The Australian Antarctic Territory (AAT) is a part of East Antarctica claimed by Australia as an external territory. It is administered by the Australian Antarctic Division, an agency of the federal Department of Climate Change, Energy, the Environment and Water. The territory's history dates to a claim on Enderby Land made by the United Kingdom in 1841, which was subsequently expanded and eventually transferred to Australia in 1933. It is the largest Antarctica claimed by any by area. Australia is an original signatory to the Antarctic Treaty of 1961. Under section 4, all territorial claims are held in abeyance. Only four other countries accept Australia's claim to sovereignty, being New Zealand, the United Kingdom, France and Norway, all of whom have territorial claims in Antarctica and mutually accept each other’s claims.[1]
Australian Antarctic Territory | |
|---|---|
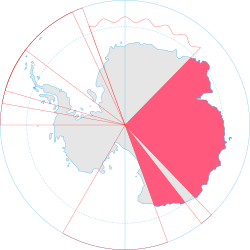 Map of Antarctica indicating Australian territorial claim (red area) | |
| Sovereign state | |
| British claim | 1841 |
| Claim transferred to Australia | 1933 |
| Main base and administrative centre | Davis Station 68°34′36″S 77°58′03″E / 68.576667°S 77.9675°E |
| Official languages | English |
| Government | Dependency under a constitutional monarchy |
• Monarch | Charles III |
| Sam Mostyn | |
• Australian government minister | Tanya Plibersek |
• Chief Scientist | Nicole Webster |
| Area | |
• Total | 5,896,500 km2 (2,276,700 sq mi) |
| Population | |
• Estimate | less than 1,000 |
| Currency | Australian dollar (AU$) (AUD) |
| Calling code | +672 1x |
| Internet TLD | |
Area
editThe AAT consists of all the islands and territory south of 60°S and between 44°38′E and 160°E, except for Adélie Land (136°E to 142°E), which divides the territory into Western AAT (the larger portion) and Eastern AAT.[2] It is bounded by Queen Maud Land in the West and by the Ross Dependency in the East. The Australian Antarctic Territory is the largest of any claims to the continent, and covers nearly 5.9 million square kilometres.[3] This makes up about 42% of Antarctica, and would cover about 80% of Mainland Australia.[4] It also corresponds to roughly twice the size of Queen Maud Land, India, Argentina or Kazakhstan.[5][6][7]
The territory is mostly inhabited by the staff of research stations. The Australian Antarctic Division administers the area primarily by maintaining three year-round stations—Mawson, Davis, and Casey—which support various research projects.[8]
Subdivisions
editThe territory is divided into nine districts, which are from west to east:[9]
| # | District | Area (km2) | Western border |
Eastern border |
Width |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Enderby Land | 449,900 | 044°38′ E | 056°25′ E | 011°47′ |
| 2 | Kemp Land | ... | 056°25′ E | 059°34′ E | 003°09′ |
| 3 | Mac. Robertson Land | 260,000 | 059°34′ E | 072°35′ E | 013°01′ |
| 4 | Princess Elizabeth Land | 437,500 | 072°35′ E | 087°43′ E | 015°08′ |
| 5 | Kaiser Wilhelm II Land | ... | 087°43′ E | 091°54′ E | 003°11′ |
| 6 | Queen Mary Land | 422,000 | 091°54′ E | 100°30′ E | 008°36′ |
| 7 | Wilkes Land | 2,160,000 | 100°30′ E | 136°11′ E | 035°41′ |
| 8 | George V Land | 483,000 | 142°02′ E | 153°45′ E | 011°43′ |
| 9 | Oates Land | ... | 153°45′ E | 160°00′ E | 006°15′ |
| Total | 5,897,000 | 153°45′ E | 160°00′ E | 097°44′ |
These regions are split into two separate areas geographically, with George V Land and Oates Land lying to the east of the French Territorial claim of Adélie Land, and all other districts lying to its west.
Exclusive economic zone
editAustralia claims an exclusive economic zone (EEZ) from the Australian Antarctic Territory. However, the Australian proclamation of an Antarctic EEZ is contested. The effect of Article IV of the 1959 Antarctic Treaty (which prohibits new territorial claims or the extension of existing claims in the Antarctic) would seem to be that an EEZ cannot be claimed in relation to territory to which that Treaty applies (south of 60° South).[citation needed] The provisions of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS) define the exclusive economic zone of a coastal state as up to 200 nautical miles (370 km) from the baseline from which the territorial sea is measured.[10]
Whaling
editWhaling in Australian Antarctic territorial waters is controversial and has received international attention.[11] Anti-whaling protest groups, in particular Sea Shepherd Conservation Society, have been active within the Australian Antarctic territorial waters. Sea Shepherd small boat crews have had multiple encounters with Japanese ships that claim to be on research expeditions while opponents argue this is only a "cover" for banned commercial whaling.[12][13] The Australian Whale Sanctuary, in Australian Antarctic territory, is not recognised by the government of Japan.[11] Anti-whaling legislation passed by the Australian Government applies to Australian territorial waters. However, Australia's claims of sovereignty over the Australian Antarctic Territory—and thus sovereignty over Australian Antarctic territorial waters—are recognised by only the United Kingdom, New Zealand, France and Norway.[14]
Stations
editActive and closed stations in the territory, from West to East:
History
editIn 1933, a British imperial order stated:
That part of His Majesty's dominions in the Antarctic Seas which comprises all the islands and territories other than Adélie Land which are situated south of the 60th degree of South Latitude and lying between the 160th degree of East Longitude and the 45th degree of East Longitude is hereby placed under the authority of the Commonwealth of Australia.[15]
In 1933, the Australian Antarctic Territory Acceptance Act 1933 stated:
That part of the territory in the Antarctic seas which comprises all the islands and territories, other than Adelie Land, situated south of the 60th degree south latitude and lying between the 160th degree east longitude and the 45th degree east longitude, is hereby declared to be accepted by the Commonwealth as a Territory under the authority of the Commonwealth, by the name of the Australian Antarctic Territory.C2004C00416 / Australian Antarctic Territory Acceptance Act 1933 ( Cth )
The borders with Adélie Land were fixed definitively in 1938. In 1947, Britain transferred Heard Island and McDonald Islands to the territory. On 13 February 1954,[16] Mawson Station was established as the first Australian station on the continent proper.
Recognition and promotion of Australian sovereignty
editAustralia's claim to sovereignty over the Australian Antarctic Territory is recognised by only the United Kingdom, New Zealand, France and Norway.[17] Ships of Japan conduct whaling in Australian Antarctic territorial waters.[18]
In 2016, the Australian Government formulated an Antarctic Strategy and 20 Year "Action Plan" to improve overland transport capabilities and aviation access to the continent. The plan incorporated a strategy to protect the Antarctic environment and maintain an indefinite ban on mining and oil drilling. The construction of a research and resupply icebreaker vessel was also planned.[19] The 25,000-tonne RSV Nuyina was delivered in 2021 and was immediately employed in support of the Casey Station. It is envisaged that the ship will support scientific research over the next 30 years.[20]
Through "Operation Southern Discovery", elements of the Australian Defence Force also provide annual support for the Australian Antarctic Division and the Australian Antarctic Program (AAP) in regional scientific, environmental and economic activities.[21] The Royal Australian Air Force provides air logistical support using C-17 transport aircraft supported by KC-30 tanker aircraft to supply Wilkins airfield in Antarctica.[22]
Mining in Antarctica
editDuring the early 1980s, there was a brief debate in Australia on whether or not to allow mining on the mineral-rich continent.[23] Several mining proposals have been discussed and have all been rejected.[24]
On 9 August 2011, the influential Australian think-tank, the Lowy Institute, published a report warning Canberra against complacency when it comes to its claim.[25] The global treaty banning resource exploitation becomes reviewable in 2041,[26] and some states may then decide to withdraw from it considering the continent's mineral deposits. These include coal seams, manganese, iron and uranium, while Antarctica's forecast oil reserves are estimated as among the largest in the world after Saudi Arabia and Venezuela. Lowy's national security fellow Ellie Fogarty said in the paper that Australia cannot adequately patrol its claim, lacking the kind of ski-planes it needs to reach some areas.
Postage stamps
editAustralia issues postage stamps for the Australian Antarctic Territory. The first issues came in 1957, and sporadically thereafter, settling into a pattern of an annual issue by the 1990s. All have been Antarctic-themed, and all are valid for postage in Australia and its territories, including Antarctica.
Telephone connections
editAssigned the country calling code +672 1[0-4] XXXX, the four stations and the Aurora Australis operated by the Australian Antarctic Division can be reached by direct calling from anywhere in the world. The area codes are 10 for Davis, 11 for Mawson, 12 for Casey, 13 for Macquarie Island and 14 for Wilkins and the Aurora Australis, in each case followed by four additional digits.
People
editAs of May 2018, the AAT was believed to have a population of around 80 people during winters and 200 during summers.[27]
See also
editReferences
edit- ^ Humane Society International Inc v Kyodo Senpaku Kaisha Ltd FCA 3 (15 January 2008), Federal Court of Australia, §13.
- ^ "Australian Antarctic Territory". antarctica.gov.au. 15 April 2016. Retrieved 5 October 2019.
- ^ "National recovery plan for Albatrosses and Giant-petrels: Section 4.1.6 Australian Antarctic Territory, Geography". Australian Government, Department of the Environment, Water, Heritage and the Arts. Archived from the original on 17 August 2008. Retrieved 16 July 2008.
- ^ "Australian Antarctic Territory". antarctica.gov.au. 15 April 2016. Archived from the original on 23 January 2023. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ "India - The World Factbook". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 11 January 2021.
2,973,193 sq km
- ^ "Argentina - The World Factbook". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 27 February 2023.
2,736,690 sq km
- ^ "Kazakhstan - The World Factbook". The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 27 February 2023.
2,699,700 sq km
- ^ The Parliament of the Commonwealth of Australia (2018). Maintaining Australia’s national interests in Antarctica: Inquiry into Australia’s Antarctic Territory. Joint Standing Committee on the National Capital and External Territories.
- ^ "The Australian Antarctic Territory: History and Present Status". WorldAtlas. 4 February 2020. Retrieved 9 November 2021.
- ^ "Part V. Exclusive Economic Zone. Article 57. Breadth of the exclusive economic zone". United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea. Retrieved 15 January 2018.
- ^ a b "Japanese whalers told to keep out of Australian territory". The New Zealand Herald. 16 January 2008. Retrieved 17 September 2011.
- ^ "'Stink' attack on Japan's whalers, BBC, 27 December 2008
- ^ "Japanese whaling ship detains 2 protesters", NBC News, 15 January 2008
- ^ "An honorable way out of the whaling débâcle", Sydney Morning Herald, 19 January 2008
- ^ Antarctica and international law: a collection of inter-state and national documents, Volume 2. pp. 143. Author: W. M. Bush. Editor: Oceana Publications, 1982. ISBN 0-379-20321-9, ISBN 978-0-379-20321-9
- ^ "A Brief History of Mawson". Australian Government – Australian Arctic Division. Archived from the original on 27 July 2008. Retrieved 16 July 2008.
- ^ "Chapter 6: Antarctic Territories" (PDF). Parliament of Australia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 June 2008. Retrieved 29 March 2013.
- ^ Humane Society International Inc v Kyodo Senpaku Kaisha Ltd [2008] FCA 3 at [13], (2008) 165 FCR 510 (15 January 2008), Federal Court (Australia).
- ^ "Antarctica". 2017 Foreign Policy White Paper. November 2017. Retrieved 23 August 2023.
- ^ "RSV NUYINA – AUSTRALIA'S NEW ICEBREAKER". Government of Australia. 6 October 2022. Retrieved 23 August 2023.
- ^ "Operation Southern Discovery". Australian Government - Defence. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ Layton, Peter; Hallen, Travis; Bishop, Lauren (2019). "Australia's Antarctic National Air Power Futures" (PDF). Commonwealth of Australia. Retrieved 23 August 2023.
- ^ "Mining". In the 1980s, the question of possible mineral exploitation (including the hydrocarbons oil and gas) was addressed by the nations of the Antarctic Treaty. They negotiated an agreement called the Convention on the Regulation of Antarctic Mineral Resource Activities (CRAMRA) which would have regulated mining should it have ever been contemplated. CRAMRA did not come into force. Instead, the Madrid Protocol was negotiated and it includes a ban on Antarctic mining. Australian Government. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ^ "No mining in Antarctica, say Aussies". Despite the current global appetite for minerals, which has underpinned two decades of economic growth in Australia, the country currently has no plans to allow any mining in Antarctica. IOL. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ^ "Antarctica: Assessing and Protecting Australia's National Interests" (PDF). International interest in Antarctica is rising. Lowy Institute. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 July 2013. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ^ Swan, Robert. "2041". In the year 2041, the Protocol on Environmental Protection to the Antarctic Treaty could potentially be modified or amended. 2041.com. Archived from the original on 5 August 2013. Retrieved 26 June 2013.
- ^ "The Parliament of the Commonwealth of Australia (2018). Maintaining Australia's national interests in Antarctica: Inquiry into Australia's Antarctic Territory. Joint Standing Committee on the National Capital and External Territories". aph.gov.au.