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 273; Magdalino 2002, pp. 184–185, 189.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 629–637; Angold 2009, pp. 609–610.
- ^ Holmes 2008, pp. 273–274; Angold 2009, p. 611.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 639–642; Holmes 2008, p. 275; Magdalino 2002, p. 190.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 642–644; Holmes 2008, p. 275; Angold 2009, pp. 611–612.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 275; Magdalino 2002, p. 190; Angold 2009, p. 621–623.
- ^ Holmes 2008, pp. 274–275; Angold 2009, pp. 612–613, 619–621, 623–625; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 645–647, 659–663.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 274; Magdalino 2009, pp. 629–630.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 275; Magdalino 2009, pp. 631–633; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 664–670.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 669; Holmes 2008, p. 275.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 670, 676–677; Magdalino 2009, pp. 644–646.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 678, 683–688; Holmes 2008, pp. 275–276.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 679–681; Magdalino 2009, pp. 637–638.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 682–683; Magdalino 2002, p. 194; Magdalino 2009, pp. 638–641.
- ^ Magdalino 2009, pp. 643–644; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 692–693.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 695.
- ^ Magdalino 2002, p. 194; Holmes 2008, p. 276.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 276; Magdalino 2002, pp. 194–195; Magdalino 2009, p. 655.
- ^ Magdalino 2002, pp. 195–196; Magdalino 2009, pp. 648–651; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 706–710.
- ^ Holmes 2008, p. 276.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 718–720; Magdalino 2009, pp. 651–652.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 720–724; Magdalino 2009, pp. 652–653.
- ^ a b Laiou 2008, p. 280; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 733–734; Reinert 2002, pp. 250–253; Angold 2009b, p. 731.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 755–758; Angold 2009b, p. 737.
- ^ Laiou 2008, p. 283; Reinert 2002, p. 254; Angold 2009b, pp. 737–738; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 766–770.
- ^ Reinert 2002, p. 253; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 760–762.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 771; Laiou 2008, pp. 282–283.
- ^ Angold 2009b, p. 740; Laiou 2008, pp. 282–283; Kaldellis 2023, p. 772.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 774–781; Reinert 2002, p. 254.
- ^ Laiou 2008, p. 283; Reinert 2002, p. 254.
- ^ Reinert 2002, p. 257.
- ^ Reinert 2002, p. 261.
- ^ Vasiliev 1964, pp. 617–619.
- ^ Reinert 2002, p. 268; Vasiliev 1964, p. 622.
- ^ Reinert 2002, p. 270.
- ^ Runciman 1990, pp. 84–86.
- ^ Runciman 1990, pp. 84–85.
- ^ Hindley 2004, p. 300.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 35, 189, 222; Nicol 1988, p. 63; Howard-Johnston 2024, p. 8.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 35; Howard-Johnston 2024, p. 8; Browning 1992, p. 98.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 338; Treadgold 1997, p. 326; Nicol 1988, p. 64.
- ^ Nicol 1988, p. 63.
- ^ Louth 2005, pp. 306–308; Treadgold 1997, pp. 82–83.
- ^ Louth 2005, p. 303; Treadgold 1997, pp. 430–431; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 418, 421.
- ^ Browning 1992, p. 98; Kaldellis 2023, p. 185.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 397, 407–409, 536; Howard-Johnston 2024, p. 67; Browning 1992, p. 98.
- ^ Obolensky 1994, p. 3.
- ^ a b Zhang 2023, p. 221.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 322–323, 325, 366–367, 511.
- ^ Neumann 2006, pp. 4–5; Chrysos 1990, p. 35; Shepard 1990a, pp. 61–66.
- ^ Zhang 2023, p. 221; Sinnigen 1963, p. [1]; Haldon 1990, pp. 281–282; Shepard 1990a, pp. 65–67.
- ^ Whitby 2008, pp. 122–123.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 309; Whitby 2008, pp. 122–123, 125; Haldon 1990, p. 282-283.
- ^ Chrysos 1990, pp. 25, 36; Haldon 1990, p. 289.
- ^ Haldon 1990, p. 289; Chrysos 1990, pp. 25, 33, 35; Neumann 2006, pp. 4–5.
- ^ Chrysos 1990, pp. 33, 35; Neumann 2006, pp. 4–5; Kaldellis 2023, p. 338.
- ^ Chrysos 1990, pp. 33, 35; Zhang 2023, p. 221.
- ^ Kazhdan 1990, p. 4; Kennedy 1990, pp. 134, 137, 143.
- ^ Kazhdan 1990, pp. 7, 10; Kennedy 1990, p. 134; Chrysos 1990, pp. 28–29; Howard-Johnston 2008, p. 949; Haldon 1990, pp. 286, 949.
- ^ Howard-Johnston 2008, p. 949.
- ^ Kazhdan 1990, pp. 5, 11, 13, 20.
- ^ Kazhdan 1990, pp. 20–21.
- ^ Howard-Johnston 2008, p. 945; Oikonomides 1990, p. 74-77.
- ^ Chitwood 2017, p. 16; Stein 1999, pp. 3–4, 8, 16; Longchamps de Berier 2014, pp. 217–218.
- ^ Stein 1999, pp. 14, 16.
- ^ Gregory 2010, p. 135; Kaldellis 2023, p. 168; Stein 1999, p. 27.
- ^ Dingledy 2019, pp. 2–14; Kaiser 2015, p. 120.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 168; Stein 1999, pp. 14, 16, 28; Kaiser 2015, p. 120.
- ^ Gregory 2010, p. 135; Stein 1999, pp. 33–35; Dingledy 2019, pp. 2–14; Kaiser 2015, pp. 123–126.
- ^ Stein 1999, p. 8; Merryman & Pérez-Perdomo 2007, p. 21.
- ^ Stolte 2015, pp. 356, 370; Stolte 2018, pp. 231–232.
- ^ Chitwood 2017, p. 23.
- ^ Chitwood 2017, p. 185.
- ^ Chitwood 2017, p. 185; Nicol 1988, p. 65.
- ^ Chitwood 2017, pp. 23, 132, 364.
- ^ Browning 1992, p. 97; Kaldellis 2023, p. 529; Chitwood 2017, pp. 25–32, 44.
- ^ Browning 1992, pp. 97–98; Chitwood 2017, pp. 32–35; Kaldellis 2023, p. 529.
- ^ Stein 1999, p. 35.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 59, 194; Haldon 2008b, p. 554; Treadgold 1997, p. 50.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 331.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 454–455; Haldon 2008b, p. 555.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 421–422, 437; Haldon 2008b, pp. 555–556; Treadgold 1997, pp. 430–431; Neville 2004, p. 7.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 562; Treadgold 1995, p. 206.
- ^ Haldon 2008b, p. 555; Treadgold 1997, pp. 281, 432, 489.
- ^ Haldon 2008b, p. 556; Blöndal 1979, pp. 17, 20–22, 178–179.
- ^ Kaldellis 2021a, p. 463; Haldon 2008b, p. 556; Treadgold 1997, pp. 730–734, 737; Treadgold 1995, p. 29.
- ^ Kaldellis 2021a, p. 463; Haldon 2008b, p. 555; Treadgold 1997, pp. 735–736.
- ^ Haldon 2008b, p. 557; Treadgold 1997, pp. 737, 794–796, 810.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 634; Haldon 2008b, p. 557.
- ^ Haldon 2008b, p. 557; Treadgold 1997, pp. 825–826.
- ^ Haldon 2008b, p. 557; Treadgold 1997, pp. 905–906.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 562, 656; Pryor 2008, p. 483.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 399, 442; Blöndal 1979, p. 29; Haldon 2008b, p. 555.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 502; Blöndal 1979, pp. 16, 29–30; Haldon 2008b, p. 560.
- ^ Pryor 2008, p. 487; Pryor 2017, p. 401; Markis 2002a, p. 92.
- ^ MacGeorge 2002, p. 311.
- ^ Pryor 2008, p. 488; Pryor 2017, p. 403; Markis 2002a, p. 93.
- ^ Pryor 2008, p. 489.
- ^ Howard-Johnston 2008b, p. 240.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 489; Blöndal 1979, p. 29; Treadgold 1995, p. 33; Howard-Johnston 2008, p. 947.
- ^ Pryor 2008, p. 489; Pryor 2017, pp. 404, 408.
- ^ Haldon 2008b, p. 558; Treadgold 1997, pp. 975, 1084.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 812, 860–861; Treadgold 1997, pp. 989, 1024.
- ^ Haldon 2008b, p. 558.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 1881; Haldon 2008b, p. 559; Treadgold 1997, p. 1112.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 896; Haldon 2008b, pp. 558–559.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, pp. 197, 384–385; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 21–22; Stathakopoulos 2008, p. 310.
- ^ Stathakopoulos 2008, p. 312; Treadgold 1997, pp. 931–932.
- ^ Stathakopoulos 2008, p. 313; Treadgold 1997, p. 1112.
- ^ Stathakopoulos 2008, pp. 310, 314; Stathakopoulos 2023, p. 31; Kaldellis 2023, p. 21.
- ^ Markopoulos 2008, p. 786; Jeffreys 2008, p. 798.
- ^ Markopoulos 2008, p. 789.
- ^ Constantelos 1998, p. 19"The fifth century marked a definite turning point in Byzantine higher education. Theodosios ΙΙ founded in 425 a major university with 31 chairs for law, philosophy, medicine, arithmetic, geometry, astronomy, music, rhetoric and other subjects. Fifteen chairs were assigned to Latin and 16 to Greek. The university was reorganized by Michael III (842–867) and flourished down to the fourteenth century."
- ^ Kazhdan & Wharton 1990, p. 122.
- ^ Rosser 2011, p. xxx.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 40; Rotman 2022, p. 32; Lavan 2016, pp. 16, 19.
- ^ Rotman 2009, pp. 18, 179; Rotman 2022, p. 59.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 39; Lenski 2021, pp. 473–474.
- ^ Rotman 2009, pp. 30–31; Kaldellis 2023, p. 425; Rotman 2022, p. 42; Lenski 2021, p. 470; Rotman 2010.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 140; Rotman 2009, Chapter 2; Rotman 2022, pp. 37–38, 53; Lenski 2021, pp. 461–462.
- ^ Harper 2010, p. 237.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 40; Rotman 2022, p. 53; Lenski 2021, pp. 467–468.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 38; Brandes 2008, p. 563.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 39; Harvey 2008, p. 329.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 39; Harvey 2008, p. 331.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 444; Rotman 2022, p. 85; Lenski 2021, pp. 464–465.
- ^ Talbot 1997, p. 121; Kazhdan 1990a, p. 132.
- ^ Rotman 2022, p. 83; Talbot 1997, p. 121; Kaldellis 2023, p. 41; Stathakopoulos 2008, pp. 309, 313.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 88, 321, 444, 529, 588, 769; Talbot 1997, pp. 119, 122, 128.
- ^ Harris 2017, p. 13; Kaldellis 2023, p. 41; Garland 2006, p. xiv.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 40.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 40, 592; Stephenson 2010, p. 66.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 40, 592; Talbot 1997, p. 129; Garland 2006, p. xvi.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 40; Talbot 1997, pp. 118–119.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 40; Talbot 1997, pp. 126–127; Karras 2004, pp. 309–314.
- ^ Talbot 1997, pp. 130–131; Harris 2017, p. 133; Garland 2006, p. xiv; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 40–41.
- ^ Talbot 1997, p. 131; Kazhdan 1990a, p. 136.
- ^ Grosdidier de Matons 1967, pp. 23–25; Garland 1999, pp. 11–39.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 40; Karras 2004, p. 310.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 529; Harris 2017, p. 133.
- ^ Rochette 2023, p. 285; Goldhill 2024, p. 850.
- ^ Dickey 2023, p. 4.
- ^ Rochette 2018, p. 108; Millar 2006, pp. 97–98; Treadgold 1997, p. 5–7.
- ^ McDonnell 2006, p. 77; Millar 2006, pp. 97–98; Oikonomides 1999, pp. 12–13.
- ^ Rochette 2023, pp. 263, 268; Rochette 2018, pp. 114–115, 118; Wallace-Hadrill 1998, pp. 80–83.
- ^ Rochette 2011, pp. 560, 562–563; Rochette 2018, p. 109.
- ^ Dawkins 1916.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 191; Rochette 2023, p. 283; Rochette 2011, p. 562; Wickham 2009, p. 90.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 289; Rochette 2011, p. 562; Rochette 2023, p. 283.
- ^ Oikonomides 1999, pp. 12–13.
- ^ Pei & Gaeng 1976, pp. 76–81.
- ^ Sedlar 1994, pp. 403–440.
- ^ Apostolides 1887, pp. 25–26; Rochette 2023, p. 283; Rance 2010, pp. 63–64.
- ^ Runciman 1933, p. 232.
- ^ Oikonomides 1999, p. 20; Harris 2014, p. 12.
- ^ Beaton 1996, p. 10; Jones 1986, pp. 991–997; Versteegh 1977, p. 1; Harris 2014, p. 12.
- ^ Kaldellis 2007, p. 95; Nicol 1993, pp. 1–2.
- ^ Laiou 2007, p. 13; Whittow 2009, p. 473.
- ^ Laiou 2007, p. 24.
- ^ Whittow 2009, p. 467; Laiou 2007, p. 246.
- ^ Laiou 2007, p. 24; Whittow 2009, pp. 472, 474, 479.
- ^ Laiou 2007, pp. 25–26.
- ^ Laiou 2007, pp. 25–26, 232; Whittow 2009, p. 465, 471.
- ^ Laiou 2007, pp. 44–46.
- ^ Whittow 2009, pp. 473–474.
- ^ Laiou 2007, pp. 19–22, 24.
- ^ Laiou 2007, pp. 90–92; Whittow 2009, pp. 476.
- ^ Whittow 2009, pp. 473–476.
- ^ Laiou 2007, p. 233.
- ^ Laiou 2007, pp. 167–168; Magdalino 2002b, p. 535; Kaldellis 2023, p. 739.
- ^ Matschke 2002, pp. 805–806.
- ^ Laiou 2007, p. 203; Whittow 2009, pp. 477.
- ^ Laiou 2007, p. 168.
- ^ Laiou 2007, pp. 232–235; Whittow 2009, p. 471.
- ^ Shepard 2009, p. 69; Ball 2005, p. 4; Dawson 2006, pp. 41, 43.
- ^ Ball 2005, pp. 57, 75–76, 118–119.
- ^ Ball 2005, pp. 35, 177.
- ^ Ball 2005, pp. 12, 29.
- ^ Ball 2005, pp. 24, 30, 32, 34; Dawson 2006, p. 43.
- ^ Ball 2005, p. 9.
- ^ Ball 2005, p. 6.
- ^ Ash 1995, p. 244; Bryer 2008, p. 673-675; Decker 2008, p. 496.
- ^ Ash 1995, p. 244; Davidson 2014, p. 123; Bryer 2008, p. 671; Faas 2005, p. 184-185; Vryonis 1971, p. 482; Salaman 1986, p. 184.
- ^ "Medieval Sourcebook: Liutprand of Cremona: Report of his Mission to Constantinople". Internet History Sourcebooks Project, Fordham University. 17 October 2014. p. 47. Archived from the original on 17 October 2014. Retrieved 2 December 2024.
- ^ Davidson 2014, p. 123.
- ^ Bryer 2008, pp. 672–673; Unwin 2010, p. 185.
- ^ Horn & Schädler 2019.
- ^ Jeffreys 2008a, pp. 681–682; Kaldellis 2023, p. 13, 138.
- ^ Jeffreys 2008a, p. 680.
- ^ Jeffreys 2008a, pp. 678–683; Kaldellis 2023, p. 187, 233.
- ^ Kazhdan 1991a, p. 2137, "Tzykanisterion"; Kazanaki-Lappa 2002, p. 643; Jeffreys 2008a, p. 683; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 672, 844.
- ^ Jeffreys 2008a, p. 683.
- ^ Spawforth 1993, p. 254; Kaldellis 2023, pp. 19–20, 60, 71.
- ^ Ando 2011, p. 46. Reviewed with commentary in Kokkinia 2012.
- ^ Papaconstantinou 2016, p. xxxii; Cameron 2016, p. 31; Cameron 2006b, pp. 544–551; Drake 2007, pp. 418, 422; Greatrex 2008, p. 236.
- ^ Salzman 1993, p. 364; Drake 2007, pp. 412, 414, 425; Greatrex 2008, p. 236; Friell & Williams 2005, p. 121; Kaldellis 2023, p. 178; Treadgold 1997, pp. 72, 94.
- ^ Greatrex 2008, p. 236; Kaldellis 2023, p. 138; Salzman 1993, p. 364; Drake 2007, p. 425.
- ^ Remijsen 2015, pp. 47–49.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 138.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 25, 67–68, 179, 181, 340; Treadgold 1997, pp. 71, 252–253.
- ^ Wallace-Hadrill 1998, pp. 79–91; Goldhill 2024, pp. 847–848; Rochette 2018, p. 108; Millar 2006, pp. 97–98; Treadgold 1997, pp. 5–7.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 111, 180; Jones 1986, p. 991; Treadgold 1997, pp. 27–28, 175–176.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, pp. 141, 186, 342.
- ^ Fousek et al 2018, p. 3/14, Fig. 1.
- ^ Brown 1976, p. 8; Löhr 2007, p. 9.
- ^ Kaldellis 2023, p. 390; Cameron 2017, A United Church, chapter 1.
- ^ Berndt & Steinacher 2014, pp. 1–2, 8–19; Löhr 2007, p. 14.
- ^ Sabo 2018, p. vi9; Löhr 2007, p. 14-23.
- ^ Adams 2021, pp. 366; Micheau 2006, pp. 373, 375.
- ^ Micheau 2006, pp. 373–374, 376.
- ^ CasidayNorris 2007a, p. 3; Nicholson 1960, pp. 54, 60.
- ^ Louth 2008, p. 47; Kolbaba 2008, pp. 214–215.
- ^ Kolbaba 2008, pp. 213–215, 218–221.
- ^ Meyendorff 1979, pp. 95, 97 101; Kolbaba 2008, p. 223.
- ^ Brown 2008, p. 13; Kolbaba 2008, p. 223.
- ^ Dowley 2018, p. 342.
- ^ Dowley 2018, p. 342; Kitromilides 2006, p. 187.
- ^ Kitromilides 2006, pp. 187, 191; Kenworthy 2008, p. 173.
- ^ Kenworthy 2008, p. 173.
- ^ Cormack 2018, p. 39.
- ^ a b c James 2003, § para. 3.
- ^ James 2003, § paras. 2 and 13.
- ^ Rodley 1994, p. 2; Cormack 2018, pp. 11–12.
- ^ Rodley 1994, pp. 12–14.
- ^ Rodley 1994, p. 34; James 2003, § paras. 3–4.
- ^ Rodley 1994, pp. 32–33, 56–57; Cormack 2018, p. 14.
- ^ James 2003, § para. 10; Cormack 2018, pp. 33–40; Curl & Wilson 2021, § paras. 3 and 5.
- ^ Rodley 1994, p. 67.
- ^ James 2003, § para. 7.
- ^ James 2003, § para. 4; Cormack 2018, p. 39.
- ^ James 2003, § paras. 4–5.
- ^ Rodley 1994, pp. 101–102; Cormack 2018, p. 2.
- ^ Lowden 1997, pp. 147–148.
- ^ Matthews & Platt 1997, p. 185.
- ^ Rodley 1994, pp. 115–116; Lowden 1997, pp. 147–151.
- ^ Rodley 1994, p. 132; Lowden 1997, pp. 187–188.
- ^ James 2003, § para. 3; Cormack 2018, pp. 146–147.
- ^ Curl & Wilson 2021, § para. 7.
- ^ Rodley 1994, p. 166; Cormack 2018, pp. 159, 186; Andronikou 2022, pp. 2–4.
- ^ a b c Browning 2022, § para. 1.
- ^ Papaioannou 2021a, pp. 1–2, 5–7.
- ^ Browning 1991a.
- ^ Papaioannou 2021a, p. 10.
- ^ Kazhdan 1999, p. 1; van Dieten 1980, pp. 101–105.
- ^ Browning 2022, § paras. 1–2; Kaldellis 2021, pp. 162–163.
- ^ a b c d e f Kazhdan 1991b, p. 1236.
- ^ Martín 2021, p. 685.
- ^ Kazhdan 1991b, pp. 1236–1237.
- ^ a b Kazhdan 1991b, p. 1237.
- ^ Ring 1994, p. 318.
- ^ Velimirović 1990, pp. 28–29; Conomos 1991, pp. 1426.
- ^ Conomos 1991, pp. 1424–1426; Levy & Troelsgård 2016, § Introduction.
- ^ Velimirović 1990, pp. 26–27, 29.
- ^ Velimirović 1990, pp. 45–46; Conomos 1991, p. 1425; Levy & Troelsgård 2016, §5 "System of eight modes ('oktōēchos')", §7 "Formulaic chants".
- ^ Velimirović 1990, p. 29; Levy & Troelsgård 2016, §7 "Formulaic chants".
- ^ Velimirović 1990, pp. 26–27.
- ^ Levy & Troelsgård 2016, §10 "Syllabic hymn settings".
- ^ Velimirović 1990; Levy & Troelsgård 2016, §3 "Melodic notation".
- ^ Conomos 1991, p. 1425; Levy & Troelsgård 2016, §3 "Melodic notation"; Mellas 2020, p. 2.
- ^ Conomos 1991, pp. 1425–1426.
- ^ Touliatos 2001, § Introduction.
- ^ Touliatos 2001, § "Sources".
- ^ Conomos & Kazhdan 1991, p. 1426.
- ^ a b Conomos & Kazhdan 1991, p. 1426; Touliatos 2001, §2 "Instruments and performing practice".
- ^ Touliatos 2001, §3 "Genres and composers".
- ^ Saliba 2006.
- ^ a b Robins 1993, p. 8.
- ^ a b Tatakes & Moutafakis 2003, p. 189.
- ^ Anastos 1962, p. 409.
- ^ Jones 2005.
- ^ Lindberg 1992, p. 162; Wildberg 2018.
- ^ "Greek Fire | Weaponry". Encyclopedia Britannica. Archived from the original on 10 March 2018. Retrieved 1 March 2018.
- ^ Partington 1999, p. 13.
- ^ Lindberg 1992, p. 162.
- ^ Lindberg 1992, p. 349; Nutton 1984, p. 9; Miller 1997, pp. ix, 3–4.
- ^ Nicol 1993, pp. 396, 401; Reinert 2002, p. 283.
- ^ Kalligas 2002, pp. 886, 888.
- ^ Nicol 1993, pp. 407–408.
- ^ Üre 2020, p. 46.
- ^ Clark 2000, p. 213.
- ^ Seton-Watson 1967, p. 31.
- ^ Cameron 2009, pp. 277–281.
- ^ Shepard 2006, pp. 4–5, 7–8.
- ^ Harris 2014, p. 7.
- ^ Cameron 2009, pp. 186–277.
- ^ Poppe 1991, p. 25.
- ^ Ivanič 2016, p. 127.
- ^ a b Cameron 2009, p. 261.
- ^ Stolte 2015, pp. 10–11; Merryman & Pérez-Perdomo 2007, pp. 367–368; Stein 1999, p. 36.
- ^ Salogubova & Zenkov 2018.
- ^ Bideleux & Jeffries 1998, p. 71; Béhar 1999, p. 38.
Sources
- Adams, Robert Merrihew (2021). "Nestorius and Nestorianism". The Monist. 104 (3): 366–375. doi:10.1093/monist/onab005.
- Anastos, Milton V. (1962). "The History of Byzantine Science. Report on the Dumbarton Oaks Symposium of 1961". Dumbarton Oaks Papers. 16: 409–411. doi:10.2307/1291170. ISSN 0070-7546. JSTOR 1291170.
- Ando, Clifford (2011). Law, Language, and Empire in the Roman Tradition. Empire and After. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press. doi:10.9783/9780812204889. ISBN 978-0-8122-4354-3.
- Andronikou, Anthi (2022). Italy, Cyprus, and Artistic Exchange in the Medieval Mediterranean. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781009039055. ISBN 978-1-316-51092-6.
- Angold, Michael, ed. (2006). The Cambridge History of Christianity. Vol. 5. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139054089.
- Kitromilides, Paschalis. "Orthodoxy and the West: Reformation to Enlightenment". In Angold (2006), pp. 187–209.
- Micheau, Françoise. "Eastern Christianities (Eleventh to Fourteenth Century): Copts, Melkites, Nestorians and Jacobites". In Angold (2006), pp. 371–403.
- Shepard, Jonathan. "The Byzantine Commonwealth 1000–1550". In Angold (2006), pp. 1–52.
- Apostolides, Evangelinos Sophocles (1887). Greek Lexicon of the Roman and Byzantine Periods. Hildesheim: Georg Olms. ISBN 978-3-487-05765-1.
- Aschenbrenner, Nathanael; Ransohoff, Jake (2022). The Invention of Byzantium in Early Modern Europe. Washington, D.C.: Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-88402-484-2.
- Aschenbrenner, Nathanael; Ransohoff, Jake (2022a). Introduction. In Aschenbrenner & Ransohoff (2022), pp. 1–23.
- Kaldellis, Anthony. "From "Empire of the Greeks" to "Byzantium"". In Aschenbrenner & Ransohoff (2022), pp. 349–367.
- Ash, John (1995). A Byzantine Journey. New York: Random House. ISBN 978-1-84511-307-0.
- Ball, Jennifer (2005). Byzantine Dress: Representations of Secular Dress in Eighth- to Twelfth-Century Painting. The New Middle Ages (1st ed.). New York: Palgrave Macmillan. ISBN 978-1-4039-6700-8. OCLC 60402087.
- Beaton, Roderick (1996). The Medieval Greek Romance. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-12032-6.
- Béhar, Pierre (1999). Vestiges d'Empires: La Décomposition de l'Europe Centrale et Balkanique [Vestiges of Empires: The Decay of Central and Balkan Europe] (in French). Paris: Éditions Desjonquères. ISBN 978-2-84321-015-0.
- Berndt, Guido M. [in German]; Steinacher, Roland (2014). Arianism: Roman Heresy and Barbarian Creed (1st ed.). London & New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-4094-4659-0.
- Blöndal, Sigfús (1979). Benedikz, Benedict (ed.). The Varangians of Byzantium. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521035521.
- Bideleux, Robert; Jeffries, Ian (1998). A History of Eastern Europe: Crisis and Change. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-16111-4.
- Brown, Peter (1976). "Eastern and Western Christendom in Late Antiquity: A Parting of the Way". Studies in Church History. 13: 1–24. doi:10.1017/S0424208400006574.
- Browning, Robert (1992). The Byzantine Empire. Washington, DC: The Catholic University of America Press. ISBN 978-0-8132-0754-4.
- ——— (2022). "Greek Literature: Byzantine Literature". In Lucas, Donald William; Mackridge, Peter A. (eds.). Encyclopædia Britannica. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica.
- Cameron, Averil (2017). Byzantine Christianity: A Very Brief History. London: Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge. ISBN 9780281076147.
- ——— (2016). "Late Antiquity and Byzantium: An Identity Problem". Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies. 40 (1): 27–37. doi:10.1017/byz.2015.4.
- ——— (2009). Οι Βυζαντινοί [The Byzantines] (in Greek). Athens: Psychogios. ISBN 978-960-453-529-3.
- ——— (2002). "The 'Long' Late Antiquity: A Twentieth-Century Model". In Wiseman, T. P. (ed.). Classics in Progress: Essays on Ancient Greece and Rome. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 165–191. ISBN 9780197263235. Archived from the original on 9 February 2024. Retrieved 12 December 2023.
- Casiday, Augustine; Norris, Frederick W., eds. (2007). The Cambridge History of Christianity. Vol. 2. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781139054133.
- Casiday, Augustine; Norris, Frederick W. (2007a). Introduction. In Casiday & Norris (2007).
- Drake, Harold A. "The Church, Society and Political Power". In Casiday & Norris (2007), pp. 403–428.
- Löhr, Winrich. "Western Christianities". In Casiday & Norris (2007), pp. 7–51.
- Chitwood, Zachary (2017). Byzantine Legal Culture and the Roman Legal Tradition, 867–1056. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781316861547. ISBN 978-1-107-18256-1.
- Clark, Victoria (2000). Why Angels Fall: A Journey through Orthodox Europe from Byzantium to Kosovo. London: Macmillan. ISBN 978-0-312-23396-9.
- Constantelos, Demetrios (1998). Christian Hellenism: Essays and Studies in Continuity and Change. Studies in the Social & Religious History of the Medieval Greek World. Vol. 3. New Rochelle, New York and Athens: Aristides D. Caratzas. ISBN 978-0-89241-588-5.
- Cormack, Robin; Haldon, John F.; Jeffreys, Elizabeth, eds. (2008). The Oxford Handbook of Byzantine Studies. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1917-4352-8.
- Brandes, Wolfram. "Revenues and Expenditure". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 562–570.
- Bryer, Anthony. "Food, Wine, and Feasting". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 669–676.
- Decker, Michael. "Everyday Technologies". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 492–502.
- Greatrex, Geoffrey. "Political-Historical Survey, c. 250–518". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 233–248.
- Haldon, John F (2008a). "Political-Historical Survey, c. 518–800". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 249–263.
- Haldon, John F (2008b). "The Army". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 554–561.
- Harvey, Alan. "The Village". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 328–334.
- Holmes, Catherine. "Political-Historical Survey, 800–1204". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 264–279.
- Howard-Johnston, James F. "Byzantium and Its Neighbours". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 939–956.
- Jeffreys, Elizabeth (2008a). "Entertainments, Theatre, And Hippodrome". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 677–684.
- Jeffreys, Michael. "Literacy". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 796–802.
- Laiou, Angeliki. "Political-Historical Survey, 1204–1453". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 280–294.
- Markopoulos, Athanasios. "Education". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 785–795.
- Pryor, John. "Shipping and Seafaring". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 482–491.
- Stathakopoulos, Dionysios Ch. "Population, Demography, and Disease". In Cormack, Haldon & Jeffreys (2008), pp. 309–316.
- Cormack, Robin (2018) [2000]. Byzantine Art (2nd ed.). Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-877879-0.
- Curl, James Stevens; Wilson, Susan (2021). "Byzantine Architecture". The Oxford Dictionary of Architecture (3rd Edition Revised ed.). Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-191874-2.
- Davidson, Alan (2014). Jaine, Tom (ed.). The Oxford Companion to Food. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-967733-7. Archived from the original on 14 May 2016. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Dawkins, R. M. (1916). Modern Greek in Asia Minor. A Study of the Dialects of Siĺli, Cappadocia and Phárasa, with Grammar, Texts, Translations and Glossary. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Dickey, Eleanor (2023). Latin Loanwords in Ancient Greek: A Lexicon and Analysis (1st ed.). Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781108888387. ISBN 978-1-108-88838-7. S2CID 258920619. Archived from the original on 9 February 2024. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- Dingledy, Frederick (2 May 2019). The Corpus Juris Civilis: A Guide to Its History and Use. doi:10.31228/osf.io/meq6c. Retrieved 26 August 2024.
- Dowley, Tim (2018). A Short Introduction to the History of Christianity. Minneapolis: Fortress Press. ISBN 978-1-5064-4597-7.
- Faas, Patrick (2005) [1994]. Around the Roman Table: Food and Feasting in Ancient Rome. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 978-0-226-23347-5. Archived from the original on 30 July 2016. Retrieved 20 June 2015.
- Fousek, Jan; Kaše, Vojtěch; Mertel, Adam; Výtvarová, Eva; Chalupa, Aleš (26 December 2018). "Spatial Constraints on the Diffusion of Religious Innovations: The Case of Early Christianity in the Roman Empire". PLOS ONE. 13 (12): e0208744. Bibcode:2018PLoSO..1308744F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0208744. PMC 6306252. PMID 30586375.
- Friell, Gerard; Williams, Stephen (2005). Theodosius: The Empire at Bay. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-78262-7.
- Garland, Lynda (1999). Byzantine Empresses: Women and Power in Byzantium, AD 527–1204. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-14688-3. Archived from the original on 16 January 2021. Retrieved 21 June 2022.
- Garland, Lynda (2006). Byzantine Women: Varieties of Experience, 800–1200. Publications for the Centre for Hellenic Studies, King's College, London. Aldershot, Burlington (Vt.): Ashgate. ISBN 978-0-7546-5737-8.
- Dawson, Timothy. "Propriety, Practicality, Pleasure: The Parameters of Women's Dress in Byzantium, A.D. 1000-1200". In Garland (2006), pp. 41–76.
- Gregory, Timothy E. (2010). A History of Byzantium. Malden: Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-1-4051-8471-7.
- Goldhill, Simon (31 January 2024). "Latin Literature and Greek". In Gibson, Roy; Whitton, Christopher (eds.). The Cambridge Critical Guide to Latin Literature. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. pp. 847–906. ISBN 978-1-108-36330-3.
- Grosdidier de Matons, Jean (1967). "La Femme dans l'Empire Byzantin" [Women in the Byzantine Empire]. Histoire Mondiale de la Femme [World History of Women] (in French). Vol. I. Paris: Nouvelle librairie de France. pp. 11–43. OCLC 490034792.
- Harper, Kyle (2010). "Slave Prices in Late Antiquity (and in the Very Long Term)". Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte. 59 (2): 206–238. doi:10.25162/historia-2010-0013. ISSN 0018-2311. JSTOR 27809564. S2CID 160720781.
- Harris, Jonathan (2014). Byzantium and the Crusades (2nd ed.). London, New Delhi, New York and Sydney: Bloomsbury. ISBN 978-1-78093-767-0.
- ——— (2017). Constantinople: Capital of Byzantium (Second ed.). London, Oxford, New York, New Delhi and Sydney: Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 978-1-4742-5466-3.
- Hindley, Geoffrey (2004). A Brief History of the Crusades. London: Robinson. ISBN 978-1-84119-766-1.
- Horn, Fred; Schädler, Ulrich (31 May 2019). "3.4 Forensic Game Reconstruction". Foundations of Digital Archæoludology. pp. 9–10. arXiv:1905.13516. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1905.13516. Retrieved 10 January 2025.
{{cite conference}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - Howard-Johnston, James (2008b). "John H. Pryor and Elizabeth M. Jeffreys, The Age of the ΔPOMΩN: the Byzantine Navy ca. 500–1204. Leiden-Boston: Brill, 2006. Pp. lxxvii, 754". Byzantine and Modern Greek Studies. 32 (2): 239–241. doi:10.1017/S030701310000536X. ISSN 0307-0131.
- Howard-Johnston, James (2024). Byzantium: Economy, Society, Institutions 600–1100. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198897880.
- Ivanič, Peter (2016). "The Origins of Christianity in the Territory of Czech and Slovak Republics Within the Contexts of Written Sources". European Journal of Science and Theology. 12 (6): 123–130. Archived from the original on 6 June 2023. Retrieved 9 June 2023.
- James, Liz (2003) [2001]. "Byzantine Art". In Brigstocke, Hugh (ed.). The Oxford Companion to Western Art. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-866203-7.
- Johnson, Scott Fitzgerald, ed. (2015). The Oxford Handbook of Late Antiquity. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-027753-6.
- Kaiser, Wolfgang. "Justinian and the Corpus Iuris Civilis". In Johnson (2015), pp. 119–148.
- Stolte, Bernard H. "The Law of New Rome: Byzantine Law". In Johnson (2015), pp. 355–373.
- Jones, A. H. M. (1986). The Later Roman Empire 284–602. Vol. II. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- Jones, Alexander (2005). "The Works of Archimedes: Translation and Commentary. Volume 1: The Two Books On the Sphere and the Cylinder" (PDF). Notices of the AMS. 52 (5): 520–525. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2 March 2022.
- Kaldellis, Anthony (2007). Hellenism in Byzantium: The Transformations of Greek Identity and the Reception of the Classical Tradition. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-87688-9.
- ——— (18 September 2015). "Late Antiquity Dissolves". Marginalia: Forum on Late Antiquity and the Humanities. Archived from the original on 13 December 2023. Retrieved 12 December 2023.
- ——— (2021a). "The Byzantine Empire (641–1453 CE)". In Fibiger Bang, Peter; Bayly, C. A.; Scheidel, Walter (eds.). The Oxford World History of Empire: Volume Two: The History of Empires. New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 450–467. ISBN 9780197532768.
- ——— (2023). The New Roman Empire: A History of Byzantium. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0197549322.
- Karras, Valerie A. (2004). "Female Deacons in the Byzantine Church". Church History. 73 (2): 272–316. doi:10.1017/S000964070010928X. ISSN 0009-6407. JSTOR 4146526. S2CID 161817885. Archived from the original on 5 March 2016. Retrieved 2 February 2024.
- Kazhdan, Alexander Petrovich; Wharton, Annabel Jane (1990). Change in Byzantine Culture in the Eleventh and Twelfth Centuries. Transformation of the Classical Heritage. Vol. 7. Berkeley, Los Angeles and London: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520069626.
- Kazhdan, Alexander Petrovich, ed. (1991a). Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Vol. 2. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-504652-6.
- Browning, Robert. "Language". In Kazhdan (1991a), pp. 1175–1177.
- Conomos, Dimitri E. (1991). "Music". In Kazhdan (1991a), pp. 1424–1426.
- Conomos, Dimitri E.; Kazhdan, Alexander (1991). "Musical Instruments". In Kazhdan (1991a), pp. 1426–1427.
- Kazhdan, Alexander Petrovich (1991b). "Literature". In Kazhdan (1991a), pp. 1234–1237.
- Kazhdan, Alexander (1990a). "Byzantine Hagiography and Sex in the Fifth to Twelfth Centuries". Dumbarton Oaks Papers. 44: 131–143. doi:10.2307/1291623. ISSN 0070-7546. JSTOR 1291623. Retrieved 30 January 2024.
- ——— (1999). A History of Byzantine Literature (650–850). Athens: Institute for Byzantine Research. ISBN 978-960-371-010-3.
- Kenworthy, Scott M. (2008). "Beyond Schism: Restoring Eastern Orthodoxy to the History of Christianity". Reviews in Religion and Theology. 15 (2): 171–178. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9418.2007.00377_1.x.
- Kokkinia, Christina (10 June 2012). "Review of: Law, Language, and Empire in the Roman Tradition. Empire and After". Bryn Mawr Classical Review. ISSN 1055-7660.
- Laiou, Angeliki E., ed. (2002a). The Economic History of Byzantium. From the Seventh Through the Fifteenth Century. Vol. 1. Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks. ISBN 9780884022886.
- Markis, George. "Ships". In Laiou (2002a), pp. 89–98.
- Laiou, Angeliki E., ed. (2002b). The Economic History of Byzantium. From the Seventh Through the Fifteenth Century. Vol. 2. Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks. ISBN 978-0884022886.
- Kalligas, Haris (2002). "Monemvasia, Seventh–Fifteenth Centuries". In Laiou (2002b), pp. 878–897.
- Kazanaki-Lappa, Maria (2002). "Medieval Athens". In Laiou (2002b), pp. 625–632.
- Laiou, Angeliki E. (2002c). "Exchange and Trade, Seventh-Twelfth Centuries". In Laiou (2002b), pp. 681–754.
- Magdalino, Paul (2002b). "Medieval Constantinople: Built Environment and Urban Development". In Laiou (2002b), pp. 519–527.
- Matschke, Klaus-Peter (2002). "Commerce, Trade, Markets, and Money: Thirteenth-Fifteenth Centuries". In Laiou (2002b), pp. 771–806.
- Laiou, Angeliki E. (2007). The Byzantine Economy. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-84978-4.
- Lavan, Myles (2016). "The Spread of Roman Citizenship, 14–212 ce: Quantification in the Face of High Uncertainty". Past & Present (230): 3–46. doi:10.1093/pastj/gtv043. hdl:10023/12646. ISSN 0031-2746.
- Lenski, Noel (12 August 2021). "Slavery in the Byzantine Empire". The Cambridge World History of Slavery. Vol. 2: AD 500–AD 1420. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. pp. 453–481. ISBN 978-1-139-02472-3.
- Levy, Kenneth (2016) [2001]. "Byzantine Chant". In Troelsgård, Christian (ed.). Grove Music Online. Revised by Christian Troelsgård. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/gmo/9781561592630.article.04494. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0. (subscription or UK public library membership required)
- Lindberg, David (1992). The Beginnings of Western Science. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. ISBN 9780226482057.
- Longchamps de Berier, Franciszek (2014). "The Praetor as a Promoter of "Bonum Commune"". LR Legal Roots. 3: 217–231. ISBN 978-88-495-2825-1. ISSN 2280-4994.
- Lowden, John (1997). Early Christian & Byzantine Art. London: Phaidon Press. ISBN 978-0-7148-3168-8.
- Louth, Andrew (2005). "The Byzantine Empire in the Seventh Century". In Fouracre, Paul (ed.). New Cambridge Medieval History. Vol. 1: c. 500 – c. 700. pp. 289–316. ISBN 9781139053938.
- MacGeorge, Penny (2002). Late Roman Warlords. Oxford Classical Monographs. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-925244-2.
- Mango, Cyril A., ed. (2002). The Oxford History of Byzantium. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-814098-6. OCLC 50270189.
- Magdalino, Paul. "The Medieval Empire (780–1204)". In Mango (2002), pp. 169–213.
- Reinert, Stephen W. "Fragmentation (1204–1453)". In Mango (2002), pp. 248–283.
- Sarris, Peter. "The Eastern Roman Empire from Constantine to Heraclius (306–641)". In Mango (2002), pp. 19–70.
- Treadgold, Warren. "The Struggle for Survival (641–780)". In Mango (2002), pp. 129–152.
- Matthews, Roy T.; Platt, F. DeWitt (1997). The Western Humanities. East Lansing: Michigan State University. ISBN 9781559344333.
- McDonnell, Myles Anthony (2006). Roman Manliness: Virtus and the Roman Republic. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-82788-1.
- Mellas, Andrew (2020). Liturgy and the Emotions in Byzantium: Compunction and Hymnody. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781108767361. ISBN 978-1-108-76736-1. S2CID 225623021.
- Merryman, John Henry; Pérez-Perdomo, Rogelio (2007). The Civil Law Tradition: An Introduction to the Legal Systems of Europe and Latin America (3rd ed.). Stanford, Calif: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-5568-9. OCLC 81252739.
- Meyendorff, John [in Russian] (1979). Byzantine Theology: Historical Trends and Doctrinal Themes (PDF) (illustrated, reprint, revised ed.). New York: Fordham University Press. ISBN 978-0-8232-0967-5. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 August 2024.
- Millar, Fergus (2006). A Greek Roman Empire: Power and Belief under Theodosius II (408–450). Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-24703-1.
- Miller, Timothy S. (1997). The Birth of the Hospital in the Byzantine Empire. Baltimore and London: Johns Hopkins University Press. doi:10.56021/9780801826764. ISBN 9780801856570.
- Mitchell, Margaret M.; Young, Frances, eds. (2006). The Cambridge History of Christianity. Vol. 1. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-05483-6.
- Cameron, Averil (2006b). "Constantine and the 'Peace of the Church'". In Mitchell & Young (2006), pp. 538–551.
- Neumann, Iver B. (2006). "Sublime Diplomacy: Byzantine, Early Modern, Contemporary" (PDF). Millennium: Journal of International Studies. 34 (3): 865–888. doi:10.1177/03058298060340030201. ISSN 1569-2981. S2CID 144773343. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 July 2020.
- Neville, Leonora Alice (2004). Authority in Byzantine Provincial Society, 950–1100. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-83865-8.
- Nicholson, Graham (1960). "The Understanding of Papal Supremacy as Revealed in the Letters of Pope Gregory the Great" (PDF). Theological Studies. 11: 25–51. Archived (PDF) from the original on 7 November 2023.
- Nicol, Donald M. (1988). "Byzantine Political Thought". In Burns, J. H. (ed.). The Cambridge History of Medieval Political Thought, c. 350–c. 1450. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 51–79. ISBN 978-0-52-142388-5.
- ——— (1993). The Last Centuries of Byzantium, 1261–1453 (2nd ed.). London: Rupert Hart-Davis. ISBN 9780521439916. Archived from the original on 9 July 2023. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- Noble, Thomas F. X.; Smith, Julia M. H., eds. (2008). The Cambridge History of Christianity. Vol. 3. Cambridge and New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-05422-5.
- Brown, Peter. "Introduction: Christendom, c. 600". In Noble & Smith (2008), pp. 1–18.
- Kolbaba, Tia M. "Latin and Greek Christians". In Noble & Smith (2008), pp. 213–229.
- Louth, Andrew. "The Emergence of Byzantine Orthodoxy, 600–1095". In Noble & Smith (2008), pp. 46–64.
- Nutton, Vivian (1984). "From Galen to Alexander, Aspects of Medicine and Medical Practice in Late Antiquity". In Scarborough, John (ed.). Symposium on Byzantine Medicine. Dumbarton Oaks Papers. Vol. 38. Washington, D. C.: Dumbarton Oaks. pp. 1–14. ISBN 9780884021391. JSTOR 1291489.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - Obolensky, Dimitri (1994). Byzantium and the Slavs. Yonkers: St Vladimir's Seminary Press. ISBN 978-0-88141-008-2.
- Oikonomides, Nikos (1999). "L᾽"Unilinguisme" Officiel de Constantinople Byzantine" [The Official Monolingualism of Byzantine Constantinople]. Byzantina Symmeikta (in French). 13: 9–22. doi:10.12681/byzsym.857. ISSN 1105-1639.
- Papaconstantinou, Arietta (2016). "Introduction". Conversion in Late Antiquity: Christianity, Islam, and Beyond. London: Routledge. pp. xv–xxxvii. ISBN 978-1-4094-5738-1.
- Papaioannou, Stratis, ed. (2021). The Oxford Handbook of Byzantine Literature. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-935176-3.
- Kaldellis, Anthony. "The Reception of Classical Literature and Ancient Myth". In Papaioannou (2021), pp. 162–179.
- Martín, Inmaculada Pérez. "Modes of Manuscript Transmission (Ninth–Fifteenth Centuries)". In Papaioannou (2021), pp. 682–706.
- Papaioannou, Stratis (2021a). "What Is Byzantine Literature? An Introduction". In Papaioannou (2021), pp. 1–18.
- Partington, J. R. (1999). A History of Greek Fire and Gunpowder. Baltimore and London: The Johns Hopkins University Press. ISBN 9780801859540.
- Pei, Mario; Gaeng, Paul A. (1976). The Story of Latin and the Romance Languages. New York: Harper & Row. ISBN 978-0-06-013312-2.
- Poppe, Andrzej (1991). "Christianity and Ideological change in Kievan Rus': The First Hundred Years". Canadian-American Slavic Studies. 25 (1–4): 3–26. doi:10.1163/221023991X00038.
- Pryor, John H. (2017). "The Dromōn and the Byzantine Navy". In Buchet, Christian; Balard, Michel (eds.). The Sea in History - The Medieval World. Suffolk and New York: Boydell and Brewer. pp. 401–411. doi:10.1017/9781782049104.037. ISBN 978-1-78204-910-4. JSTOR 10.7722/j.ctt1kgqt6m.41. Retrieved 18 August 2024.
- Rance, Philip (2010). "The De Militari Scientia or Müller Fragment as a Philological Resource. Latin in the East Roman Army and Two New Loanwords in Greek: Palmarium and *Recala". Glotta. 86 (1–4): 63–92. doi:10.13109/glot.2010.86.14.63. ISSN 0017-1298. JSTOR 41219881. Archived from the original on 7 April 2023. Retrieved 23 December 2023.
- Remijsen, Sofie (2015). The End of Greek Athletics in Late Antiquity. Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/cbo9781107279636. ISBN 978-1-107-27963-6.
- Ring, Trudy (1994). International Dictionary of Historic Places: Middle East and Africa. Vol. 4. London and New York: Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-884964-03-9. Archived from the original on 9 June 2019. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- Robins, Robert Henry (1993). The Byzantine Grammarians: Their Place in History. Berlin and New York: Mouton de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-013574-9.
- Rochette, Bruno (2011). "Language Policies in the Roman Republic and Empire". In Clackson, James (ed.). A Companion to the Latin Language. London: John Wiley & Sons. pp. 549–563. doi:10.1002/9781444343397.ch30. hdl:2268/35932. ISBN 9781405186056. Archived from the original on 9 February 2024. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ——— (2018). "Was There a Roman Linguistic Imperialism During the Republic and the Early Principate?". Lingue e Linguaggio (1/2018): 107–128. doi:10.1418/90426. ISSN 1720-9331. Archived from the original on 4 October 2023. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ——— (2023). "The Attitude of the Roman Emperors towards Language Practices". In Mullen, Alex (ed.). Social Factors in the Latinization of the Roman West (1st ed.). Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-888729-4. Retrieved 22 December 2023.
- Rodley, Lyn (1994). Byzantine Art and Architecture: An Introduction. Cambridge, New York and Melbourne: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-35724-1.
- Rosser, John H. (2011). Historical Dictionary of Byzantium. Lanham, Maryland: Scarecrow Press. ISBN 9780810874770.
- Rotman, Youval (2009). Byzantine Slavery and the Mediterranean World. Cambridge (Mass.): Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-03611-6.
- Rotman, Youval (2 July 2010). "Review of: Response: Rotman on Lenski on Youval Rotman, Byzantine Slavery and the Mediterranean World". Bryn Mawr Classical Review. ISSN 1055-7660. Archived from the original on 9 January 2024. Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- ——— (2022). Slaveries of the First Millennium. Amsterdam: Amsterdam University Press. doi:10.2307/j.ctv2175h0p. ISBN 978-1-64189-172-1. JSTOR j.ctv2175h0p.
- Runciman, Steven (1933). Byzantine Civilisation. London: Methuen.
- Runciman, Steven (1990). The Fall of Constantinople, 1453. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-39832-9.
- Sabo, Theodore (2018). From Monophysitism to Nestorianism: AD 431–681. Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing. ISBN 978-1-5275-0959-7.
- Salaman, Rena (1986). "The Case of the Missing Fish, or Dolmathon Prolegomena". In Jaine, Tom (ed.). Oxford Symposium on Food & Cookery 1984 & 1985: Cookery: Science, Lore & Books: Proceedings (Introduction by Alan Davidson). London: Prospect Books. pp. 184–187. ISBN 978-0-907325-16-1.
- Saliba, George (27 April 2006). "Islamic Science and the Making of Renaissance Europe". Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 29 June 2006. Retrieved 1 March 2008.
- Salogubova, Elena; Zenkov, Alan (15 June 2018). "Roman Law's Influence on Russian Civil Law and Procedure" (PDF). Russian Law Journal. 6 (2): 118–133. ISSN 2312-3605. Archived (PDF) from the original on 10 January 2025.
- Salzman, Michele Renee (1993). "The Evidence for the Conversion of the Roman Empire to Christianity in Book 16 of the 'Theodosian Code". Historia: Zeitschrift für Alte Geschichte. 42 (3): 362–378. JSTOR 4436297.
- Sedlar, Jean W. (1994). East Central Europe in the Middle Ages, 1000–1500. Vol. III. Seattle: University of Washington Press. ISBN 978-0-295-97290-9.
- Seton-Watson, Hugh (1967). The Russian Empire, 1801–1917. London: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-1982-2152-4.
- Shepard, Jonathan, ed. (1990). Byzantine Diplomacy: Papers of the Twenty-fourth Spring Symposium of Byzantine Studies. Cambridge: Variorum. ISBN 9780860783381.
- Kazhdan, Alexander. "1: The Notion of Byzantine Diplomacy". In Shepard (1990), pp. 3–24.
- Chrysos, Evangelos. "2: Byzantine Diplomacy, AD 300–800". In Shepard (1990), pp. 25–40.
- Shepard, Jonathan (1990a). "3: Byzantine Diplomacy, AD 800–1204". In Shepard (1990), pp. 41–72.
- Oikonomides, Nikolaos. "4: Byzantine Diplomacy, AD 1204–1453". In Shepard (1990), pp. 73–90.
- Kennedy, Hugh. "7: Byzantine-Arab Diplomacy in the Near East from the Islamic Conquests to the Mid-Eleventh Century". In Shepard (1990), pp. 133–144.
- Haldon, John. "18: Blood and Ink: Some Observations on Byzantine Attitudes towards Warfare and Diplomacy". In Shepard (1990), pp. 281–294.
- Shepard, Jonathan, ed. (2009). The Cambridge History of the Byzantine Empire c. 500–1492. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-5117-5670-2.
- Angold, Michael. "Belle Époque or Crisis? (1025–1118)". In Shepard (2009), pp. 583–626.
- Angold, Michael (2009b). "After the Fourth Crusade: the Greek Rump States and the Recovery of Byzantium". In Shepard (2009), pp. 731–758.
- Auzépy, Marie-France. "State of Emergency (700–850)". In Shepard (2009), pp. 251–291.
- Kaegi, Walter Emil. "Confronting Islam: Emperors Versus Caliphs (641 – c. 850)". In Shepard (2009), pp. 365–394.
- Louth, Andrew (2009a). "Justinian and his legacy (500–600)". In Shepard (2009), pp. 97–129.
- Louth, Andrew (2009b). "Byzantium Transforming (600–700)". In Shepard (2009), pp. 221–248.
- Magdalino, Paul. "The Empire of the Komnenoi (1118–1204)". In Shepard (2009), pp. 627–663.
- Moorhead, John. "Western Approaches (500–600)". In Shepard (2009).
- Shepard, Jonathan (2009b). "Equilibrium to Expansion (886–1025)". In Shepard (2009), pp. 493–536.
- Tougher, Shaun. "After Iconoclasm (850–886)". In Shepard (2009), pp. 292–304.
- Whittow, Mark. "The Middle Byzantine Economy (600–1204)". In Shepard (2009), pp. 465–492.
- Sinnigen, William G. (1963). "Barbaricarii, Barbari and the Notitia Dignitatum". Latomus. 22 (4): 806–815. JSTOR 41524218.
- Spawforth, A. J. S. (1993). "K. Buraselis, ΘΕΙΑ ΔΩΡΕΑ. ΜΕΛΕΤΕΣ ΠΑΝΩ ΣΤΗΝ ΠΟΛΙΤΙΚΗ ΤΗΣ ΔΥΝΑΣΤΕΙΑΣ ΤΩΝ ΣΕΒΗΡΩΝ ΚΑΙ ΤΗΝ CONSTITUTIO ANTONINIANA (with English summary) (Academy of Athens monograph 1). Athens, p. 254, 1989". Journal of Roman Studies. 83: 224. doi:10.2307/301038. ISSN 0075-4358. JSTOR 301038.
- Stathakopoulos, Dionysios Ch. (2023). A Short History of the Byzantine Empire. Short Histories. London and New York: Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 978-1-350-23340-9.
- Stein, Peter (1999). Roman Law in European History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/cbo9780511814723. ISBN 978-0-521-64372-6.
- Stephenson, Paul, ed. (2010). The Byzantine World. London and New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-1-136-72787-0.
- Stolte, Bernard (2018). Pihlajamäki, Heikki; Dubber, Markus D.; Godfrey, Mark (eds.). Byzantine Law. Vol. 1. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 231–232. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780198785521.013.10.
- Talbot, Alice-Mary (1997). "Chapter 5: Women". In Cavallo, Guglielmo (ed.). The Byzantines. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. pp. 117–143. ISBN 978-0-226-09791-6.
- Tatakes, Vasileios N.; Moutafakis, Nicholas J. (2003). Byzantine Philosophy. Indianapolis: Hackett. ISBN 978-0-8722-0563-5.
- Treadgold, Warren T. (1995). Byzantium and its Army: 284–1081. Stanford: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-3163-8.
- Treadgold, Warren (1997). A History of the Byzantine State and Society. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-2630-2.
- Touliatos, Diane (2001). "Byzantine Secular Music". Grove Music Online. Oxford: Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/gmo/9781561592630.article.48192. ISBN 978-1-56159-263-0. (subscription or UK public library membership required)
- Unwin, P. T. H. (2010). Wine and the Vine: An Historical Geography of Viticulture and the Wine Trade. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-14416-2.
- Üre, Pinar (2020). Reclaiming Byzantium: Russia, Turkey and the Archaeological Claim to the Middle East in the 19th Century. London and New York: Bloomsbury Academic. ISBN 978-1-78831-012-3.
- van Dieten, Jan Louis (1980). "Die Byzantinische Literatur – Eine Literatur Ohne Geschichte?" [Byzantine Literature – A Literature Without History?]. Historische Zeitschrift (in German). 231 (H 1): 101–109. doi:10.1524/hzhz.1980.231.jg.101. JSTOR 27621785.
- Vasiliev, Aleksandr Aleksandrovich (1964). History of the Byzantine Empire, 324–1453. Madison, Wisconsin and London: University of Wisconsin Press. ISBN 978-0-299-80925-6. Archived from the original on 8 August 2021. Retrieved 19 July 2021.
- Velimirović, Miloš (1990). "Byzantine Chant". In Crocker, Richard; Hiley, David (eds.). The New Oxford History of Music. Vol. II: The Early Middle Ages To 1300 (2nd ed.). Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 26–68. ISBN 978-0-19-316329-4.
- Versteegh, Cornelis H. M. (1977). Greek Elements in Arabic Linguistic Thinking. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-9-0040-4855-3.
- Vryonis, Speros (1971). The Decline of Medieval Hellenism in Asia Minor and the Process of Islamization from the Eleventh through the Fifteenth Century. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-01597-5. Archived from the original on 26 June 2020. Retrieved 25 June 2016.
- Wallace-Hadrill, Andrew (1998). "To Be Roman, Go Greek Thoughts on Hellenization at Rome". Bulletin of the Institute of Classical Studies. Supplement (71): 79–91. ISSN 2398-3264. JSTOR 43767621. Archived from the original on 28 December 2023. Retrieved 1 January 2024.
- Whitby, Michael (2008). "Byzantine Diplomacy: Good Faith, Trust and Co-operation in International Relations in Late Antiquity". In de Souza, Philip; France, John (eds.). War and Peace in Ancient and Medieval History. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 120–140. doi:10.1017/cbo9780511496301.008. ISBN 978-0-521-81703-5. Retrieved 26 July 2024.
- Wickham, Chris (2009). The Inheritance of Rome: A History of Europe from 400 to 1000. New York: Viking Penguin. ISBN 978-0-670-02098-0.
- Wildberg, Christian (2018). "John Philoponus". In Zalta, Edward N. (ed.). The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Archived from the original on 22 August 2019. Retrieved 8 March 2018.
- Zhang, Yongjin (2023). "Barbarism and Civilization". The Oxford Handbook of History and International Relations. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 218–232. doi:10.1093/oxfordhb/9780198873457.013.15. ISBN 978-0-19-887345-7. Retrieved 26 July 2024.
External links
- Byzantine Empire on In Our Time at the BBC
- 12 Byzantine Rulers Archived 18 July 2016 at the Wayback Machine by Lars Brownworth of The Stony Brook School; audio lectures.
- 18 centuries of Roman Empire by Howard Wiseman (Maps of the Roman/Byzantine Empire throughout its lifetime).
- Byzantine studies homepage at Dumbarton Oaks. Includes links to numerous electronic texts.
- Byzantium: Byzantine studies on the Internet Archived 8 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Links to various online resources.
- Translations from Byzantine Sources: The Imperial Centuries, c. 700–1204. Online sourcebook.
- De Re Militari. Resources for medieval history, including numerous translated sources on the Byzantine wars.
- Medieval Sourcebook: Byzantium Archived 14 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Numerous primary sources on Byzantine history.
- Bibliography on Byzantine Material Culture and Daily Life. Hosted by the University of Vienna; in English.
- Constantinople Home Page. Links to texts, images and videos on Byzantium.
- Byzantium in Crimea: Political History, Art and Culture.
- Institute for Byzantine Studies of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (with further resources and a repository with papers on various aspects of the Byzantine Empire)