Butyl PBD or b-PBD (short for butyl-phenyl-bipheny-oxydiazole[1]) is a fluorescent organic compound used in the Liquid Scintillator Neutrino Detector (LSND) at Los Alamos National Laboratory, USA.[1]
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
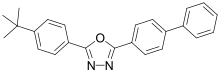
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-([1,1′-Biphenyl]-4-yl)-5-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole | |
| Other names
2-(4-tert-Butylphenyl)-5-(4-biphenylyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole
2-(4-Biphenylyl)-5-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.035.563 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C24H22N2O | |
| Molar mass | 354.44 g mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
The fluorescent emission of b-PBD is at λem = 364 nm for excitation at λex = 305 nm (in ethanol solution).[2] As a scintillant in the LSND, it was used at a concentration of 31 mg/L (87 μmol/L) dissolved in mineral oil.[1]
References
edit- ^ a b c Athanassopoulos, C.; Auerbach, L. B.; Bauer, D.; Bolton, R. D.; Burman, R. L.; Cohen, I.; Caldwell, D. O.; Dieterle, B. D.; Donahue, J. B.; Eisner, A. M.; Fazely, A.; Federspiel, F. J.; M. Gray, G. T. Garvey; Gunasingha, R. M.; Highland, V.; Imlay, R.; Johnston, K.; Kim, H. J.; Louis, W. C.; Lu, A.; Margulies, J.; Mills, G. B.; McIlhany, K.; Metcalf, W.; Reeder, R. A.; Sandberg, V.; Schillaci, M.; Smith, D.; Stancu, I.; Strossman, W.; Tayloe, R.; Van Dalen, G. J.; Vernon, W.; Wang, Y-X.; White, D. H.; Whitehouse, D.; Works, D.; Xiao, Y.; Yellin, S. (1997), "The Liquid Scintillator Neutrino Detector and LAMPF Neutrino Source", Nucl. Instrum. Methods A, 388: 149–72, arXiv:nucl-ex/9605002v1, Bibcode:1997NIMPA.388..149A, doi:10.1016/S0168-9002(96)01155-2.
- ^ B8378 2-(4-tert-Butylphenyl)-5-(4-biphenylyl)-1,3,4-oxadiazole ≥99%, Sigma-Aldrich, retrieved 2010-05-22.