Blairmorite is a very rare[1] porphyritic volcanic rock named after the community of Blairmore in southwestern Alberta, Canada.[2][3] It is characterized by dominant analcime phenocrysts in a matrix of analcime, sanidine and alkalic pyroxene with accessory titanite, melanite and nepheline. It is a leucocratic variety of analcimite (a foidite).[4] Blairmorite has also been described as an analcime-rich variety of phonolite.[5][6]
| Extrusive igneous rock | |
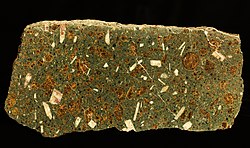 A specimen of blairmorite from the Crowsnest Formation. The amber mineral is analcime, the pale mineral is sanidine and the small black minerals are melanite garnet. | |
| Composition | |
|---|---|
| Primary | Analcime, sanidine, pyroxene |
| Secondary | Titanite, melanite, nepheline |
This extrusive igneous rock is known from only two geological formations worldwide. The foremost blairmorite occurrence is the Crowsnest Formation in the Canadian province of Alberta where it is associated with agglomerates and tuffs from explosive eruptions. The other locality is the Lupata Gorge in Mozambique.[2]
References
edit- ^ MacKenzie, W.S., Donaldson, C.H. and Guilford, C. (1982). Atlas of igneous rocks and their textures. Harlow: Longman. p. 121. ISBN 0-582-30082-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b Pearce, T.H. (1993). "Analcime phenocrysts in igneous rocks: Primary or secondary? – Discussion" (PDF). American Mineralogist. 78: 225–229.
- ^ Johannsen, A. 1933. A descriptive petrography of the igneous rocks, Appendix III, p. 244. Univ. of Chicago Press.
- ^ Le Maitre, R.W. (editor) (2002). Igneous Rocks — A Classification and Glossary of Terms (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. pp. 55, 64. ISBN 0-521-66215-X.
{{cite book}}:|author=has generic name (help) - ^ Peterson, T.D.; Currie, K.L. (1993). Analcite-bearing igneous rocks from the Crowsnest Formation, southwestern Alberta (Current Research report 93-B1) (PDF). Geological Survey of Canada. pp. 51–56.
- ^ Deer, W.A.; Howie, R.A.; Zussman, J. (2013). An Introduction to the Rock-Forming Minerals (3rd ed.). London: Mineralogical Society. ISBN 9780903056274.