This article may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. The specific problem is: Sentences need to be reformatted and put in appropriate sections to fit MOS; sections talking about ophiuroids in general should be moved to that page. (July 2024) |
Astroboa nuda, the naked basket star or the giant basket star,[1][2][3][4] is a type of basket star from Gorgonocephalidae family. [5] [6] Its large arms (up to 1.0 metre (3.3 ft) wide) are highly branched. It inhabits reef slopes exposed to current throughout the Indo-Pacific, ranging from the Red Sea to New Caledonia. During the day it coils into a tight ball. At night it spreads arms to form a basket to feed on plankton. [7] They are part of the class Ophiuroidea, which is the largest class of echinoderms. The name Ophiuroidea comes from the roots, ophis, meaning snake and oura, which means tail, referring to the thin, spiraling shape of the basket stars’ arms.[8]
| Astroboa nuda | |
|---|---|

| |
| Astroboa nuda feeding at night (Red Sea, Egypt) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Echinodermata |
| Class: | Ophiuroidea |
| Order: | Phrynophiurida |
| Family: | Gorgonocephalidae |
| Genus: | Astroboa |
| Species: | A. nuda
|
| Binomial name | |
| Astroboa nuda Lyman, 1874
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
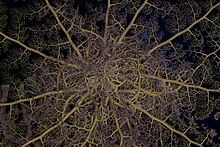
Description
editAstroboa nuda is a typical basket star, with arms divided into five sections,[clarification needed] with many smaller arms branching off of these sections.[8] The arms can range throughout a variety of lengths both within and among individuals of Astroboa nuda. Shorter arms help the basket stars attach themselves to a substrate, and may also help carry food from the longer arms, which catch prey, to the mouth.[9]
The type specimen was described in 1874 as Astrophyton nudum, from a specimen collected in the Philippines by "Semper". The specimen was noted as having "No tentacle scales on pores. Disk and arms quite smooth; the latter ringed with faint lines, which, magnified, are seen to be rows of minute conical papillae. One large madreporic body." The species possesses twenty arms which are smooth, lacking spines or "grains"; upon closer inspection a network of "cross-lines" are visible. Each joint of the arms is marked by a ridge of papillae, which are made up of hooks that become more annular farther up the arm, "encircling the arm in a single row" on the distal-most part of the arms. The disk is "essentially naked" or unornamented, which may be the reason for this basket star's name, although this was not directly stated. The "mouth-papillae", teeth, and "tooth-papillae" are of a uniform spiniform shape, three of which "represent teeth" are longer than the others. The madreporic body is at the "inner angle" of the interbrachial space, near the delineation of the animal's upper and lower surface. This specimen's color lightens at the tips, being yellowish brown after some time in alcohol.[10]
Live A. nuda are usually dark violet, black, or dark brown in color, but can occasionally be pale yellow. Typically, the yellow A. nuda tend to be larger. This variation in color and size have not been shown to cause differences in behavior.[9]
In terms of the structure of A. nuda, they have no anus or intestines, and the mouth is found on the underside of the body. In addition, they have a simple digestive system consisting of an esophagus, along with a sac-like stomach.[8] The waste product of basket stars comes in the form of ammonia, and is removed from the body through diffusion.[11]
Habitat and Distribution
editAstroboa nuda live in a variety of habitats, but are commonly found on the seafloor or at depths greater than twenty meters, burrowing into the sandy bottom.[12] They are also found buried in mud, or within the holes of rocks or coral in tropical waters in areas such as Madagascar, Indonesia and Indo-Pacific regions, and occasionally in submarine canyons.[12] Unlike some other species within Ophiuroidea that group together to form large clusters, Astroboa nuda are usually found alone or in groups of two to four.[9]
Ecology
editAstroboa nuda is a filter feeder and usually feeds on plankton, along with the larvae of decapods and copepods, as well as those of fish.[8] They may also occasionally obtain food from the surface of the substrate which they attach to.[9] Typically, due to their light sensitivity, A. nuda hide in nearby shelters during the day, but branch out at night to feed. They feed from approximately two hours after sunset, to about one hour before sunrise.[9] They usually return to the same spot every night, and are active during all seasons of the year. In addition, they try to place themselves near calm, barely touched waters.[13] If the water in the area is heavily disturbed one night, they will usually stay sheltered behind coral heads, or other sections of the reef.[9]
A. nuda serves as a host to large copepod populations. These copepods live in the stomach of the basket stars.[13]
The class Ophiuroidea usually reproduces sexually, although asexual reproduction by fission can occur as well.[8] Typically, there are separate male and female basket stars, which release sperm and eggs into the water. The sperm and eggs then join, and the larvae develop in the water. This process is known as broadcast spawning.[8]
Predators
editBasket stars generally have very few predators, as they are low in nutritional value, but are preyed upon by some fish.[11] Basket stars are often also caught by humans as part of by-catch during commercial fishing.[12] They may break off part or all of their arm in order to escape, but these arms will regenerate.[11]
Studies and research
editNot much research has been done regarding Astroboa nuda and basket stars in general. However, during one study, A. nuda were found to be very light sensitive. For this study, a high power electric torch was used to observe the basket stars, but once the torch was pointed directly towards the individuals, the arms began to coil inwards, with the thinner arms folding first and the entire organism eventually hiding, due to the resemblance between the light from the torch and daylight.[9] When the discovery of basket stars and brittle stars began in the 18th century, the rate of research on these organisms reached its peak, however this rate leveled out and eventually lowered as time went on, with very little research being conducted currently.[8] Furthermore, when looking at the fossil record, not much evidence has been found regarding the origin of basket stars, but some evidence shows they first began as brittle stars and diverged from there.[8]
References
edit- ^ "Naked Basket Star Astroboa nuda". inaturalist.org. iNaturalist. Retrieved 13 July 2024.
- ^ "Giant Basket Star". MoalBoal Reef Species. Moalboal Reef Species. Retrieved 13 July 2024.
- ^ Spangler, Randall. "Giant Basket Star (Astroboa nuda)". Spangler's Scuba. Retrieved 13 July 2024.
- ^ "Astroboa nuda (Lyman, 1874)". sealifebase. SeaLifeBase. Retrieved 13 July 2024.
- ^ The World Ophiuroidea Database - Astroboa nuda (Lyman, 1874)
- ^ Naked Basket Star (Astroboa nuda) - Information on Naked Basket Star - Encyclopedia of Life
- ^ Lieske, Ewald; Myers, Robert (2004). Coral reef guide. Red Sea. p. 342. ISBN 9780007741731.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Stöhr S, O'Hara TD, Thuy B (2012) Global Diversity of Brittle Stars (Echinodermata: Ophiuroidea). PLOS ONE 7(3): e31940. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031940
- ^ a b c d e f g Tsurnamal, M. & Marder, J.. (2013). Observations on the basket star Astroboa nuda (LYMAN) on coral reefs at Elat (Gulf of Aqaba). Israel Journal of Zoology. 15. 9-17. 10.1080/00212210.1966.10688225.
- ^ Bulletin of the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard College (3 ed.). Harvard University. 1871–1876. pp. 251–254. Retrieved 13 July 2024.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ^ a b c Matsumoto, H. (1915). A New Classification of the Ophiuroidea: With Descriptions of New Genera and Species. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, 67(1), 57-58. Retrieved February 27, 2020, from www.jstor.org/stable/4063659
- ^ a b c Sink, Kerry & Boshoff, Willem & Samaai, Toufiek & Timm, P.G. & Kerwath, Sven. (2006). Observations of the habitats and biodiversity of the submarine canyons at Sodwana Bay. South African Journal of Science. 102.
- ^ a b Humes, Arthur. (2005). Two new species of Copepoda associated with the basket star Astroboa nuda (Ophiuroidea) in the Moluccas. Zoologica Scripta. 15. 323 - 332. 10.1111/j.1463-6409.1986.tb00233.x.