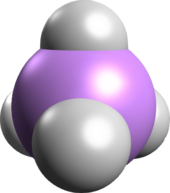
The arsonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula AsH+
4. An arsonium salt is a salt containing either the arsonium (AsH+
4) cation, such as arsonium bromide (AsH+
4Br−
) and arsonium iodide (AsH+
4I−
), which can be synthesized by reacting arsine with hydrogen bromide or hydrogen iodide.[1] Or more commonly, as organic derivative such as the quaternary arsonium salts Ph
4As+
Cl−
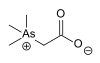
(CAS: 123334-18-9 , hydrate form) and the zwitterionic compound arsenobetaine.

| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
Arsonium | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| 322800 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| AsH+ 4 | |
| Molar mass | 78.954 g·mol−1 |
| Conjugate base | Arsine |
| Structure | |
| Tetrahedral | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
ammonium phosphonium |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
References
edit- ^ Muñoz-Hernández, M. Á. (2006). Arsenic: Inorganic Chemistry. Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry. pp 4. DOI: 10.1002/0470862106.ia013